When you're trading stocks, a long position is one where you buy a stock and try to sell it at a higher price. You can think of it as holding a stock for a long time, even though it might only be a few minutes. A short is when you borrow and sell a stock or stocks.
What does it mean to long and short a stock?
What's the Difference Between a Long and Short Trade?
- Long Trades. When a day trader is in a long trade, they have purchased an asset and are waiting to sell when the price goes up.
- Short Trades. Shorting a stock is confusing to most new traders. In the real world, you have to own something to sell it.
- Special Considerations for Shorting. Shorting stocks is popular with professional traders. ...
Which is better long term or short term investment?
The following types of financial instruments fall under the category of short-term investments:
- Treasury bills: These bills can be redeemed within 91 days. ...
- Gilt Funds: These funds invest only in government securities. ...
- Ultra short term debt funds: The maturity period ranges between three and six months. ...
- Low duration debt funds: The maturity period ranges between six and 12 months. ...
What are the benefits of holding stocks long term?
Key Takeaways
- The main reason to buy and hold stocks over the long-term is that long-term investments almost always outperform the market when investors try and time their investments.
- Emotional trading tends to hamper investor returns.
- Over a 20-year time period, the S&P 500 has always posted a positive return, no matter when you would have invested.
What is short and long in finance?
Short-term financing is normally used to support the working capital gap of business whereas the long term is required to finance big projects, PPE, etc. The third thing is the cost of financing which is higher in case of short-term and comparatively lower in case of long-term barring abnormal economic conditions.
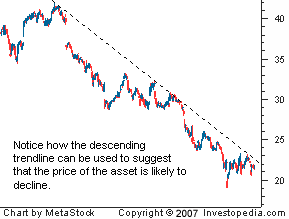
Is it better to short or long a stock?
A simple long stock position is bullish and anticipates growth, while a short stock position is bearish. This position allows the investor to collect the option premium as income with the possibility of delivering their long stock position at a guaranteed, usually higher, price.
What is to short a stock?
Short selling involves borrowing a security and selling it on the open market. You then purchase it later at a lower price, pocketing the difference after repaying the initial loan. For example, let's say a stock is trading at $50 a share. You borrow 100 shares and sell them for $5,000.
What is a long position in stocks?
The Long Position – Buy Low, Sell High Buying stocks on a Long Position is the action of purchasing shares of stock(s) anticipating the stock's value will rise over time. For example: Gary decides to purchase 100 shares of stock in Nike, Incorporated.
What does it mean to buy short or long?
In a long trade, you purchase an asset and wait to sell when the price goes up. "Buy" and "long" are used interchangeably. When you're in a short trade, you borrow an asset, sell it, and hope to buy it back when the price goes down. "Sell" and "short" are used interchangeably.
What is short selling example?
Example of Short Selling for a Profit Imagine a trader who believes that XYZ stock—currently trading at $50—will decline in price in the next three months. They borrow 100 shares and sell them to another investor. The trader is now “short” 100 shares since they sold something that they did not own but had borrowed.
How long can you short a stock?
There is no mandated limit to how long a short position may be held. Short selling involves having a broker who is willing to loan stock with the understanding that they are going to be sold on the open market and replaced at a later date.
When should I take long position?
Taking a long position essentially means buying a security, such as a stock, with the expectation that it will rise in value. For example, a trader who is bullish on a company might go long on that company with the hope that its stock price will eventually go up.
When should you open a long position?
A long—or a long position—refers to the purchase of an asset with the expectation it will increase in value—a bullish attitude. A long position in options contracts indicates the holder owns the underlying asset. A long position is the opposite of a short position.
Is shorting easier than going long?
Short selling is riskier than going long on a stock because, theoretically, there is no limit to the amount you could lose. Speculators short sell to capitalize on a decline, while hedgers go short to protect gains or minimize losses.
What happens when you buy long?
Having a “long” position in a security means that you own the security. Investors maintain “long” security positions in the expectation that the stock will rise in value in the future. The opposite of a “long” position is a “short” position.
Is long same as buy?
What's the difference? There's the distinction between long and buy. Long not only conveys the action taken, but also current ownership, and therefore, it is much more descriptive than buy. The same distinctions can apply to selling versus short.
When should you sell a stock for profit?
Here's a specific rule to help boost your prospects for long-term stock investing success: Once your stock has broken out, take most of your profits when they reach 20% to 25%. If market conditions are choppy and decent gains are hard to come by, then you could exit the entire position.
What does "long" mean in stock?
Long means buy or bought. If someone says “I’m long WXYZ stock” it means that person owns (they bought) shares in WXYZ. If someones says “I’m going long WXYZ at $14” it means they intend to buy WXYZ stock at $14. In this case they don’t own it yet, but they plan to.
What does it mean when you short something?
You short or short sell assets you believe will fall in value. When someone says they are going short it usually infers that they believe the price of an asset will fall in value.
What does it mean when someone says they are long?
When someone says they are long it usually infers that they believe the stock (or other asset) will rise in value. When you are long (own shares), to exit the position you sell the shares. For example, if you go long 100 shares at $10, you need to sell them at some point to collect your profit.
What are the two words that describe the long and short term?
Two words related to long and short are “bullish” and “bearish.”. These words also indicate which direction the price of an asset is moving, or which direction a trader thinks it will move. The term bull or bullish comes from the animal, attacking with an upward thrust. Therefore, “bull” means upward trend or price direction.
Why do traders short sell?
Short selling allows traders to make money when prices are falling, and going long allows them to make money in rising markets.
What does it mean when you sell 100 shares?
When you sell the 100 shares you are “flat.”. Flat means you have no position–you are neither long or short. Selling is flattening or reducing a long position, which is a bit different than going short….
What does "goigng short" mean?
Goigng short means to sell without first owning. It is also referred to as short selling or shorting.
What does "short" mean in trading?
When you're in a short trade, you borrow an asset, sell it, and hope to buy it back when the price goes down. "Sell" and "short" are used interchangeably.
When Do I Use a Long or Short Trade?
You would go long or use a long trade on a stock that you believe or know will rise in price. A long trade to a day trader is, at most, one trading day. If you find an opportunity to enter a trade, and you know the stock price will increase (and be desirable for another trader after you buy it), you'd go long on that stock.
Why do you buy a short call?
You buy a short call to have the right to sell a stock (make another trader buy it) at a specific price; you buy a short put to have the right to repurchase a stock (make another trader sell it to you) at a specific price. The stop loss prevents you from losing too much on a trade if the price moves against you.
What is a short trade?
In day trading, "long" and "short" trades refer to whether a trade was initiated with a purchase or a sale. In a long trade, you purchase an asset and wait to sell when the price goes up. "Buy" and "long" are used interchangeably. When you're in a short trade, you borrow an asset, sell it, and hope to buy it back when the price goes down.
What does it mean to go long on XYZ?
You might hear a trader say they are "going long" or "go long" to indicate interest in buying a particular asset. If you go long on (buy) 1,000 shares of XYZ stock at $10, the transaction costs you $10,000. If you can sell them at $10.20 per share, you receive $10,200. You get a nice profit of $200 before commissions. This is what you're hoping for by going long.
What happens if you sell stock at $9.90?
The flip side to an increase in price is a decrease. If you sell your shares at $9.90, you receive $9,900 back on your $10,000 trade. You'd lose $100 and have to pay commission fees on top of it.
Can you short a stock if you know the price is going to decline?
You would go short on a trade if you know the price was going to decline. Your broker must borrow the shares from the owner (probably another broker) or lend them to you if they own them. If the broker can't borrow the shares for you, you're not going to be able to short the stock.
What does it mean to be short?
A "short" position is generally the sale of a stock you do not own. Investors who sell short believe the price of the stock will decrease in value. If the price drops, you can buy the stock at the lower price and make a profit. If the price of the stock rises and you buy it back later at the higher price, you will incur a loss.
Why do people short sell stocks?
Investors who sell stock short typically believe the price of the stock will fall and hope to buy the stock at the lower price and make a profit. Short selling is also used by market makers and others to provide liquidity in response to unanticipated demand, or to hedge the risk of an economic long position in the same security or in ...
What is short selling?
Short selling is for the experienced investor. Short Sales. A short sale is the sale of a stock that an investor does not own or a sale which is consummated by the delivery of a stock borrowed by, or for the account of, the investor.
What is a broker lending stock?
Brokerage firms typically lend stock to customers who engage in short sales, using the firm’s own inventory, the margin account of another of the firm’s customers, or another lender. As with buying stock on margin, short sellers are subject to the margin rules and other fees and charges may apply (including interest on the stock loan).
How are short sales settled?
Short sales are normally settled by the delivery of a security borrowed by or on behalf of the investor. The investor later closes out the position by returning the borrowed security to the stock lender, typically by purchasing securities on the open market.
What does it mean to be long in a security?
Having a “long” position in a security means that you own the security. Investors maintain “long” security positions in the expectation that the stock will rise in value in the future. The opposite of a “long” position is a “short” position.
What is a long short?
Long-short seeks to augment traditional long-only investing by taking advantage of profit opportunities from securities identified as both under-valued and over-valued.
What Is Long-Short Equity?
Long-short equity is an investing strategy that takes long positions in stocks that are expected to appreciate and short positions in stocks that are expected to decline. A long-short equity strategy seeks to minimize market exposure while profiting from stock gains in the long positions, along with price declines in the short positions. Although this may not always be the case, the strategy should be profitable on a net basis.
What is an example of a long-short equity strategy with a broad mandate?
An example of a long-short equity strategy with a broad mandate would be a global equity growth fund, while an example of a relatively narrow mandate would be an emerging markets healthcare fund.
How are long and short equity strategies differentiated?
Long-short equity strategies can be differentiated from one another in a number of ways—by market geography (advanced economies, emerging markets, Europe, etc.), sector (energy, technology, etc.), investment philosophy (value or growth), and so on.
Is long short equity profitable?
Although this may not always be the case, the strategy should be profitable on a net basis. The long-short equity strategy is popular with hedge funds, many of which employ a market-neutral strategy, in which dollar amounts of both long and short positions are equal.
Do hedge funds have a long or short bias?
While many hedge funds also employ a long-short equity strategy with a long bias (such as 130/30, where long exposure is 130% and short exposure is 30%), comparatively fewer hedge funds employ a short bias to their long-short strategy. It is historically more difficult to uncover profitable short ideas than long ideas.
What does it mean to be long in the stock market?
"Long" and "short" refer to whether you've staked your money on a stock's price rising or falling.
What happens if you short a stock?
Shorting a stock carries potentially catastrophic risks if the price rises instead of falls, so if you're going short, you'd better know what you're doing. Say you sold your borrowed shares for $10 and the price rises to $11 a share. Covering your short will leave you with a loss of $1 a share.
What is short position?
Short Positions. In a short position, you're doing just the opposite: You've got your money riding on the price of particular stock falling. "Going short" is considerably more complicated than going long. First, you borrow some shares of the stock from your broker. Next, you sell those shares on the open market at the market price.
What is a long position in stock?
Long Positions. When you're in a long position in a stock, you've bought it expecting the price to go up. In a long position, you run the risk of the stock price falling, in which case your investment will lose money. But your risk is limited to the amount you've invested.
How much can you lose by covering a short?
Covering your short will leave you with a loss of $1 a share. If the stock really goes nuts and jumps to $20, your loss has been magnified to $10 a share. In theory, there's no limit to how much you can lose.
How is a Long Different from a Short?
A short position is the opposite of a long position, in that it profits when the prices of securities go down.
What does "long" mean in investing?
The most common meaning of long refers to the length of time an investment is held. However, the term long has a different meaning when used in options and futures contracts.
What Is a Long Position?
The term long position describes what an investor has purchased when they buy a security or derivative with the expectation that it will rise in value.
What is the meaning of "going long" in investing?
With a long-position investment, the investor purchases an asset and owns it with the expectation that the price is going to rise. This investor normally has no plan to sell the security in the near future.
Why are call options long?
When a trader buys or holds a call options contract from an options writer, they are long, due to the power they hold in being able to buy the asset. An investor who is long a call option is one who buys a call with the expectation that the underlying security will increase in value.
Why do people hold long put options?
The holder of a long put option believes the price of an asset will fall. They hold the option with the hope that they will be able to sell the underlying asset at an advantageous price by the expiry.
What does it mean to be long on an option?
A long position is the opposite of a short position. In options, being long can refer either to outright ownership of an asset or being the holder of an option on the asset . Being long on a stock or bond investment is a measurement of time.
Why do you short a stock?
Usually, you would short stock because you believe a stock's price is headed downward. The idea is that if you sell the stock today, you'll be able to buy it back at a lower price in the near future.
What happens when you short a stock?
When you short a stock, you expose yourself to a large financial risk. One famous example of losing money due to shorting a stock is the Northern Pacific Corner of 1901. Shares of the Northern Pacific Railroad shot up to $1,000.
Why Sell Short?
Usually, you would short stock because you believe a stock's price is headed downward. The idea is that if you sell the stock today, you'll be able to buy it back at a lower price in the near future.
How Is Short Selling Different From Regular Investing?
Shorting a stock has its own set of rules, which are different from regular stock investing, including a rule designed to restrict short selling from further driving down the price of a stock that has dropped more than 10% in one day, compared to the previous day's closing price. 4
How to profit from a stock decline?
Two of the most common ways to profit from a stock's decline without shorting are options and inverse ETFs. Buying a put option gives you the right to sell a stock at a given "strike price," so the buyer hopes the stock goes down and they can make more money by selling at the strike price. Inverse ETFs contain swaps and contracts that effectively replicate a short position. For example, SQQQ is an inverse ETF that moves in the opposite direction of QQQ. If you believe the price of QQQ shares will go down, then shorting QQQ, buying a put option on QQQ, and buying shares in SQQQ will all allow you to profit from a move down.
What happens if you buy 10 shares of a stock for $250?
If the price of the stock goes down to $25 per share, you can buy the 10 shares again for only $250. Your total profit would be $250: the $500 profit you made at first, minus the $250 you spend to buy the shares back. But if the stock goes up above the $50 price, you'll lose money.
How does shorting stock work?
How Shorting Stock Works. Usually, when you short stock, you are trading shares that you do not own. For example, if you think the price of a stock is overvalued, you may decide to borrow 10 shares of ABC stock from your broker. If you sell them at $50 each, you can pocket $500 in cash.
Why is it dangerous to short a stock?
That is because the potential for a profit is limited to the stock’s distance to zero. However, a stock could potentially rise for years, making a series of higher highs. One of the most dangerous aspects of being short is the potential for a short-squeeze .
What is a naked short?
There are two types of short positions: naked and covered. A naked short is when a trader sells a security without having possession of it. However, that practice is illegal in the U.S. for equities. A covered short is when a trader borrows the shares from a stock loan department; in return, the trader pays a borrow-rate during the time ...
Why do short positions have a finite potential?
That is because the potential for a profit is limited to the stock’s distance to zero. However, a stock could potentially rise for years, making a series of higher highs.
Can a stock rise for years?
However, a stock could potentially rise for years, making a series of higher highs. One of the most dangerous aspects of being short is the potential for a short-squeeze . A short-squeeze is when a heavily shorted stock suddenly begins to increase in price as traders that are short begin to cover the stock.
Is it illegal to short stocks?
However, that practice is illegal in the U.S. for equities. A covered short is when a trader borrows the shares from a stock loan department; in return, the trader pays a borrow-rate during the time the short position is in place.
What is a long short equity strategy?
Long-short equity strategy is a type of portfolio management strategy where the manager attempts to minimize market risk by taking both long and short positions. The idea is that if the market declines and the long positions take losses, the short positions will provide gains and minimize overall losses and keep the portfolio profitable.
Where did the long short strategy originate?
The long-short strategy originated in hedge funds and is now also used with managing mutual funds. It is less common among individual traders. Let’s look at a few examples of how the strategy works.
What is a BlackRock fund?
For example, BlackRock offers a long-short equity fund called The BlackRock Global Long/Short Equity Fund that uses traditional fundamental analysis to pick long and short positions in global equities. The fund aims to minimize volatility with diversification. It also aims to minimize net exposure to the market by using various hedging strategies that focus on sectors, geographies, and market neutrality.
What is the benefit of balancing long and short equity?
Balancing long and short strategies can help investors develop a portfolio that is less correlated with market movements. So, they have the opportunity to earn gains that beat the broader market.
Why is the expense ratio higher in long-short funds?
The higher expense ratio with many long-short funds is due in part to the higher costs from leveraging, shorting, and more frequent trading in the funds.
Do long-short equity funds have higher fees?
Individual investors considering long-short equity funds should consider their fees, which tend to be higher than an average mutual fund. Higher fees, of course, can affect your profits.
Can a long and short position make profits?
With both long and short positions, the fund can potentially earn profits in both bull and bear markets. This concept of trying to make gains regardless of market conditions is also referred to as absolute return investing strategy, or hedging .

What Is Long-Short Equity?
- Long-short equity is an investing strategy that takes long positions in stocks that are expected to appreciate and short positions in stocks that are expected to decline. A long-short equity strategy seeks to minimize market exposurewhile profiting from stock gains in the long positions, along with price declines in the short positions. Although th...
How Long-Short Equity Works
- Long-short equity works by exploiting profit opportunities in both potential upside anddownside expected price moves. This strategy identifies and takes long positions in stocks identified as being relatively underpriced while selling short stocks that are deemed to be overpriced. While many hedge funds also employ a long-short equity strategy with a long bias (such as 130/30, wh…
Long-Short Equity vs. Equity Market Neutral
- A long-short equity fund differs from an equity market neutral(EMN) fund in that the latter attempts to exploit differences in stock prices by being long and short in closely related stocks that have similar characteristics. An EMN strategy attempts to keep the total value of their long and short holdings roughly equal, as this helps to lower the overall risk. To maintain this equival…
Long-Short Equity Example: The Pair Trade
- A popular variation of the long-short model is that of the “pair trade," which involves offsetting a long position on a stock with a short positionon another stock in the same sector. For example, an investor in the technology space may take a long position in Microsoft and offset that with a short position in Intel. If the investor buys 1,000 shares of Microsoft at $33 each, and Intel is trading a…