
What caused the stockmarket crash of 1987?
Oct 19, 2017 · On October 19, 1987, the stock market, along with the associated futures and options markets, crashed, with the S&P 500 stock market index falling about 20 percent.
What caused Black Monday, the stock market crash of 1987?
Nov 22, 2013 · Stock Market Crash of 1987 October 1987 The first contemporary global financial crisis unfolded on October 19, 1987, a day known as “Black Monday,” when the Dow Jones Industrial Average dropped 22.6 percent. Composite of newspaper headlines reporting the Stock Market Crash of 1987 (Associated Press)
What was the 1987 stock market crash foretold?
On October 19, 1987, a date that subsequently became known as"Black Monday," the Dow Jones Industrial Average plummeted 508 points, losing 22.6% of its …
Could the 1987 stock market crash happen again?
Jan 22, 2021 · The stock market crash of 1987 was a rapid and severe downturn in U.S. stock prices that occurred over several days in late October 1987. While the crash originated in the U.S., the event impacted...
Why did the stock market crash in 1987?
The 1987 stock market crash was a shock to the stability of the financial system, not just because of the size of the drop in price , but importantly because market functioning was significantly impaired.
What report reported that banks were more attentive to the collateral posted by the brokers and dealers?
The SEC reported that banks were more attentive to the collateral posted by the brokers and dealers, but in general extended credit following existing lending procedures (SEC Report 1988, pp. 5-24-5-29).
What did the Federal Reserve say before the opening of the financial markets?
Before the opening of financial markets on Tuesday, the Federal Reserve issued a short statement that said: The Federal Reserve, consistent with its responsibilities as the Nation's central bank, affirmed today its readiness to serve as a source of liquidity to support the economic and financial system.
Who reported the stock market crash of 1987?
Composite of newspaper headlines reporting the Stock Market Crash of 1987 (Associated Press) by Donald Bernhardt and Marshall Eckblad, Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago.
How much did the stock market gain in 1987?
Stock markets raced upward during the first half of 1987. By late August, the DJIA had gained 44 percent in a matter of seven months, stoking concerns of an asset bubble. 4 In mid-October, a storm cloud of news reports undermined investor confidence and led to additional volatility in markets. The federal government disclosed a larger-than-expected ...
What did the Fed do in 1987?
In a statement on October 20, 1987, Fed Chairman Alan Greenspan said, “The Federal Reserve, consistent with its responsibilities as the Nation's central bank, affirmed today its readiness to serve as a source of liquidity to support the economic and financial system ” (Carlson 2006, 10). Behind the scenes, the Fed encouraged banks to continue to lend on their usual terms. Ben Bernanke, writing in 1990, noted that “making these loans must have been a money-losing strategy from the point of view of the banks (and the Fed); otherwise, Fed persuasion would not have been needed. But lending was a good strategy for the preservation of the system as a whole” (Bernanke 1990). According to Bernanke, the 10 largest New York banks nearly doubled their lending to securities firms during the week of October 19 even though discount window borrowings didn’t themselves increase (Garcia 1989).
Why did the New York Stock Exchange put circuit breakers in place?
According to the New York Stock Exchange’s current website: “In response to the market breaks in October 1987 and October 1989, the New York Stock Exchange instituted circuit breakers to reduce volatility and promote investor confidence.
What were the problems with Black Monday?
A number of structural flaws in the market exacerbated the Black Monday losses; in the years that followed, regulators would address these structural flaws with reforms. At the time of the crisis, stock, options, and futures markets used different timelines for the clearing and settlements of trades, creating the potential for negative trading account balances and, by extension, forced liquidations. 10 Additionally, securities exchanges had been powerless to intervene in the face of large-volume selling and rapid market declines. 11 After Black Monday, regulators overhauled trade-clearing protocols to bring uniformity to all prominent market products. They also developed new rules, known as circuit breakers, allowing exchanges to halt trading temporarily in instances of exceptionally large price declines. 12 For example, under current rules, the New York Stock Exchange will temporarily halt trading when the S&P 500 stock index declines 7 percent, 13 percent, and 20 percent in order to provide investors “the ability to make informed choices during periods of high market volatility.” 13 In the wake of the Black Monday episode, risk managers also recalibrated the way they valued options. 14
What caused the Black Monday crisis?
The first contemporary global financial crisis unfolded in the autumn of 1987 on a day known infamously as “Black Monday.” 1 A chain reaction of market distress sent global stock exchanges plummeting in a matter of hours.
Who said lending was a good strategy for the preservation of the system as a whole?
Ben Bernanke, writing in 1990, noted that “making these loans must have been a money-losing strategy from the point of view of the banks (and the Fed); otherwise, Fed persuasion would not have been needed. But lending was a good strategy for the preservation of the system as a whole” (Bernanke 1990).
Why did the stock market crash in 1987?
The 1987 stock market crash was due to a poor monetary policy. Member commercial bank legal reserves declined at their sharpest rate for both Sept & Oct 87 since the beginning of their series in 1913.
What happened to the stock market in 1987?
However, studies show that during the 1987 U.S. Crash, other stock markets which did not use program trading also crashed, some with losses even more severe than the U.S. market. During the Crash, trading mechanisms in financial markets were not able to deal with such a large flow of sell orders.
What did the 1987 crash accomplish?
Bruce Bartlett: What the 1987 crash ultimately accomplished was to teach politicians that markets heed their words and actions carefully, reacting immediately when threatened. Thus the crash initiated a new era of market discipline on bad economic policy.
Why were stocks not traded on the New York Stock Exchange?
Many common stocks in the New York Stock Exchange were not traded until late in the morning of October 19 because the specialists could not find enough buyers to purchase the amount of stocks that sellers wanted to get rid of at certain prices. As a result, trading was terminated in many listed stocks.
How did the anti-takeover legislation affect the stock market?
Two economists from the Securities and Exchange Commission, Mark Mitchell and Jeffry Netter, published a study in 1989 concluding that the anti-takeover legislation did trigger the crash. They note that as the legislation began to move through Congress, the market reacted almost instantaneously to news of its progress. Between Tuesday, October 13, when the legislation was first introduced, and Friday, October 16, when the market closed for the weekend, stock prices fell more than 10 percent -- the largest 3-day drop in almost 50 years. In addition, those stocks that led the market downward were precisely those most affected by the legislation. [Ultimately, the legislation was stripped of the provisions that concerned the stock market before being enacted into law.] 4
What was the trigger for the market crash?
Another important trigger in the market crash was the announcement of a large U.S. trade deficit on October 14, which led Treasury Secretary James Baker to suggest the need for a fall in the dollar on foreign exchange markets.
How long did the 1987 Dow crash last?
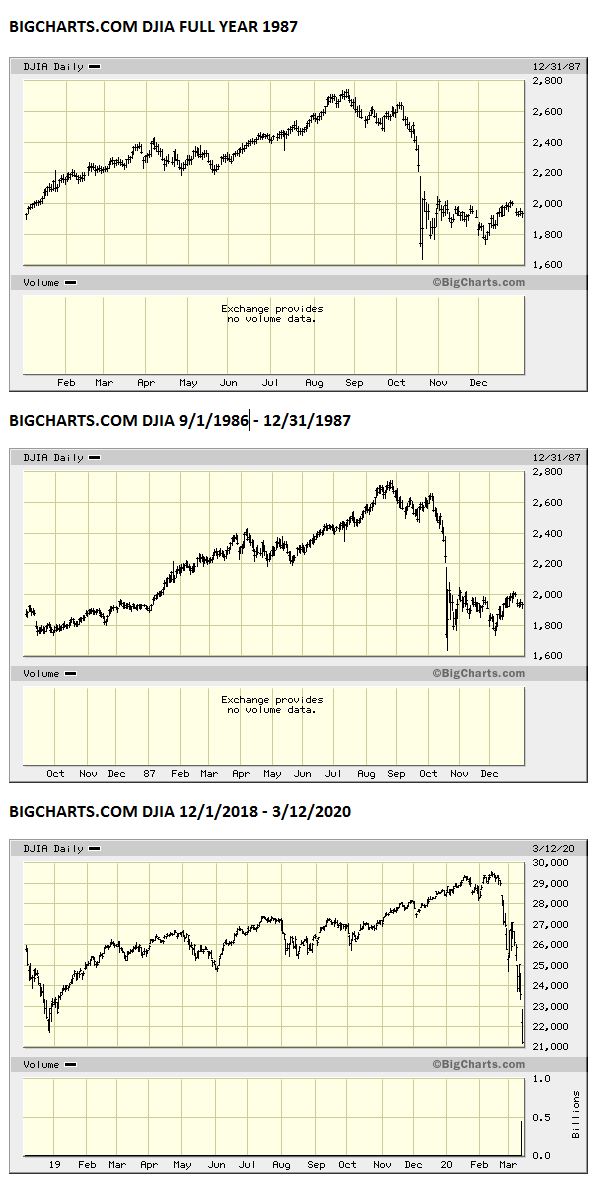
According to Facts on File, an authoritative source of current-events information for professional research and education, the 1987 crash"marked the end of a five-year 'bull' market that had seen the Dow rise from 776 points in August 1982 to a high of 2,722.42 points in August 1987." Unlike what hapopened in 1929, however, the market rallied immediately after the crash, posting a record one-day gain of 102.27 the very next day and 186.64 points on Thursday October 22. It took only two years for the Dow to recover completely; by September of 1989, the market had regained all of the value it had lost in the '87 crash. 2
What was the stock market crash in 1987?
The stock market crash of 1987 was a rapid and severe downturn in U.S. stock prices that occurred over several days in late October 1987. While the crash originated in the U.S., the event impacted every other major stock market in the world. In the five years leading up to the 1987 crash, the Dow Jones Industrial Average ( DJIA) ...
What was the impact of the 1987 stock market crash?
The stock market crash of 1987 revealed the role of financial and technological innovation in increased market volatility. In automatic trading, also called program trading, human decision-making is taken out of the equation, and buy or sell orders are generated automatically based on the price levels of benchmark indexes or specific stocks. Leading up to the crash, the models in use tended to produce strong positive feedback, generating more buy orders when prices were rising and more sell orders when prices began to fall.
What happened in 1987?
In the five years leading up to the 1987 crash, the Dow Jones Industrial Average ( DJIA) had more than tripled. On October 19, 1987—known as Black Monday —the DJIA fell by 508 points, or by 22.6%. Up to this point in history, this was the largest percentage drop in one day. The crash sparked fears of extended economic instability around ...
What mechanism did the Federal Reserve use to stop stock market?
After this crash, the Federal Reserve and stock exchanges intervened by installing mechanisms called " circuit breakers ," designed to slow down future plunges and stop trading when stocks fall too far or too fast. 2
What were the causes of the Persian Gulf crash?
Heightened hostilities in the Persian Gulf, a fear of higher interest rates, a five-year bull market without a significant correction, and the introduction of computerized trading have all been named as potential causes of the crash. There were also deeper economic factors that may have been to blame.
What was the peak of the stock market in 1987?
After five days of intensifying declines in the stock market, selling pressure hit a peak on October 19, 1987, also known as Black Monday. Steep price declines were created as a result of significant selling; total trading volume was so large that the computerized trading systems could not process them. Some orders were left unfilled for over an hour, and these order imbalances prevented investors from discovering the true price of stocks.
What countries did the Federal Reserve depreciate the dollar?
Under the Plaza Accord of 1985, the Federal Reserve made an agreement with the central banks of the G-5 nations—France, Germany, the United Kingdom, and Japan— to depreciate the U.S. dollar in international currency markets in order to control mounting U.S. trade deficits.
Why did the stock market crash in 1987?
Portfolio Insurance refers to a strategy to hedge or limit losses by buying and selling stocks and futures. People tend to buy in a rising market, which may create a bubble and sell in a falling market, which may lead to a crash, which it did. They short sell futures in expectation of the falling market, and if the market falls further, they short sell even more , thus destabilizing the market.
What happened in 1987?
Stock Market Crash in 1987, also known as Black Monday, was one where DJIA (Dow Jones Industrial Average) fell 22% (508 points) on a single day (19 October 1987) and had a contagious effect in the sense that the fall not only affected the US, but the whole world.
What happened when the stock market opened?
When the stock market opened, the difference between futures and market was huge. Futures that are supposed to trade at a premium were trading at a huge discount. It created panic among investors, and they started winding up their positions. Many arbitrage traders also took this opportunity to make a riskless profit from this situation by buying futures and selling spots. Due to both these factors gap between futures and spots narrowed down, but it caused a stock market crash.
What happened to margin calls in the stock market?
When the market fell, margin calls were triggered, which required futures position holders to deposit a margin, failing, which resulted in the selling future position. Due to large and sudden fall in the stock market, many futures position holders were not able to deposit margin, which led to the liquidation of their holding.
Why did the futures market go down?
Meanwhile, the futures market was open, and due to large sell orders, prices went down in the future market. When the stock market opened, the difference between futures and market was huge. Futures that are supposed to trade at a premium were trading at a huge discount.
How long did it take for the world to recover from the Great Depression?
It took almost 10 years for the world to come out of the great depression of 1929. The depression had affected the world vastly, and it took a lot of time to recover from the recession. Markets in 1987 recouped in 2 years without going into depression and gave stellar returns afterward.
When did futures trade?
But on 19 October 1987, futures were trading at a discount whereas futures trade at a premium to their underlying. Due to selling pressure across the world on that day, large sell orders were placed on the stock market in the US.
What was the stock market crash in 2008?
In addition, the 7 percent stock market decline on Sept. 29, 2008 is often considered a stock market crash. That drop was one of many in a falling stock market that ultimately lost half its value before recovering. Combined with the plummeting housing market, it is considered an underlying factor of the Great Recession of 2008.
What was the average inflation rate in 1987?
(In 1987, the average inflation rate, or the rate at which prices for many goods and services was rising, was over 3.6 percent.
What is a market crash?
A market crash denotes a precipitous loss, and the 1987 stock market crash was a stomach-churning example . The event began on Oct. 14, 1987, when markets began to show daily losses, and culminated with Black Monday 2, on Oct. 19, 1987, when the Dow Jones Industrial Average (also known as the Dow) lost a nerve-wracking 508.32 points—which at ...
How much do stocks fall in one day?
First, it’s important to separate a stock market downturn from an actual crash. The technical definition of a market crash is that stocks fall by 10 percent or more in one day, compared to a downturn, which is just any downward movement in the markets. The type of fall that indicates a crash is uncommon, as illustrated above.
What happens if the stock market drops to level 3?
And if the market reaches Level 3 at any time during the trading day, the market will stop for the rest of the day. These precautions were introduced after the 1987 stock market crash to avoid the conditions that caused that day’s panicked selling.
When did Black Monday happen?
The first Black Monday occurred on Oct. 28, 1929, when the stock market plummeted 13 percent in one day, falling an additional 12 percent the following day. As with the 1987 stock market crash, this drop followed a period of growth, along with the hindsight realization that stocks had been overpriced. This 1929 market crash is often considered ...
When did the stock market recover?
Two years later, by September 1989 , the market had recovered all of its value, a huge relief when compared to the aftermath of the stock market crash that preceded the Great Depression of 1929.
How much did stocks fall in 1929?
By comparison, the notorious Black Tuesday crash of October 24, 1929, that preceded the Great Depression, saw stocks fall by only 13% . Many of the statistics quoted in ABC’s special report appear quaint in retrospect: Currently, a 500-point down day would only amount to a 2.2% drop in the Dow Jones Industrial Average.
How many points did the Dow Jones Industrial Average drop in 1987?
October 19, 1987 the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA or the Dow) plunged by a then-record 508 points—a 22% decline in the index.
What song ended the year at number 1?
What song ended the year at number 1? “Faith,” by George Michael. How apropos.
How many times has Apple happened since 1987?
It has happened 17 times since 1987. Today, it is not uncommon for 1–1.5 billion shares to be traded on a given day. On October 19, 1987, Apple was only 6% of the size of IBM, then the largest company in the nation. Presently, Apple Inc.’s market capitalization is 6X (or 600%) that of IBM’s.
When did inflation start to rise?
Inflation: Following 59 months of economic expansion, a steep and prolonged decline in the consumer price index, and persistent dollar weakness, inflation began to rise by the beginning of 1987. Many investors believed that the stagflation of the 1970s was coming back.
What happened in the Middle East on October morning?
Conflict in the Middle East: On that October morning of the market crash, U.S. warships attacked an Iranian oil production platform in the Persian Gulf in response to a missile that had hit an American tanker off the coast of Kuwait the prior week .
What were the consequences of the 1987 financial crisis?
The crash of 1987 also altered implied volatility patterns that arise in pricing financial options.
What happened on Black Monday 1987?
Before the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) opened on Black Monday, October 19, 1987, there was pent-up pressure to sell stocks. When the market opened, a large imbalance immediately arose between the volume of sell orders and buy orders, placing considerable downward pressure on stock prices. Regulations at the time permitted designated market makers (also known as "specialists") to delay or suspend trading in a stock if the order imbalance exceeded that specialist's ability to fulfill orders in an orderly manner. The order imbalance on the 19th was so large that 95 stocks on the S&P 500 Index (S&P) opened late, as also did 11 of the 30 DJIA stocks. Importantly, however, the futures market opened on time across the board, with heavy selling.
What happened on October 14 1987?
As the day continued, the DJIA dropped 95.46 points (3.81%) to 2,412.70, and it fell another 58 points (2.4%) the next day, down over 12% from the August 25 all-time high. On Friday, October 16, the DJIA fell 108.35 points (4.6%) to close at 2,246.74 on record volume. The drop on the 14th was the earliest significant decline among all countries that would later be affected by Black Monday.
How much did the Dow Jones Industrial Average rise in 1987?
From August 1982 to its peak in August 1987, the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) rose from 776 to 2,722, including a 44% year-to-date rise as of August 1987. The rise in market indices for the nineteen largest markets in the world averaged 296% during this period.
What were the causes of the Black Monday crash?
Discussions of the causes of the Black Monday crash frequently focus on two theoretical models, which differ in whether they focus on variables that are exogenous or endogenous. The first framework searches for exogenous factors, such as significant news events, that affect investor perceptions and behavior. These events are taken as "triggers" of market behavior. The second, "cascade theory" or "market meltdown", attempts to identify endogenous internal market dynamics and interactions of systemic variables or trading strategies such that an order imbalance leads to a price change, this price change in turn leads to further order imbalance, which leads to further price changes, and so on in a spiralling cascade. It is possible that both could occur, if a trigger sets off a cascade.
What was the biggest drop in the Dow Jones Industrial Average?
The Black Monday decline was, and currently remains, the biggest drop on the List of largest daily changes in the Dow Jones Industrial Average. (Saturday, December 12, 1914, is sometimes erroneously cited as the largest one-day percentage decline of the DJIA.
What was the worst drop in the stock market?
The worst decline among world markets was in Hong Kong, with a drop of 45.8%. In its biggest-ever single fall, the Hang Seng Index of the Hong Kong Stock Exchange dropped 420.81 points on Black Monday, eliminating HK$65 billion' (10%) of the value of its shares. Noting the continued fall of New York markets on their next trading day, and fearing steep drops or even total collapse of their own exchanges, in Hong Kong the Stock Exchange Committee and the committee of the Futures Exchange announced the following morning that both markets would be closed. Their closure lasted for four working days. Their decision was motivated in part by the very real possibility that market collapse could have extremely serious consequences for the entire financial system of Hong Kong, perhaps resulting in rioting in the streets, with the added threat of intervention by the army of the People's Republic of China. According to Neil Gunningham, a further motivation for the closures was brought on by a significant conflict of interest: many of these committee members were themselves futures brokers, and their firms were in danger of substantial defaults from their clients.
What happened in 1987?
The Crash of 1987. During this crash, 1/2 trillion dollars of wealth were erased. The markets hit a new high on August 25, 1987 when the Dow hit a record 2722.44 points. Then, the Dow started to head down. On October 19, 1987, the stock market crashed. The Dow dropped 508 points or 22.6% in a single trading day.
What happened to the stock market after the 1929 crash?
After the crash, the stock market mounted a slow comeback. By the summer of 1930, the market was up 30% from the crash low. But by July 1932, the stock market hit a low that made the 1929 crash. By the summer of 1932, the Dow had lost almost 89% of its value and traded more than 50% below the low it had reached on October 29, 1929.
How much wealth was lost in the 2000 crash?
The Crash of 2000. A total of 8 trillion dollars of wealth was lost in the crash of 2000. From 1992-2000, the markets and the economy experienced a period of record expansion. On September 1, 2000, the NASDAQ traded at 4234.33. From September 2000 to January 2, 2001, the NASDAQ dropped 45.9%.
How much did the Dow drop in 1987?
On October 19, 1987, the stock market crashed. The Dow dropped 508 points or 22.6% in a single trading day. This was a drop of 36.7% from its high on August 25, 1987.
How much wealth was lost in the 1929 stock market crash?
The Crash of 1929. In total, 14 billion dollars of wealth were lost during the market crash. On September 4, 1929, the stock market hit an all-time high. Banks were heavily invested in stocks, and individual investors borrowed on margin to invest in stocks.
What is a stock crash?
Stock Market Crash is a strong price decline across majority of stocks on the market which results in the strong decline over short period on the major market indexes (NYSE Composite, Nasdaq Composite DJIA and S&P 500).
When did banks go out of business?
When these banks started to invest heavily in the stock market, the results proved to be devastating, once the market started to crash. By 1932, 40% of all banks in the U.S. had gone out of business.