How is a restricted stock award taxed?
How is a restricted stock award taxed? The general rule says you don’t have any taxable income from a restricted share award until the shares become vested, meaning when your ownership is no longer restricted.
When do you have to notify the IRS of a restricted stock?
If you decide to make the election, you must notify the IRS either before the restricted stock is transferred to you or within 30 days after that date. Your tax pro can help you with the election details. The tax rules for restricted stock are fairly straightforward.
What is a vesting period for restricted stock awards?
Vesting periods for Restricted Stock Awards may be time-based (a stated period from the grant date), or performance-based (often tied to achievement of corporate goals.) When a Restricted Stock Award vests, the employee receives the shares of company stock or the cash equivalent (depending on the company’s plan rules) without restriction.
What is a restricted stock deal?
In a typical restricted stock deal, you receive company stock subject to one or more restrictions. The most common restriction is a requirement that you must continue working for the company until some magic date. If you leave too soon, you forfeit the restricted shares, which are usually issued at minimal or no cost to you.

How are restricted stock awards taxed?
If you're granted a restricted stock award, you have two choices: you can pay ordinary income tax on the award when it's granted and pay long-term capital gains taxes on the gain when you sell, or you can pay ordinary income tax on the whole amount when it vests.
Do you have to pay taxes when RSUs vest?
Taxation. With RSUs, you are taxed when the shares are delivered, which is almost always at vesting. Your taxable income is the market value of the shares at vesting. You have compensation income subject to federal and employment tax (Social Security and Medicare) and any state and local tax.
Do you pay taxes on RSUs twice?
You would be paying tax twice on the income from receiving RSU shares—and that's paying tax on an extra $10,000 of gain! One additional note to be aware of: The tax you pay on the sale of your shares follows the normal rules for gains and losses on investments.
How do I avoid paying taxes on RSU?
The first way to avoid taxes on RSUs is to put additional money into your 401(k). The maximum contribution you can make for 2021 is $19,500 if you're under age 50. If you're over age 50, you can contribute an additional $6,000.
How do I report RSU on tax return?
Any dividends you receive on RSUs are considered employee income and should only be reported on your W-2. List them on your Schedule B with your tax return with a note that you've included them as wages if you receive a 1099-DIV for the value of your RSU dividends.
Why are RSUs taxed so high?
Since RSUs amount to a form of compensation, they become part of your taxable income, and because RSU income is considered supplemental income, the withholding rate can vary from 22% to 37%.
Should you sell RSU as soon as they vest?
Usually, it is recommended to sell the RSU immediately after the vesting period is complete to avoid any additional taxes. Insiders and employees that hold the RSU, need a RSU selling strategy. But for investors with a different and more diverse portfolio, holding on to the RSU is the choice to make.
How is capital gains tax calculated on RSU?
You can calculate capital gain by deducting the market value of your RSU shares on the vesting date from the selling price. For instance, you sold your 200 shares above which were valued at $10 on the vesting date at $15.
What should I do with my restricted stock units?
So, when is the best time to sell your RSUs? If your company is public, the best thing to do is to cash them out as soon as they vest. The reason is that RSUs essentially function like a cash bonus, being taxed at the time they vest.
What is the capital gains tax rate for 2021?
2021 Long-Term Capital Gains Tax RatesTax Rate0%15%SingleUp to $40,400$40,401 to $445,850Head of householdUp to $54,100$54,101 to $473,750Married filing jointlyUp to $80,800$80,801 to $501,600Married filing separatelyUp to $40,400$40,401 to $250,8001 more row•Feb 17, 2022
What happens if an employee accepts restricted stock?
Once an employee is granted a Restricted Stock Award, the employee must decide whether to accept or decline the grant. If the employee accepts the grant, he may be required to pay the employer a purchase price for the grant.
What is restricted stock?
A Restricted Stock Award Share is a grant of company stock in which the recipient’s rights in the stock are restricted until the shares vest (or lapse in restrictions). The restricted period is called a vesting period. Once the vesting requirements are met, an employee owns the shares outright and may treat them as she would any other share ...
What happens if stock prices fall during vesting?
If the stock price declined during the vesting period, there is a risk that more taxes would be paid based on the fair market value on the grant date than would have been paid at vesting. Timing of tax payment.
What is the amount of income subject to tax?
The amount of income subject to tax is the difference between the fair market value of the grant at the time of vesting minus the amount paid for the grant, if any. For grants that pay in actual shares, the employee’s tax holding period begins at the time of vesting, and the employee’s tax basis is equal to the amount paid for the stock plus ...
When does the holding period begin?
Holding period. Holding period begins at vesting date, when the compensation element of restricted stock is included in income. Holding period begins at grant date, when the compensation element of restricted stock is included in income. Subsequent sale of shares (assuming shares held as capital asset)
When do you file a special tax 83b?
A Special Tax 83 (b) election must by filed in writing with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) no later than 30 days after the date of the grant. Additionally, the employee must send a copy of the Special Tax 83 (b) election form to their employer, and include a copy when filing their yearly income tax return.
Can restricted stock be forfeited?
Risk of forfeiture. If the restricted stock award is forfeited (e.g., by leaving the company before the stock vests), a loss cannot be claimed for tax purposes with respect to the restricted stock award. Additionally, there is no refund on the tax paid on the restricted stock award.
What is restricted stock?
Restricted stock is, by definition, a stock that has been granted to an executive that is nontransferable and subject to forfeiture under certain conditions, such as termination of employment or failure to meet either corporate or personal performance benchmarks.
What is the rule for insider trading?
Although there are some exceptions, most-restricted stock is granted to executives who are considered to have "insider" knowledge of a corporation, thus making it subject to the insider trading regulations under SEC Rule 144. 1 Failure to adhere to these regulations can also result in forfeiture.
What is Section 83 B?
Section 83 (b) Election. Shareholders of restricted stock are allowed to report the fair market value of their shares as ordinary income on the date that they are granted, instead of when they become vested if they so desire. 2 The capital gains treatment still applies, but it begins at the time of grant.
What are the advantages of stock compensation?
This type of compensation has two advantages: It reduces the amount of cash that employers must dole out, and also serves as an incentive for employee productivity. There are many types of stock compensation, and each has its own set of rules and regulations.
How much does Sam have to report in vesting?
Sam will have to report a whopping $900,000 of the stock balance as ordinary income in the year of vesting, while Alex reports nothing unless the shares are sold, which would then be eligible for capital gains treatment.
Can you deliver stock until vesting and forfeiture requirements have been satisfied?
Therefore, the shares of stock cannot be delivered until vesting and forfeiture requirements have been satisfied and release is granted. Some RSU plans allow the employee to decide within certain limits exactly when to receive the shares, which can assist in tax planning.
Is there a forfeiture risk in Section 83 B?
Unfortunately, there is a substantial risk of forfeiture associated with the Section 83 (b) election that goes above and beyond the standard forfeiture risks inherent in all restricted stock plans.
What are the tax rules for restricted stock?
The tax rules for restricted stock are fairly straightforward. The major tax planning consideration is deciding whether or not to make the Section 83 (b) election. You might tentatively conclude that the risks of making the election are greater than the potential tax-savings, but consider consulting with your tax pro before making the call.
How long do you have to notify the IRS of restricted stock?
If you decide to make the election, you must notify the IRS either before the restricted stock is transferred to you or within 30 days after that date. Your tax pro can help you with the election details.
How long after vesting stock can you hold it?
Any appreciation after the shares vest is treated as capital gain. So if you hold the stock for more than one year after the vesting date, you will have a lower-taxed long-term capital gain on any post-vesting-date appreciation.
Why are restricted stock awards so popular?
The reason: options can lose most or all of their value if the price of the underlying stock takes a dive.
What happens if you leave a company too soon?
If you leave too soon, you forfeit the restricted shares, which are usually issued at minimal or no cost to you.
What does a restricted share legend mean?
To ensure that the non-transferable requirement is met, restricted shares are commonly stamped with a legend that discloses the restriction (s) placed on them and/or indicating that they are not transferable.
When does Section 83 B make sense?
The Section 83 (b) election only makes sense when: (1) you expect to stay on board with your company until the restricted shares vest and (2) you expect substantial share-price appreciation. But right now, there’s another reason to consider the election.
Why are restricted stock awards used?
One of the reasons for the shift to restricted stock is the reduced charge against income provided by restricted stock awards as compared to stock option grants. Restricted stock is also less dilutive to the company’s stock than options, because value to the employee can be achieved with fewer shares.
Why do employers issue restricted stock units?
Some employers choose to issue restricted stock units (RSUs) to employees rather than restricted stock, because employees cannot make a Sec. 83 (b) election in connection with restricted stock units. RSUs are unfunded promises to pay cash or stock to the employee based on a vesting schedule. One RSU is typically equal in value to one share ...
Why is the Sec 83 B election invalid?
83 (b) election was invalid because the company held the shares in escrow and they were not legally transferred to him.
Why is restricted stock less dilutive than options?
Restricted stock is also less dilutive to the company’s stock than options, because value to the employee can be achieved with fewer shares. Executive compensation practices came under increased congressional scrutiny when abuses at corporations such as Enron became public.
What is a capital loss deduction?
1.83-2 (a) does permit a capital loss deduction for the excess paid for forfeited stock above any amount realized upon the forfeiture, including any amount of the purchase price restored by the employer to the employee. Regs. Sec. 1.83-2 (a) also warns that a sale or other disposition of the property ...
Do CPAs have to be familiar with restricted stock awards?
With the increased popularity of restricted stock, CPA tax practitioners must be familiar with the rules governing taxation of restricted stock awards when advising clients who have been or may be offered restricted stock awards, as well as when advising corporations that make the awards.
Is 83 B deductible?
83 (b) carries at least two risks to the employee. One is that the property may not in fact appreciate but, rather, depreciate during the restricted period. In such case, the amount included in income when the employee made the election is not now deductible.
What is the FMV of restricted stock?
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) allows for restricted stock shareholders to report the fair market value (FMV) of the stock when it is granted, as opposed to when the employee earns it through vesting. This is called the Section 83 (b) Election.
When are RSUs taxed?
Ordinary Income Tax : RSUs are taxed at the ordinary income rate when issued, typically after a vesting schedule. Capital Gains Tax : RSUs are only exposed to capital gains tax if the stockholder holds onto the stock and it appreciates in value before selling it.
What is the most important thing to understand about RSUs, vesting, and taxes?
The most important thing to understand about RSUs, vesting, and taxes is when the RSUs vest, their ownership is transferred to the employee or executive and they immediately have tax liability on the value of the RSUs.
Why do corporations grant RSUs?
Many corporations grant RSUs to executive with the purpose of incentivizing them to add as much value to the company as possible so they can benefit in the increasing stock price. RSUs are a form of restricted stock, which means they are ‘restricted’ in some form.
Is restricted stock a legal form?
RSUs and other forms of employee compensation are typically put in place using a legal agreement. If you need help with this type of employee compensation agreement, feel free to post a job in the ContractsCounsel marketplace for free to get bids from qualified lawyers.
Does restricted stock go on W-2?
Given restricted stock is routinely granted as a form of employee compensation, you will usually see it reported on your W-2. Typically, employees withhold taxes on behalf of their employees, which will go against what you owe when doing your taxes.
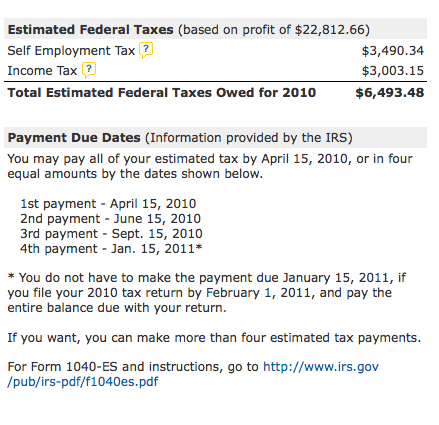
Do you have to send quarterly tax payments?
With all estimated taxes, you’ll need to send the IRS quarterly payments which estimate the amount of tax you’ll be liable for at the end of the year. Restricted stock is also regulated by the Securities Exchange Commission (SEC) since it is routinely granted to executives that are ‘in the know’ about a company.
Why do executives take restricted stock?
Many executives will take restricted stock along with a lower salary since there is potential for significant gain if the company succeeds and increases in value. Bottom Line. Restricted stock, whether RSAs or RSUs, can hold a lot of potential value and are often coveted forms of compensation.
What happens if you sell stock before the FMV?
If you sell before that, you’ll pay short-term capital gains tax , which is the same as your income tax rate. So imagine you take Section 83(b) on an award of 100 shares and pay $5 a share, which is much lower than the fair market value (FMV) of $20.
What happens if a company's stock tanked?
If the company’s stock tanks, it will be worth little or nothing if you sell. In either case, you’ve paid income tax on the strike price, but you won’t see a profit. In effect you’ll have paid taxes on income you never received. Every RSA is different, as are the conditions in which they’re granted.
What happens if you sell a company under 83(b)?
Under Section 83(b), you declare no income, and you’ll only pay capital gains when you sell . There can be risks with a Section 83(b) election. If you lose your job before the RSA shares vest, they usually are repurchased by the company. If the company’s stock tanks, it will be worth little or nothing if you sell.
Can a restricted stock grant be paid?
The recipient of a restricted stock grant may sometimes have to pay for the shares, in addition to fulfilling the vesting requirements.
Is RSA taxed as income?
Under Section 83(b), the RSA is taxed as income, and there will be no taxes when the shares vest unless you sell them. When you do sell the shares, they are subject to capital gains tax, which is much lower than income tax if you hold the shares for longer than a year.
RSU Tax at Vesting and Promise to Pay
RSUs are a unique form of equity compensation because they become taxable to you as they vest. Let’s compare RSUs to your salary.
How to Calculate RSU Taxable Income
To determine the amount of RSUs that are taxable to you in a given year, you take the following:
RSU and Salary Tax Withholding
Every few weeks, your employer pays you and also sets aside some taxes on your behalf. This happens because the IRS has rules that require people to set money aside before filing their taxes.
RSU Tax Situation After Vesting
As we’ve discussed, your RSUs vest and become fully taxable to you. When this happens, the entire vested amount is now considered to be your “cost basis.”
Capital Gains and Capital Losses
There are two types of Capital Gains and two types of Capital Losses, however, for this article we’re going to say all Capital Losses are the same.
Putting It All Together: When Do You Owe Taxes on RSUs
For example, let’s say you received a grant of $14,400 of RSUs on 1/1/2020 that vests over 4 years (25% each year). You’re already making $100k so you’re pretty excited.
Recommendation on RSUs
Now that you have a better understanding of when and how you’ll be taxed on your RSUs, you’ll want to start making a plan to sell your RSUs.