Due to the perpetual nature of preferred stock, the fixed periodic dividends form a perpetuity. Where the preferred stock dividends grow at a constant rate g, its value equals the present value of a growing perpetuity. Where a preferred stock is callable or convertible, its pricing is different because of the embedded options.
Full Answer
How do you calculate the cost of preferred stock?
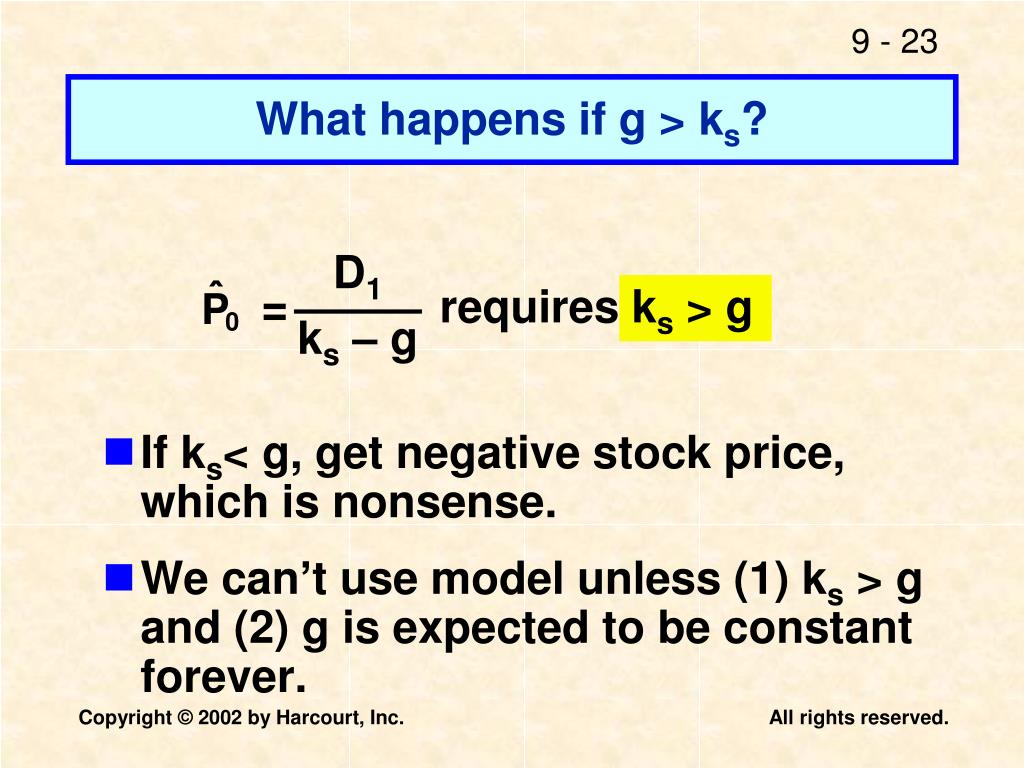
They calculate the cost of preferred stock by dividing the annual preferred dividend by the market price per share. is smaller than the growth rate. Moreover, the value per share approaches infinity if the required rate of return and growth rate have the same value, which is conceptually unsound.
How is pre-preferred stock valued?
Preferred stock valuation comes from fixed dividend payments and is safer, but with a smaller reward. Learn about the methods and calculations used to determine the value which includes the dividend discount approach and the Gordon growth model. Updated: 01/06/2022 Preferred stock is the hybrid of investments.
How to calculate the present stock price of a company?
It is determined by, Required Rate of Return = (Expected Dividend Payment/Existing Stock Price) + Dividend Growth Rate read more just by adding a dividend yield and the growth rate. By using this formula, we will be able to understand the present stock price of a company.
How do you calculate the growth rate of a stock?
You can use a mathematical formula called the constant growth model, or Gordon Growth Model, to make this calculation or find a stock valuation calculator tool online or in a smart phone app to do the computation for you.

How do you calculate preferred stock price?
The value of a preferred stock equals the present value of its future dividend payments discounted at the required rate of return of the stock. In most cases the preferred stock is perpetual in nature, hence the price of a share of preferred stock equals the periodic dividend divided by the required rate of return.
Which of the following formulas is used to determine the price of preferred stock?
Here's an easy formula for calculating the value of preferred stock: Cost of Preferred Stock = Preferred Stock Dividend (D) / Preferred Stock Price (P).
How do you calculate preferred stock WACC?
Simply multiply the cost of debt and the yield on preferred stock with the proportion of debt and preferred stock in a company's capital structure, respectively. Since interest payments are tax-deductible, the cost of debt needs to be multiplied by (1 – tax rate), which is referred to as the value of the tax shield.
How do you calculate preferred stock on a balance sheet?
For example, assume the par value of the preferred stock $12. Multiply the number of preferred shares outstanding by the par value of the preferred stock. Continuing the same example, $100,000 x $12 = $1,200,000. This figure represents the dollar value of the preferred stock outstanding.
Why is preferred stock considered a hybrid?
It's like equity in that it provides ownership and it's like debt in that preferred dividends are like the interest payments debt holders receive. It's called preferred stock because preferred stockholders get preferential treatment when it comes to receiving their dividend. Preferred stockholders are paid after the bondholders (those who own bonds issued by the company) but before the holders of common stock. So preferred stock is perceived to be less risky than common stock since there might not be anything left over after the preferred stockholders get paid.
How is fixed dividend preferred stock valued?
Fixed dividend preferred stock is valued with the dividend discount approach, which uses the traditional discounting formula to calculate the present value of the stream of dividend payments .
What is preferred dividend?
Preferred dividends typically pay a fixed dividend, meaning the dividends stay the same. They don't vary with how well the company does. Common stock, on the other hand, has a more flexible dividend, increasing when the company does well or skipped altogether when times are bad.
Is preferred stock less risky than common stock?
So preferred stock is perceived to be less risky than common stock since there might not be anything left over after the preferred stockholders get paid.
What is preferred stock?
The owners of preferred shares are part owners of the company in proportion to the held stocks, just like common shareholders. Preferred shares are hybrid securities that combine some of the features of common stock with that of corporate bonds.
What happens to preferred shares when interest rate rises?
When the market interest rate rises, then the value of preferred shares will fall. This is to account for other investment opportunities and is reflected in the discount rate used.
How do preferred shares differ from common shares?
Preferred shares differ from common shares in that they have a preferential claim on the assets of the company. That means in the event of a bankruptcy, the preferred shareholders get paid before common shareholders. 1
What is preferred shareholder?
In addition, preferred shareholders receive a fixed payment that's similar to a bond issued by the company. The payment is in the form of a quarterly, monthly, or yearly dividend, depending on the company's policy, and is the basis of the valuation method for a preferred share.
What is Gordon growth model?
If the dividend has a history of predictable growth, or the company states a constant growth will occur, you need to account for this. The calculation is known as the Gordon Growth Model .
What is call provision in stock market?
Something else to note is whether shares have a call provision, which essentially allows a company to take the shares off the market at a predetermined price. If the preferred shares are callable, then purchasers should pay less than they would if there was no call provision.
Is dividend payment easy to find?
The dividend payment is usually easy to find, but the difficult part comes when this payment is changing or potentially could change in the future. Also, finding a proper discount rate can be very difficult, and if this number is off, then it could drastically change the calculated value of the shares.
What is reacquired stock?
Treasury Stock Treasury stock, or reacquired stock, is a portion of previously issued, outstanding shares of stock which a company has repurchased or bought back from shareholders. These reacquired shares are then held by the company for its own disposition.
What is Gordon Growth Model?
The Gordon Growth Model – otherwise described as the dividend discount model – is a stock. Stock What is a stock? An individual who owns stock in a company is called a shareholder and is eligible to claim part of the company’s residual assets and earnings (should the company ever be dissolved). The terms "stock", "shares", ...
What is the seller of an option called?
A seller of the stock option is called an option writer , where the seller is paid a premium from the contract purchased by the stock option buyer. Income Statement. Income Statement The Income Statement is one of a company's core financial statements that shows their profit and loss over a period of time.
Can dividends increase at a constant rate?
In reality, it is highly unlikely that companies will have their dividends increase at a constant rate. Another issue is the high sensitivity of the model to the growth rate and discount factor used. The model can result in a negative value if the required rate of return.
TLDR
Companies often issue both common and preferred stock to reward those putting in sweat equity and those investing. Understanding which shares to issue to whom is a critical decision for startup founders.
What is Startup Preferred Stock?
Stock, or equity, is often one of the most critical assets in a startup. Equity can help a startup attract top talent as well as early-stage investors. In a new business, two types of stock are typically offered: common and preferred. Common stock is a share of ownership in the startup, typically accompanied by voting rights.
What is the Difference Between Common Stock and Preferred Stock?
As stated above, a common stock owner has purchased ownership in the startup along with voting rights, enabling them to vote on issues such as who will serve on the board of directors or on specific management decisions. The more ownership you have, the more significant impact your vote holds.
How Do You Calculate the Cost of Preferred Stock?
Calculating the price for a startup's preferred stock is often difficult as the business is new, without a track record of sales or other financial indicators of success. However, early startups' preferred stock can be priced. Let’s see how.
How to Calculate Par Value of Preferred Stock?
Par value of one share of preferred stock equals the amount upon which the dividend is calculated. In other words, par value is the face value of one share of stock.
How to Calculate Cumulative Preferred Stock?
Cumulative preferred stock is preferred stock, which pays cumulative dividends if a dividend payment was missed. A cumulative dividend is “a required fixed distribution of earnings made to shareholders.” Preferred shares are the most common stock class providing a right to receive cumulative dividends.
Benefits
It’s essential to objectively establish your business's value as a startup, which directly impacts your preferred stock price. By establishing these figures early in your business venture, you can show your business's value to potential investors, which is instrumental to growing your startup.
What are the two types of Gordon growth formulas?
This article has been a guide to Gordon Growth Model Formula. Here we discuss the two types of Gordon Growth formulas, including constant growth and zero growth, along with its uses practical examples and calculations. You may learn more about valuations from the following articles –
Is estimated dividends accurate?
The estimated dividends won’t be accurate , but the idea is to predict something that is closer to the actual future dividends. The second component has two parts – the growth rate and the required rate of return. To find out the growth rate, we need to use the following formula –.
What happens when you sell a stock at a higher price?
At a higher price, investors won't get the desired rate of return, so they'll sell the stock and lower the price. At a lower price it will be a bargain since they'll get a higher rate than required, meaning other investors will bid up the price.
When investors put money into a stock, do they hold onto the stock?
When investors put money into a stock, they often are hoping to hold onto the stock for a certain amount of time and then sell it to another investor for a higher price .
What is constant growth?
The constant growth formula is relatively straightforward for estimating a good price for a stock based on future dividends. Remember that it's extremely unlikely any company will truly continue to pay steadily rising dividends forever, so it should only be used in conjunction with other ways of evaluating the company and only for considering stable businesses.
Why is preferred stock sold?
Like other equity capital, selling preferred stock enables companies to raise funds. Preferred stock has the benefit of not diluting the ownership stake of common shareholders, as preferred shares do not hold the same voting rights that common shares do. Preferred stock lies in between common equity and debt instruments, in terms of flexibility.
How do corporations calculate the cost of preferred stock?
They calculate the cost of preferred stock by dividing the annual preferred dividend by the market price per share. Once they have determined that rate, ...
What is the term for the first cash flow payment after a liquidation?
Because of the nature of preferred stock dividends, it is also sometimes known as a perpetuity. Perpetuity Perpetuity is a cash flow payment which continues indefinitely.
Does common equity have a par value?
However, preferred stock also shares a few characteristics of bonds, such as having a par value. Common equity does not have a par value.
Is preferred stock more valuable than common stock?
In theory, preferred stock may be seen as more valuable than common stock, as it has a greater likelihood of paying a dividend and offers a greater amount of security if the company folds.
What is preferred stock?
Preferred stocks are equity securities that share many characteristics with debt instruments. Preferred stock is attractive as it offers higher fixed-income payments than bonds with a lower investment per share. Preferred stock often has a callable feature which allows the issuing corporation to forcibly cancel the outstanding shares for cash.
Why do companies issue preferred stock?
A company may choose to issue preferreds for a couple of reasons: 1 Flexibility of payments. Preferred dividends may be suspended in case of corporate cash problems. 2 Easier to market. Preferred stock is typically bought and held by institutional investors, which may make it easier to market during an initial public offering.
What is a participating preferred stock?
Participating. This is preferred stock that has a fixed dividend rate. If the company issues participating preferreds, those stocks gain the potential to earn more than their stated rate. The exact formula for participation will be found in the prospectus. Most preferreds are non-participating.
How much can you deduct from preferred stock?
Corporations that receive dividends on preferred stock can deduct 50% to 65% of the income from their corporate taxes. 1 .
Why are preferred stocks considered hybrid securities?
Because of their characteristics, they straddle the line between stocks and bonds. Technically, they are securities, but they share many characteristics with debt instruments . Preferred stocks are sometimes called hybrid securities.
Why are preferred dividends suspended?
Preferred dividends may be suspended in case of corporate cash problems. Easier to market. Preferred stock is typically bought and held by institutional investors, which may make it easier to market during an initial public offering.
What happens to preferred shares when interest rates rise?
If interest rates rise, the value of the preferred shares falls. If rates decline, the opposite would hold true.

Unique Features of Preferred Shares
- Preferred shares differ from common shares in that they have a preferential claim on the assets of the company. That means in the event of a bankruptcy, the preferred shareholders get paid before common shareholders.1 In addition, preferred shareholders receive a fixed payment that's similar to a bond issued by the company. The payment is in the form of a quarterly, monthl…
valuation Models
- If preferred stocks have a fixed dividend, then we can calculate the value by discounting each of these payments to the present day. This fixed dividend is not guaranteed in common shares. If you take these payments and calculate the sum of the present values into perpetuity, you will find the value of the stock. For example, if ABC Company pays a 25-cent dividend every month and t…
Growing Dividends
- If the dividend has a history of predictable growth, or the company states a constant growth will occur, you need to account for this. The calculation is known as the Gordon Growth Model. V=D(r−g)V=\frac{D}{(r-g)}V=(r−g)D By subtracting the growth number, the cash flows are discounted by a lower number, which results in a higher value.
Considerations
- Although preferred shares offer a dividend, which is usually guaranteed, the payment can be cut if there are not enough earnings to accommodate a distribution; you need to account for this risk. The risk increases as the payout ratio (dividend payment compared to earnings) increases. Also, if the dividend has a chance of growing, then the value of the shares will be higher than the result …
The Bottom Line
- Preferred shares are a type of equityinvestment that provides a steady stream of income and potential appreciation. Both of these features need to be taken into account when attempting to determine their value. Calculations using the dividend discount model are difficult because of the assumptions involved, such as the required rate of return, growth, or length of higher returns. Th…
What Are The Assumptions of The Gordon Growth Model?
What Is The Gordon Growth Model Formula?
- Three variables are included in the Gordon Growth Model formula: (1) D1 or the expected annual dividend per share for the following year, (2) k or the required rate of return, and (3) g or the expected dividend growth rate. With these variables, the value of the stock can be computed as: Intrinsic Value = D1 / (k – g) To illustrate, take a look at the following example: Company A’s is li…
What Is The Importance of The Gordon Growth Model?
- The Gordon Growth Model can be used to determine the relationship between growth rates, discount rates, and valuation. Despite the sensitivity of valuation to the shifts in the discount rate, the model still demonstrates a clear relation between valuation and return. Applications of the model are demonstrated more in-depth in our corporate finance ...
What Are The Limitations of The Gordon Growth Model?
- The assumption that a company grows at a constant rate is a major problem with the Gordon Growth Model. In reality, it is highly unlikely that companies will have their dividends increase at a constant rate. Another issue is the high sensitivity of the model to the growth rate and discount factor used. The model can result in a negative value if the required rate of returnis smaller than …
Additional Resources
- Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to the Gordon Growth Model. To keep advancing your career, the additional resources below will be useful: 1. Stock Options 2. Income Statement 3. Treasury Stock Method 4. Debt Schedule 5. Market Risk Premium