
When did the stock market drop in 2008?
The stock market crash of 2008 occurred on September 29, 2008. The Dow Jones Industrial Average fell by 777.68 points in intraday trading.
How long did the stock market crash of 2008 last?
The US bear market of 2007–2009 was a 17-month bear market that lasted from October 9, 2007 to March 9, 2009, during the financial crisis of 2007–2009.
When did the 2008 crash end?
June 2009The Great Recession began in December 2007 and ended in June 2009, which makes it the longest recession since World War II.
What caused the market to crash in 2008?
By the fall of 2008, borrowers were defaulting on subprime mortgages in high numbers, causing turmoil in the financial markets, the collapse of the stock market, and the ensuing global Great Recession.
Who made money in 2008 crash?
1. Warren Buffett. In October 2008, Warren Buffett published an article in the New York TimesOp-Ed section declaring he was buying American stocks during the equity downfall brought on by the credit crisis.
How much did home values drop in 2008?
The loss of home values combined with declining stock totaled nearly $100,000 on average per U.S. household at the peak. Slower economic growth cost the U.S. economy an estimated $648 billion. The Dow Jones hit bottom in the first quarter of 2009 as the bad financial news continued.Jun 4, 2019
How long did it take to recover from 2008 recession?
The recession ended in June 2009, but economic weakness persisted. Economic growth was only moderate – averaging about 2 percent in the first four years of the recovery – and the unemployment rate, particularly the rate of long-term unemployment, remained at historically elevated levels.
Who is to blame for the Great Recession of 2008?
The Biggest Culprit: The Lenders Most of the blame is on the mortgage originators or the lenders. That's because they were responsible for creating these problems. After all, the lenders were the ones who advanced loans to people with poor credit and a high risk of default. 7 Here's why that happened.
What happened in 2008 in the world?
Great Recession The financial crisis of 2008, or Global Financial Crisis, was a severe worldwide economic crisis that occurred in the early 21st century. It was the most serious financial crisis since the Great Depression (1929).
What percentage did the market drop in 2008?
On October 24, 2008, many of the world's stock exchanges experienced the worst declines in their history, with drops of around 10% in most indices. In the U.S., the DJIA fell 3.6%, although not as much as other markets.
What was the biggest stock market crash?
The stock market crash of 1929, also referred to as the Great Crash or the Wall Street crash of 1929, saw both a sudden as well as a steep decline in stock prices in the United States during late October that year.Feb 9, 2022
How long did it take for house prices to recover after 2008?
3.5 yearsIt took 3.5 years for the recovery to begin after the recession began. A lot of buyers who bought in 2008, 2009 or 2010 saw their home prices decrease before the recovery started in 2011.
What happened in 2008?
By the fall of 2008, borrowers were defaulting on subprime mortgages in high numbers, causing turmoil in the financial markets, the collapse of the stock market, and the ensuing global Great Recession.
How much did the Dow drop in 2008?
The Dow would plummet 3,600 points from its Sept. 19, 2008 intraday high of 11,483 to the Oct. 10, 2008 intraday low of 7,882. The following is a recap of the major U.S. events that unfolded during this historic three-week period.
What mortgages are lethal?
Among the most potentially lethal of the mortgages offered to subprime borrowers were the interest-only ARM and the payment option ARM, both adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs). Both of these mortgage types have the borrower making much lower initial payments than would be due under a fixed-rate mortgage. After a period of time, often only two or three years, these ARMs reset. The payments then fluctuate as frequently as monthly, often becoming much larger than the initial payments.
What is the role of Fannie and Freddie?
2 . The role of Fannie and Freddie is to repurchase mortgages from the lenders who originated them and make money when mortgage notes are paid. Thus, ever-increasing mortgage default rates led to a crippling decrease in revenue for these two companies.
What is MBS in mortgage?
An MBS is a pool of mortgages grouped into a single security. Investors benefit from the premiums and interest payments on the individual mortgages the security contains. This market is highly profitable as long as home prices continue to rise and homeowners continue to make their mortgage payments.
Why did Bear Stearns fail?
By March 2007, with the failure of Bear Stearns due to huge losses resulting from its underwriting many of the investment vehicles linked to the subprime mortgage market, it became evident that the entire subprime lending market was in trouble.
How much credit did Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac extend in 2002?
As of 2002, government-sponsored mortgage lenders Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac had extended more than $3 trillion worth of mortgage credit. In his 2002 book Conquer the Crash, Prechter stated, "confidence is the only thing holding up this giant house of cards.". 2 .
What was the Dow value in September 2008?
The day was ended at the Dow value of 11,388.44. On September 20, 2008, the bank bailout bill was sent to Congress by Secretary Paulson and Federal Reserve Chair. The Dow fell to 777.68 points during the intraday trading that increased panic in the Global Market.
How many points did the Dow drop in 2008?
By September 17, 2008, the Dow fell by 446.92 points. By the end of the week on September 19, 2008, the Fed established the Asset-Backed Commercial Paper Money Market Mutual Fund Liquidity Facility that committed to offer loans to banks to buy Commerical paper from the money market funds.
How much did the Fed lose from Lehman Brothers?
By making $85 billion loans for 79.9% equity the Fed took ownership of the AIG. With the collapse of Lehman Brothers, there was a loss of $196 billion that increased the panic among many businesses. Bank has driven up the rates as they were afraid to lend money. By September 17, 2008, the Dow fell by 446.92 points.
What was the fourth cause of the 2008 financial crisis?
The fourth cause of the crash of 2008 was found to be the depression era Glass Steagall Act (1933) that allowed banks, securities firms and other insurance companies to enter into each other’s markets resulting in the formation of the bank that was too big to fail.
What were the causes of the Federal Reserve's crash?
Some of the top reasons for the crash are: Mild Recession in the Federal Reserve. Federal Reserve the Central Bank was facing a mild recession since 2001. The recession period resulted in the reduction of the federal funds rate from 6.5 to 1.75 from May 2000 to December 2001.
What was the impact of the 2008 stock market crash?
There is no doubt behind the saying, that the crash pushed the banking system towards the edge of collapse.
How much GDP growth was there in 2007?
As per the study in 2007 by the BEA, the GDP growth estimation reveals that there was only 0.6% growth in the fourth quarter of 2007 with the loss of 17,000 jobs since 2004.
Why did the mortgage salesmen make these deals without investigating a borrower's fitness or a property's
The salesmen could make these deals without investigating a borrower's fitness or a property's value because the lenders they represented had no intention of keeping the loans. Lenders would sell these mortgages onward; bankers would bundle them into securities and peddle them to institutional investors eager for the returns the American housing market had yielded so consistently since the 1930s. The ultimate mortgage owners would often be thousands of miles away and unaware of what they had bought. They knew only that the rating agencies said it was as safe as houses always had been, at least since the Depression.
What did Jim Bunning call the bailouts?
Senator Jim Bunning of Kentucky called the bailouts "a calamity for our free-market system" and, essentially, "socialism"—albeit the sort of socialism that favored Wall Street, rather than workers. Earlier in the year, Paulson had identified Lehman as a potential problem and spoke privately to its chief executive, Richard Fuld.
What did the Glass-Steagall Act do?
the Glass-Steagall Act ), they separated these newly secure institutions from the investment banks that engaged in riskier financial endeavors.
What was the financial environment like in the early 21st century?
The financial environment of the early 21st century looked more like the United States before the Depression than after: a country on the brink of a crash. pinterest-pin-it. An employee of Lehman Brothers Holdings Inc. carrying a box out of the company's headquarters after it filed for bankruptcy.
What was the financial crisis of 2008?
The 2008 financial crisis had its origins in the housing market, for generations the symbolic cornerstone of American prosperity. Federal policy conspicuously supported the American dream of homeownership since at least the 1930s, when the U.S. government began to back the mortgage market. It went further after WWII, offering veterans cheap home loans through the G.I. Bill. Policymakers reasoned they could avoid a return to prewar slump conditions so long as the undeveloped lands around cities could fill up with new houses, and the new houses with new appliances, and the new driveways with new cars. All this new buying meant new jobs, and security for generations to come.
When did Paulson say the government would not rescue Lehman?
By the weekend of September 13-14, 2008, Lehman was clearly finished, with perhaps tens of billions of dollars in overvalued assets on its balance sheets.
What was the only institution the bankers trusted?
After decades of trying to push the U.S. government out of banking, it turned out that in the end, the U.S. government was the only institution the bankers trusted.
Why did the stock market crash in 2008?
The stock market crashed in 2008 because too many had people had taken on loans they couldn’t afford. Lenders relaxed their strict lending standards to extend credit to people who were less than qualified. This drove up housing prices to levels that many could not otherwise afford.
What was the impact of the 2008 stock market crash?
The stock market crash of 2008 was a result of a series of events that led to the failure of some of the largest companies in U.S. history. As the housing bubble burst, it affected banks and financial institutions who were betting on the continued increase in home prices.
Why did Fannie Mae offer unconventional mortgage terms?
Lenders who extended home loans to high-risk borrowers offered mortgages with unconventional terms to reflect the increased likelihood of default.
How did the bailout affect the Dow Jones?
Each bailout announcement affected the Dow Jones, sending it tumbling as markets responded to the financial instability. The Fed announced a bailout package, which temporarily bolstered investor confidence. The bank bailout bill made its way to Congress, where the Senate voted against it on September 29, 2008.
What was the largest drop in history?
The Dow plummeted 777.68, the largest single-day drop in history up to this point. Global markets were swept up in the panic, causing global instability. Congress eventually passed the bailout bill in October, but the damage was done.
What banks were involved in the bailout?
The build-up of bad debt resulted in a series of government bailouts starting with Bear Stearns, a failing investment bank. Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac (the nickname given the Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation) were next on the government-sponsored bailout train.
Why did Lehman Brothers collapse?
In September 2008, investment firm Lehman Brothers collapsed because of its overexposure to subprime mortgages. It was the largest bankruptcy filing in U.S. history up to that point. Later that month, the Federal Reserve announced yet another bailout.
2007
2008
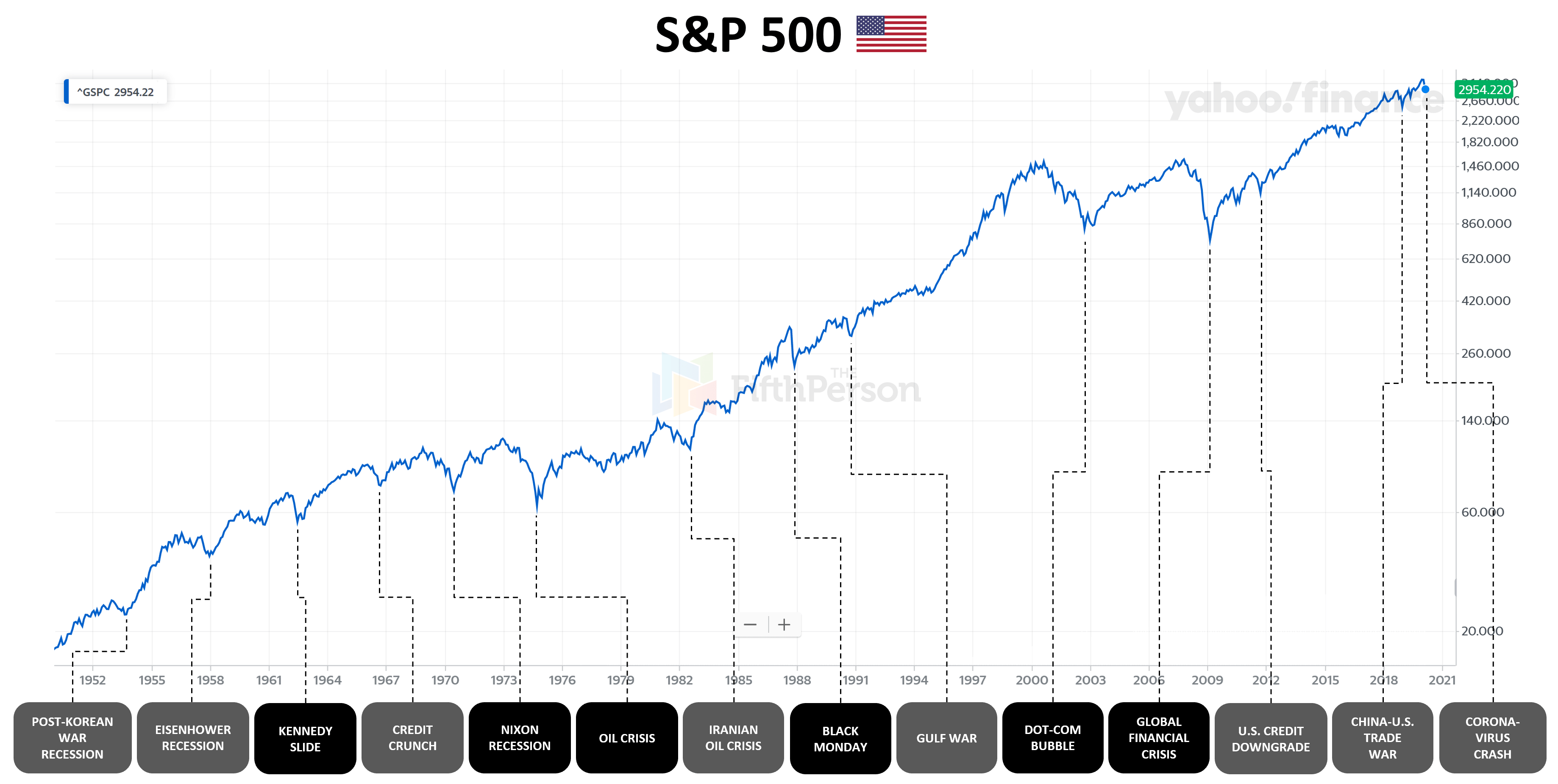
- At the end of January, the BEA revised its fourth-quarter 2007 GDP growth estimate down.9 It said growth was only 0.6%. The economy lost 17,000 jobs, the first time since 2004.10 The Dow shrugged off the news and hovered between 12,000 and 13,000 until March.2 On March 17, the Federal Reserve intervened to save the failing investment bank, Bear Stearns. The Dow dropped …
September 2008
- The month started with chilling news. On Monday, September 15, 2008, Lehman Brothers declared bankruptcy. The Dow dropped more than 200 points.2 On Tuesday, September 16, 2008, the Fed announced it was bailing out insurance giant American International Group Inc. It made an $85 billion loan in return for 79.9% equity, effectively taking ownership. AIG had run out of cash. It wa…
October 2008
- Congress finally passed the bailout bill in early October, but the damage had already been done.24 The Labor Department reported that the economy had lost a whopping 159,000 jobs in the prior month.25 On Monday, October 6, 2008, the Dow dropped by 800 points, closing below 10,000 for the first time since 2004.26 The Fed tried to prop up banks by lending $540 billion to money mar…
December 2008
- The Fed dropped the fed funds rate to 0%, its lowest level in history.29 The Dow ended the year at a sickening 8,776.39, down almost 34% for the year.2
2009
- On January 2, 2009, the Dow climbed to 9,034.69.2 Investors believed the new Obama administration could tackle the recession with its team of economic advisers. But the bad economic news continued. On March 5, 2009, the Dow plummeted to its bottom of 6,594.44.37 Soon afterward, President Barack Obama's economic stimulus plan instilled the confidence nee…
Aftermath
- Investors bore the emotional scars from the crash for the next four years. On June 1, 2012, they panicked over a poor May jobs report and the eurozone debt crisis. The Dow dropped 275 points.39 The 10-year benchmark Treasury yield dropped to 1.47.40 This yield was the lowest rate in more than 200 years.41It signaled that the confidence that evaporated during 2008 had not q…
The Bottom Line
- The stock market crash of 2008 was a result of defaults on consolidated mortgage-backed securities. Subprime housing loans comprised most MBS. Banks offered these loans to almost everyone, even those who weren’t creditworthy. When the housing market fell, many homeowners defaulted on their loans. These defaults resounded all over the financial industry, which heavily i…
Overview
The financial crisis of 2008, or Global Financial Crisis (GFC), was a severe worldwide economic crisis that occurred in the late 2000s. It was the most serious financial crisis since the Great Depression (1929). Predatory lending targeting low-income homebuyers, excessive risk-taking by global financial institutions, and the bursting of the United States housing bubbleculminated in …
History
Following is a timeline of major events during the financial crisis, including government responses, and the subsequent economic recovery:
• May 19, 2005: Fund manager Michael Burry closed a credit default swap against subprime mortgage bonds with Deutsche Bankvalued at $60 million – the first such CDS. He projected they would become volatile within two years of the lo…
Background
The crisis sparked the Great Recession, which, at the time, was the most severe global recession since the Great Depression. It was also followed by the European debt crisis, which began with a deficit in Greece in late 2009, and the 2008–2011 Icelandic financial crisis, which involved the bank failure of all three of the major banks in Icelandand, relative to the size of its economy, was the la…
Causes
While the causes of the bubble are disputed, the precipitating factor for the Financial Crisis of 2007–2008 was the bursting of the United States housing bubble and the subsequent subprime mortgage crisis, which occurred due to a high default rate and resulting foreclosures of mortgage loans, particularly adjustable-rate mortgages. Some or all of the following factors contributed to …
Economists who predicted the crisis
Economists, particularly followers of mainstream economics, mostly failed to predict the crisis. The Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania's online business journal examined why economists failed to predict a major global financial crisis and concluded that economists used mathematical models that failed to account for the critical roles that banks and other financial institutions, as opposed to producers and consumers of goods and services, play in the economy.
IndyMac
The first visible institution to run into trouble in the United States was the Southern California–based IndyMac, a spin-off of Countrywide Financial. Before its failure, IndyMac Bank was the largest savings and loan association in the Los Angeles market and the seventh largest mortgage loan originator in the United States. The failure of IndyMac Bank on July 11, 2008, was the fourth largest bank failure in United Stateshistory up until the crisis precipitated even larger fa…
Notable books and movies
• In 2006, Peter Schiff authored a book titled Crash Proof: How to Profit From the Coming Economic Collapse, which was published in February 2007 by Wiley. The book describes various features of the economy and housing market that led to the United States housing bubble, and warns of the impending decline. After many of the predictions came to pass, a second edition titled Crash Proof 2.0 was published in 2009, which included a "2009 update" addendum at the end of each c…
See also
• Banking (Special Provisions) Act 2008 (United Kingdom)
• List of bank failures in the United States (2008–present)
• 2008–2009 Keynesian resurgence
• 2010 United States foreclosure crisis