What does a price-to-book ratio of 1 mean?
A price-to-book ratio of one means that the stock price is trading in line with the book value of the company. A P/B ratio with lower values, particularly those below one, are a signal to investors that a stock may be undervalued.
What is the book value of a stock?
The book value is defined as the difference between the book value of assets and the book value of liabilities . Investors use the price-to-book value to gauge whether a stock is valued properly. A P/B ratio of one means that the stock price is trading in line with the book value of the company.
What are growth stocks?
Growth stocks are those companies expected to grow sales and earnings at a faster rate than the market average. Growth stocks often look expensive, trading at a high P/E ratio, but such valuations could actually be cheap if the company continues to grow rapidly which will drive the share price up.
What's happening to the price-to-book ratio of tech stocks?
For example, between 2010 and 2020 there was a steady rise in the average price-to-book ratio of the technology companies listed on the Nasdaq stock exchange, roughly tripling during that period.

What is a good price-to-book ratio for growth stocks?
Traditionally, any value under 1.0 is considered a good P/B value, indicating a potentially undervalued stock. However, value investors often consider stocks with a P/B value under 3.0.
How do you interpret the price-to-book ratio?
A P/B ratio that's greater than one suggests that the stock price is trading at a premium to the company's book value. For example, if a company has a price-to-book value of three, it means that its stock is trading at three times its book value. As a result, the stock price could be overvalued relative to its assets.
Do growth stocks have a high book-to-market ratio?
The book-to-market effect is well documented in finance. In general, high book-to-market stocks, also referred as value stocks, earn significant positive excess returns while low book-to-market stocks, also referred as growth stocks, earn significant negative excess returns.
Is a higher price-to-book ratio better?
The lower a company's price-to-book ratio is, the better a value it generally is. This can be especially true if a stock's book value is less than one, meaning that it trades for less than the value of its assets. Buying a company's stock for less than book value can create a "margin of safety" for value investors.
What is a negative price-to-book ratio?
A negative book value means that a company has more total liabilities than total assets. It owes more than it owns, in numerical terms.
What if book value is more than share price?
If the book value is higher than the share's market price, it means the company's assets are being traded at a lower price than what they are worth.
How do you analyze growth stocks?
Five characteristics to look for in a potential growth stock investment are: A strong leadership team. An industry poised for growth....5 Characteristics of Good Growth StocksA Strong Leadership Team. ... A Promising Growth Industry. ... Commanding Market Share. ... Strong Sales Growth. ... A Large Target Market.
What defines a growth stock?
Growth stocks are those companies expected to grow sales and earnings at a faster rate than the market average. Growth stocks often look expensive, trading at a high P/E ratio, but such valuations could actually be cheap if the company continues to grow rapidly which will drive the share price up.
What is the difference between a value stock and a growth stock?
Growth stocks are those companies that are considered to have the potential to outperform the overall market over time because of their future potential. Value stocks are classified as companies that are currently trading below what they are really worth and will thus provide a superior return.
Why do most companies have a price-to-book ratio greater than one?
A price-to-book less than 1 ratio could mean the stock is undervalued and worth buying. A price-to-book ratio greater than 1 indicates that the stock price is trading at a premium to the company's book value. It also indicates that you could be overpaying for what would be left if the company went immediately bankrupt.
Should book value be high or low?
A good price to book value is less than 1. It signals a solid undervalued company. However, a price to value of less than 3 is also accepted among value investors.
Is a high book value per share good?
If a company's BVPS is higher than its market value per share—its current stock price—then the stock is considered undervalued. If the firm's BVPS increases, the stock should be perceived as more valuable, and the stock price should increase.
Is it better to have a high or low P E ratio?
P/E ratio, or price-to-earnings ratio, is a quick way to see if a stock is undervalued or overvalued. And so generally speaking, the lower the P/E ratio is, the better it is for both the business and potential investors.
What is a good price to book ratio for a bank?
Do Banks Low P/B Ratios Indicate Good Value? The banking industry's average P/B value being down near one makes it worthy of consideration by value investors who seek out companies with P/B values below two, with a particular focus on companies showing values of one or lower.
What Does Price to Book Ratio Mean?
Price to Book Value Ratio therefore indicates the multiple that the market is willing to pay for the accumulated Equity in the company.
What is the book value of a company?
The book value of a company is equivalent to the Net Worth calculation as Book Value = Assets – Liabilities. Therefore price/book ratio is an indicator of the investor interest in paying up for the companies equity.
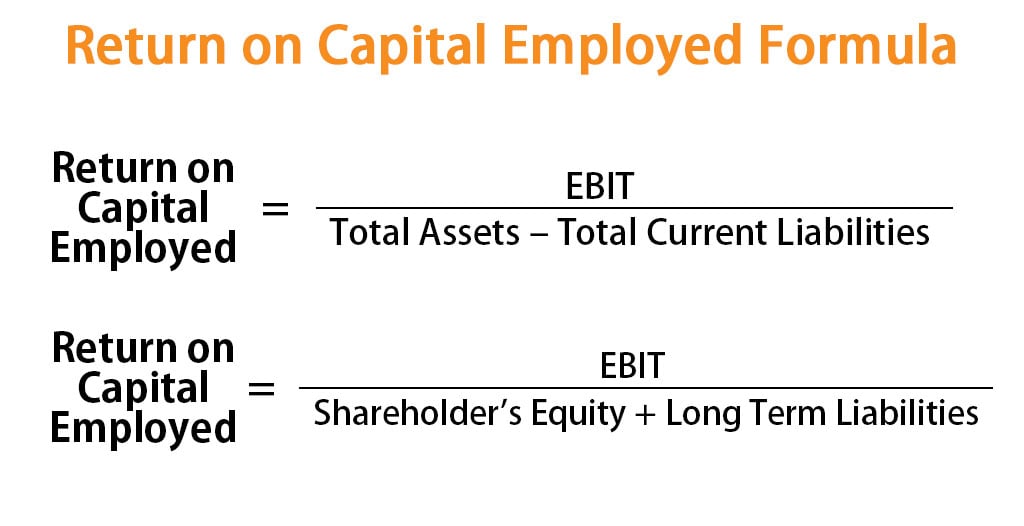
What is the P/B ratio?
Price to Book Ratio or P/B Ratio is used to determine the valuation of the company with respect to its balance sheet strength. It is calculated by one of the following two methods:
What is value investor?
As value investors, it is our job to review the assets of the company and come to our own independent judgement of the book value.
Is a stock overvalued?
Perhaps the stock is not overvalued in this case . It is always a good idea to dig deeper than just reading off the book value from the balance sheet. Some industries tend to have lower tangible assets and the stock can trade at higher book multiple naturally.
Is price to book the same as market to book?
Taking a per share approach to calculating the price to book may be easier as the price per share and bv per share are often readily available from most stock data feeds. Price to book can also be referred to as market to book or market cap to equity ratio.
Is a high price to book ratio overvalued?
Generally investors come to think of a high price to book ratio as overvalued as the price may be too high given the book value of the stock. This may be true in most cases, and indeed there is empirical evidence that a bias towards low price to book stocks tends to improve returns as it biases the portfolio towards value.
What is the market to book ratio?
The market-to-book ratio, also called the price-to-book ratio, is the reverse of the book-to-market ratio. Like the book-to-market ratio, it seeks to evaluate whether a company's stock is over or undervalued by comparing the market price of all outstanding shares with the net assets of the company.
What Does the Book-to-Market Ratio Tell You?
The book-to-market ratio is used to compare a company’s net asset value or book value to its current or market value.
How does book to market work?
The book-to-market ratio helps investors find a company's value by comparing the firm's book value to its market value. A high book-to-market ratio might mean that the market is valuing the company's equity cheaply compared to its book value. Many investors are familiar with the price-to-book ratio, which is simply the inverse ...
What does it mean when a stock is undervalued?
In basic terms, if the ratio is above 1, then the stock is undervalued. If it is less than 1, the stock is considered overvalued. A ratio above 1 indicates that the stock price of a company is trading for less than the worth of its assets. A high ratio is preferred by value managers who interpret it to mean that the company is a value stock —that is, it is trading cheaply in the market compared to its book value.
How to find book value of a company?
Book value can be calculated by subtracting total liabilities, preferred shares, and intangible assets from the total assets of a company. In effect, the book value represents how much a company would have left in assets if it went out of business today. Some analysts use the total shareholders' equity figure on the balance sheet as the book value.
What does a ratio above 1 mean?
A ratio above 1 indicates that the stock price of a company is trading for less than the worth of its assets. A high ratio is preferred by value managers who interpret it to mean that the company is a value stock —that is, it is trading cheaply in the market compared to its book value. A book-to-market ratio below 1 implies ...
How is book value calculated?
A company's book value is calculated by looking at the company's historical cost, or accounting value. A firm's market value is determined by its share price in the stock market and the number of shares it has outstanding, which is its market capitalization .
What Is a Growth Stock?
A growth stock is any share in a company that is anticipated to grow at a rate significantly above the average growth for the market. These stocks generally do not pay dividends. This is because the issuers of growth stocks are usually companies that want to reinvest any earnings they accrue in order to accelerate growth in the short term. When investors invest in growth stocks, they anticipate that they will earn money through capital gains when they eventually sell their shares in the future.
What Is an Example of a Growth Stock?
As a hypothetical example, a growth stock would be a biotech startup that has begun work on a promising new cancer treatment. Currently, the product is only in the Phase I stage of clinical trials, and there is uncertainty whether the FDA will approve the drug candidate to continue on to Phase II & III trials. If the drug passes, and is ultimately approved for use, it could mean huge profits and capital gains. If, however, the drug either doesn't work as planned or causes severe side effects, all of that R&D spending may have been in vain.
How Do You Know If a Stock Is Growth or Value?
Value stocks also tend to have strong fundamentals with comparably low price-to-book (P/B) ratios and low P/E values—the opposite of growth stocks.
Why are value stocks underpriced?
Some value stocks are underpriced simply due to poor earnings reports or negative media attention. However, one characteristic that they often have is strong dividend-payout histories. A value stock with a strong dividend track record can provide reliable income to an investor. Many value stocks are older companies that can be counted on to stay in business, even if they aren’t particularly innovative or poised to grow.
Why do investors invest in growth stocks?
This is because the issuers of growth stocks are usually companies that want to reinvest any earnings they accru e in order to accelerate growth in the short term. When investors invest in growth stocks, they anticipate that they will earn money through capital gains when they eventually sell their shares in the future.
Why do growth stocks decline?
Since investors are paying a high price for a growth stock, based on expectation, if those expectations aren't realized growth stocks can see dramatic declines.
Why do stocks fall when expected to grow?
This is because several years down the road the current stock price may look cheap in hindsight. The risk is that growth doesn't continue as expected. Investors have paid a high price expecting one thing, and not getting it. In such cases, a growth stock's price can fall dramatically.
Why use the price-to-book ratio?
In a nutshell, a lower price-to-book ratio could indicate that a stock is undervalued. When you're comparing two stocks with similar growth and profitability, P/B can be useful for determining which is the best value at a given moment.
Why is price to book important?
Price to book is useful only for evaluating certain types of businesses. If most of a business's assets are intangible -- as is the case with many technology companies -- its price to book may be unhelpfully high. Software giant Microsoft, for example, trades for more than 10 times its book value. On the other hand, price to book can be useful ...
What does it mean when a stock is less than one?
This can be especially true if a stock's book value is less than one, meaning that it trades for less than the value of its assets. Buying a company's stock for less than book value can create a "margin of safety" for value investors. However, a very low P/B ratio can also be a sign of trouble at a company, so it should be used as part ...
How to find price to book value?
To determine a company's book value, you'll need to look at its balance sheet. Also known as shareholder's equity or stockholder's equity, this amount is equal to the company's assets minus its liabilities.
Does P/B ratio tell us much?
A P/B ratio analysis doesn't tell us much all by itself. To get a more complete picture of a company's valuation, you should use it in combination with profitability metrics such as return on equity (ROE). For example, for the last five years, Bank of America 's price-to-book multiple has been lower than JP Morgan Chase 's. However, that doesn't necessarily mean that Bank of America is "cheaper." In fact, JP Morgan's ROE has been consistently higher than Bank of America's.
What Is the Price-To-Book (P/B) Ratio?
What price should investors pay for a company's equity shares? If the goal is to unearth high-growth companies selling at low-growth prices, the price-to-book ratio (P/B) offers investors an effective approach to finding undervalued companies.
What does it mean when a stock price is three times its book value?
For example, if a company has a price-to-book value of three, it means that its stock is trading at three times its book value. As a result, the stock price could be overvalued relative to its assets. A high share price versus asset value could also mean the company is earning a high ROA.
What does a high P/B ratio mean?
Investors use the price-to-book value to gauge whether a stock is valued properly. A P/B ratio of one means that the stock price is trading in line with the book value of the company. In other words, the stock price would be considered fairly valued, strictly from a P/B standpoint. A company with a high P/B ratio could mean the stock price is overvalued, while a company with a lower P/B could be undervalued.
How to calculate book value per share?
First, we need to calculate the book value per share, which is in the denominator of the P/B ratio formula . As stated earlier, we know that book value equals a company's total assets minus its liabilities. To arrive at book-value-per share, divide the book value by the number of shares outstanding, as shown in the formula below.
Why do investors use price to book value?
Investors use the price-to-book value to gauge whether a company's stock price is valued properly.
How does debt affect P/B?
Debt can boost a company's liabilities to the point where they wipe out much of the book value of its hard assets, creating artificially high P/B values. Highly leveraged companies, such as cable and wireless telecommunications companies, have P/B ratios that understate their assets.
How does a share buyback affect the balance sheet?
Share buybacks also distort the ratio by reducing the capital on a company's balance sheet.
What is the price to book ratio of stock 1?
Stock 1 has a high market capitalization relative to its net book value of assets, so its Price to Book ratio is 3.9x. Stock 2 has a lower market cap than its book value of equity, so its Market to Book ratio is 0.9x.
What is market to book ratio?
The market to book ratio is typically used by investors to show the market’s perception of a particular stock’s value. It is used to value insurance and financial companies, real estate companies, and investment trusts. It does not work well for companies with mostly intangible assets. This ratio is used to denote how much equity investors are ...
How to calculate market to book ratio?
The market to book ratio is calculated by dividing the current closing price of the stock by the most current quarter’s book value per share.
What is the market value of a stock?
The market value is the current stock price of all outstanding shares (i.e. the price that the market believes the company is worth). The book value is the amount that would be left if the company liquidated all of its assets and repaid all of its liabilities.
What does a low ratio mean?
A low ratio (less than 1) could indicate that the stock is undervalued (i.e. a bad investment), and a higher ratio (greater than 1) could mean the stock is overvalued (i.e. it has performed well). Many argue the opposite and due to the discrepancy of opinions, the use of other stock valuation methods either in addition to or instead ...
How to calculate price to book value ratio?
You can calculate the price to book value ratio with the following formula: price to book ratio = stock price / (assets - liabilities).
Why does the price to book ratio skew?
For example, if the price of a stock has been affected in the short term by market mechanics, it can skew the Price to Book Ratio to the point that it becomes irrelevant. If a company seems to have a large total assets number, but it consists mainly of slow-moving inventory, this can also skew the meaning of your result.
What does a higher P/B ratio mean?
You will find lower P/B ratios on stocks that could be undervalued. The higher the P/B ratio, the more likely the market has overvalued the stock. When you use this ratio to analyze a stock, consider the results within the context of other stocks in the same sector because baseline Price to Book Ratios will vary by industry group.
What are the metrics that value investors use to test a company's intrinsic value?
One of the metrics that value investors use to test a company's intrinsic value is the price to book or P/B ratio.
Why is P/B ratio important?
The P/B ratio helps investors evaluate companies by providing a fairly stable metric that makes intuitive sense and which investors can easily compare to a company's market price. When a firm has a period with negative earnings, the P/B ratio is still useful, unlike price-to-earnings ratios.
Why do companies always trade for more than their book value?
Ongoing, financially-sound companies will always trade for more than their book value because investors price the stock based, in part, on their anticipation of the firm's future growth.
Why is P/B ratio less useful?
The P/B ratio becomes less useful when firms classify balance sheet items differently due to the application of various accounting standards. This makes it much more difficult and less meaningful to compare P/B ratios across firms. This is especially problematic with a P/B ratio on a non-U.S. company.
What is growth stock?
Definition. Growth stocks are stocks that come with a substantially higher growth rate compared to the mean growth rate prevailing in the market. It means that the stock grows at a faster rate than the average stock in the market, consequently generating earnings at a faster rate. Value stocks are stocks that are being traded at a value lower ...
What is growth investing?
The act of investing in growth stocks is known as growth investing. Stock Investing: A Guide to Growth Investing Investors can take advantage of new growth investing strategies in order to more precisely hone in on stocks or other investments offering above-average growth potential.
Why are value stocks undervalued?
Value stocks are usually large, well-established companies that are undervalued for a variety of reasons, such as negative PR, a bad earnings season, and so on, but eventually gain back value in the long term. Value stocks usually pay dividends well and don’t reinvest the entirety of their retained earnings back into the company.
Why are value stocks so risky?
Value stocks come with lower metric ratios because they are undervalued. Value stocks are expected to gain value eventually when the market corrects their prices. In the unlikely event that the stock doesn’t appreciate in value as was expected, investors can lose their money. Hence, value stocks are relatively riskier investments.
What is value stock?
Value stocks are stocks that are being traded at a value lower than their intrinsic value. Intrinsic Value The intrinsic value of a business (or any investment security) is the present value of all expected future cash flows, discounted at the appropriate discount rate. Unlike relative forms of valuation that look at comparable companies, ...
What does intrinsic valuation mean?
. It basically means that such stocks are undervalued. Undervalued stocks are traded at a price lower than their true value.
Why are growth stocks less risky than value stocks?
Growth stocks carry relatively lesser risk because their growth rate is high and increasing. They are relatively less sensitive to adverse economic conditions than the overall market. Hence, growth stocks are relatively less risky investments. Value stocks come with lower metric ratios because they are undervalued.
Formula and Calculation of The Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio
- In this equation, book value per share is calculated as follows: (total assets - total liabilities) / number of shares outstanding). Market value per share is obtained by simply looking at the share price quote in the market. P/BRatio=MarketPriceperShareBookValueperShareP/B ~Ratio = \dfra…
What The P/B Ratio Can Tell You
- The P/B ratio reflects the value that market participants attach to a company's equity relative to the book value of its equity. A stock's market value is a forward-looking metric that reflects a company's future cash flows. The book value of equity is an accounting measure based on the historic cost principle and reflects past issuances of equity, augmented by any profits or losses, …
Example of How to Use The P/B Ratio
- Assume that a company has $100 million in assets on the balance sheet and $75 million in liabilities. The book value of that company would be calculated simply as $25 million ($100M - $75M). If there are 10 million shares outstanding, each share would represent $2.50 of book value. If the share price is $5, then the P/B ratio would be 2x (5 / 2.50). This illustrates that the m…
P/B Ratio vs. Price-to-Tangible-Book Ratio
- Closely related to the P/B ratio is the price to tangible book value ratio (PTBV). The latter is a valuation ratio expressing the price of a security compared to its hard, or tangible, book value as reported in the company's balance sheet. The tangible book value number is equal to the company's total book value less than the value of any intangible assets. Intangible assets can b…
Limitations of Using The P/B Ratio
- Investors find the P/B ratio useful because the book value of equity provides a relatively stable and intuitive metric they can easily compare to the market price. The P/B ratio can also be used for firms with positive book values and negative earnings since negative earnings render price-to-earnings ratios useless, and there are fewer companies with negative book values than compani…
What Is The Price-to-Book Ratio?
- The price-to-book ratio expresses a company's stock share price in relation to its book value per share (BVPS). "Book value" refers to a company's intrinsic, financial worth — specifically, the difference between all its assets and all its expenses and debts. Though officially a ratio, the P/B ratio is often just expressed as a single number. Some ...
How to Calculate The Price-to-Book Ratio
- Step 1:Get the current share price. That's simple enough, since it pops up quickly in an online search using the company's name or its ticker symbol. Step 2:Determine the book value per share (BVPS). The easy way is to look it up on a financial stock-listing site (you may have to scroll down a bit to find it). Or for DIY-ers: The first move is to figure out the "book value," or "net book value," …
Significance of The Price-to-Book Ratio
- Some analysts say a P/B ratio of less than 1 indicates that a stock is undervalued and, everything else being equal, it may be poised for a rise. A ratio of 1 may indicate "fair" pricing, where the market value is equal to the company's book value. A P/B ratio of 3 or higher could signal a market value that's too high and may be ready for a fall. That being said, it's tricky to determine a single …
How Accurate Is The Price-to-Book Ratio?
- "Price-to-book has a long history, but there are some drawbacks that have driven it to fall out of favor among some investors," Tadesse says. For one thing, price-to-book "doesn't account for hard-to-value intangible assets, like patents or other intellectual property," he says, adding "the book value is an accounting concept that's generally based on the lower of an asset's cost or ma…
The Bottom Line
- A price-to-book ratio can offer insight into whether an individual stock is a good buy, in relation to others in its industrial segment, or sometimes even the market overall. Focusing on fundamentals (the book value) vis-à-vis the share price, it can tune out speculative static that is currently distorting prices up or down. Comparing a single company's P/B ratio over time may help indicat…