
Preferred Stock Features
- Callable: A call option gives you the right to repurchase preferred shares at a fixed price or par value after a set date. ...
- Cumulative: You may retain the right to suspend payment of dividends. ...
- Participating: A participating feature gives preferred shareholders the right to receive a share of dividends paid to common shareholders. ...
What are the usual characteristics of preferred stock?
What are some of the major characteristics of common and preferred stock?
- The Voting Rights of Common Stock Holders.
- The Value of Common Stocks.
- Capability of Receiving Periodic Dividends.
- Profit and Risks Relation.
- Tax Exemptions (Indirect)
- Claim on Assets.
- Chances of Losing Everything in the Case of Bankruptcy.
- Right to have Capital Gain.
What are the specific advantages of preferred stock?
What are Preferred Shares?
- Features of Preferred Shares. Preferred shares have a special combination of features that differentiate them from debt or common equity.
- Types of Preferred Stock. Preferred stock is a very flexible type of security. ...
- Advantages of Preferred Shares. Preferred shares offer advantages to both issuers and holders of the securities. ...
- Related Readings. ...
What companies have preferred stock?
Preferred Stocks Directory
- Preferred shares are shares issued by a corporation as part of its capital structure.
- Preferred stock have a “coupon rate” — the interest rate you will be paid. ...
- Dividends are either cumulative — meaning that dividends continue to accrue if they have been suspended, but they are not paid until the company decides to pay them after suspension ...
What is the difference between common stock and preferred stock?
- Common Stock, implies the type of stock ordinarily issued by the company to raise capital, indicating part ownership and carry voting rights. ...
- Common Stock has high growth potential, as compared to preferred stock, whose propensity to grow is slightly low.
- Common Stockholders return on capital is neither guaranteed, nor the amount is fixed. ...

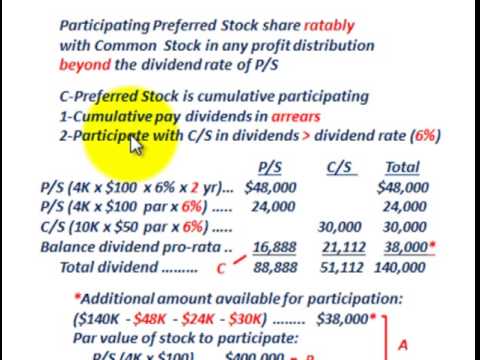
What is the cumulative feature of preferred stock?
Cumulative preferred stock is a type of preferred stock that provides a greater guarantee of dividend payments to its holders. The “cumulative” in cumulative preferred stock means that if your company suspends dividend payments, the unpaid dividends (known as dividends in arrears) owed continue to accrue.
What is the purpose of preferred stock?
Preferred shares are an asset class somewhere between common stocks and bonds, so they can offer companies and their investors the best of both worlds. Companies can get more funding with preferred shares because some investors want more consistent dividends and stronger bankruptcy protections than common shares offer.
What is preferred stock example?
What Is an Example of a Preferred Stock? Consider a company is issuing a 7% preferred stock at a $1,000 par value. In turn, the investor would receive a $70 annual dividend, or $17.50 quarterly. Typically, this preferred stock will trade around its par value, behaving more similarly to a bond.
Which of the following features is generally not associated with preferred stock?
Which feature is generally not associated with preferred stock? Which answer is not a true statement regarding voting rights? Shareholders generally get to vote on who is part of the corporate Board of Directors. Preferred stock generally does not carry voting rights.
What is preferred stock?
Preferred stocks are equity securities that share many characteristics with debt instruments. Preferred stock is attractive as it offers higher fixed-income payments than bonds with a lower investment per share. Preferred stock often has a callable feature which allows the issuing corporation to forcibly cancel the outstanding shares for cash.
Why do companies issue preferred stock?
A company may choose to issue preferreds for a couple of reasons: 1 Flexibility of payments. Preferred dividends may be suspended in case of corporate cash problems. 2 Easier to market. Preferred stock is typically bought and held by institutional investors, which may make it easier to market during an initial public offering.
What is a participating preferred stock?
Participating. This is preferred stock that has a fixed dividend rate. If the company issues participating preferreds, those stocks gain the potential to earn more than their stated rate. The exact formula for participation will be found in the prospectus. Most preferreds are non-participating.
How much can you deduct from preferred stock?
Corporations that receive dividends on preferred stock can deduct 50% to 65% of the income from their corporate taxes. 1 .
Why are preferred stocks considered hybrid securities?
Because of their characteristics, they straddle the line between stocks and bonds. Technically, they are securities, but they share many characteristics with debt instruments . Preferred stocks are sometimes called hybrid securities.
Why are preferred dividends suspended?
Preferred dividends may be suspended in case of corporate cash problems. Easier to market. Preferred stock is typically bought and held by institutional investors, which may make it easier to market during an initial public offering.
What happens to preferred shares when interest rates rise?
If interest rates rise, the value of the preferred shares falls. If rates decline, the opposite would hold true.
What is preferred stock?
Preferred shares (also known as preferred stock or preference shares) are securities that represent ownership in a corporation . Corporation A corporation is a legal entity created by individuals, stockholders, or shareholders, with the purpose of operating for profit. Corporations are allowed to enter into contracts, sue and be sued, own assets, ...
Why are preferred stock investors more secure?
The investors may benefit in the following way: Secured position in case of the company’s liquidation: Investors with preferred stock are in a more secure position relative to common shareholders in the event of liquidation, because they have a priority in claiming the company’s assets. Fixed income: These shares provide their shareholders ...
What is a convertible preferred stock?
Convertible preferred stock: The shares can be converted to a predetermined number of common shares. Cumulative preferred stock: If an issuer of shares misses a dividend payment, the payment will be added to the next dividend payment. Exchangeable preferred stock: The shares can be exchanged for some other type of security.
What are the features of a liquidation?
Although the terms may vary, the following features are common: Preference in assets upon liquidation: The shares provide their holders with priority over common stock holders to claim the company’s assets upon liquidation. Dividend payments: The shares provide dividend payments to shareholders. The payments can be fixed or floating, based on an ...
What is common stock?
Common Stock Common stock is a type of security that represents ownership of equity in a company. There are other terms – such as common share, ordinary share, or voting share – that are equivalent to common stock. in dividend payments.
Is a preferred shareholder a floating or fixed payment?
The payments can be fixed or floating, based on an interest rate benchmark such as LIBOR. . Preference in dividends: Preferred shareholders have a priority in dividend payments over the holders of the common stock. Non-voting: Generally, the shares do not assign voting rights to their holders.
Does dilution of control mean no obligation for dividends?
No obligation for dividends: The shares do not force issuers to pay dividends to shareholders.
What is preferred stock?
Preferred stock is a special class of equity that adds debt features. As with common stock, shareholders receive a share of ownership in the company. Preferred stock also receives special rights, including guaranteed dividends that must be paid out before dividends to common shareholders, priority in the event of a liquidation, ...
Why do preferred shares count as equity?
To avoid increasing your debt ratios; preferred shares count as equity on your balance sheet. To pay dividends at your discretion. Because dividend payments are typically smaller than principal plus interest debt payments. Because a call feature can protect against rising interest rates.
What happens to preferred stock when the company goes out of business?
If the company goes out of business and is liquidated, debt holders will be repaid first. Next, preferred shareholders will receive any outstanding dividends.
What is a participating feature?
Participating: A participating feature gives preferred shareholders the right to receive a share of dividends paid to common shareholders. This is in addition to preferred dividends. Convertible: Convertible preferred shares may be exchanged for common shares.
What is callable option?
Callable: A call option gives you the right to repurchase preferred shares at a fixed price or par value after a set date. You have sole discretion whether to exercise the option. Cumulative: You may retain the right to suspend payment of dividends.
What is preferred shareholder?
Preferred shareholders also have priority over common shareholders in any remaining equity. The preferred shareholder agreement sets out how remaining equity is divided. Preferred shareholders may receive a fixed amount or a certain ratio versus common shareholders.
Do preferred stock companies pay dividends?
While preferred stock is outstanding, the company must pay dividends. The dividend may be a fixed dollar amount or based on a metric such as profits. Common shareholders may not receive dividends unless preferred dividends have been fully paid. This includes any accumulated dividends.
What are the advantages of preferred stock?
Depending on your investment goals, preferred stock might be a good addition to your portfolio. Some of the main advantages of preferred stock include: 1 Higher dividends. In general, you can receive higher regular dividends with preferred shares. Payouts are also usually greater than what you’d receive with a bond because you’re assuming more risk. 2 Priority access to assets. If the company goes bankrupt, preferred shareholders are in line ahead of common shareholders, but still behind bondholders. 3 Potential premium from callable shares. Because preferred stock is callable, the company can buy it back. If the callable price is above the par value, you may receive more than you paid for the preferred stock. 4 Ability to convert preferred stock to common stock. When you buy convertible shares, you can trade in your preferred stock for common stock. If the value of the common stock drastically rises, you could convert your shares and benefit from its appreciation while investing in a less risky asset.
Why do people buy preferred stock?
Investors buy preferred stock to bolster their income and also get certain tax benefits.
What is dividend yield?
Dividend yield is a concept that helps you understand the relative value and return you get from preferred stock dividends. Par value is key to understanding preferred stock dividend yields
Why are preferred stocks more stable than common stocks?
With preferred stock, your gains are more limited. That’s because like bond prices, preferred stock prices change slowly and are tied to market interest rates. Preferred stocks do provide more stability and less risk than common stocks, though.
What is preferred stock par value?
Like bonds, shares of preferred stock are issued with a set face value, referred to as par value. Par value is used to calculate dividend payments and is unrelated to preferred stock’s trading share price. Unlike bonds, preferred stock is not debt that must be repaid. Income from preferred stock gets preferential tax treatment, ...
What happens to preferred stock in bankruptcy?
Preferred stock’s priority ahead of common stock also extends to bankruptcy. If a company goes bankrupt and is liquidated, bondholders are repaid first from the remaining assets, followed by preferred shareholders. Common stockholders are last in line, although they’re usually wiped out in bankruptcy.
How many shares of common stock do you get if you trade in preferred stock?
If you decided to trade in a share of preferred stock, you’d get 5.5 shares of common stock. Just because you can convert a preferred stock into common stock doesn’t mean it’ll be profitable, though. Before converting your preferred stock, you need to check the conversion price.
Features of Preferred Shares
- Preferred shares have a special combination of features that differentiate them from debt or common equity. Although the terms may vary, the following features are common: 1. Preference in assets upon liquidation: The shares provide their holders with priority over common stock holders to claim the company’s assets upon liquidation. 2. Dividend pay...
Types of Preferred Stock
- Preferred stock is a very flexible type of security. They can be: 1. Convertible preferred stock: The shares can be converted to a predetermined number of common shares. 2. Cumulative preferred stock:If an issuer of shares misses a dividend payment, the payment will be added to the next dividend payment. 3. Exchangeable preferred stock: The shares can be exchanged for some oth…
Advantages of Preferred Shares
- Preferred shares offer advantages to both issuers and holders of the securities. The issuers may benefit in the following way: 1. No dilution of control: This type of financing allows issuers to avoid or defer the dilution of control, as the shares do not provide voting rights or limit these rights. 2. No obligation for dividends:The shares do not force issuers to pay dividends to shareh…
Related Readings
- Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Preferred Shares. To help you advance your career, check out the additional CFI resources below: 1. Senior and Subordinated Debt 2. Retained Earnings 3. Stakeholder vs. Shareholder 4. Stockholders Equity