When interest rates rise, there are ripple effects in the broader economy. They affect stock prices because the cost of lending goes up, which drives down business growth and expansion.
What is the relationship between stocks and interest rates?
The argument suggests that when interest rates are high, fixed income investments such as bonds are more competitive and therefore this diminishes stock values. Conversely, when interest rates are low, fixed income is less competitive and therefore stock valuations will rise.
How do interest rates affect stocks?
- Interest rates are set by the Federal Reserve and can have an impact on lending, consumer goods, and the housing market.
- The stock market generally has an inverse relationship with interest rates, but not every sector of the market reacts the same.
- Changes in interest rates can cause volatility in the stock market and impact costs for businesses.
What impact could rising interest rates have?
When interest rates are low, companies and consumers can borrower cheaply and tend to spend more money, which can boost corporate profits. When interest rates rise, consumers and companies typically curb their spending, which can result in lower stock prices.
When interest rates rise stocks?
With interest rates rising, it's time to focus on MANG stocks instead of FAANG, according to Jefferies - MarketWatch A case is made that the group of Microsoft, Apple, Nvidia and Alphabet are a safer play as the Federal Reserve tightens monetary policy.
What happens to stock prices when interest rates rise?
Higher interest rates tend to negatively affect earnings and stock prices (with the exception of the financial sector). Higher interest rates also mean future discounted valuations are lower as the discount rate used for future cash flow is higher.
What is the relationship between interest rates and stock prices?
Based on historical observation, stock prices and interest rates have generally had an inverse relationship. Said plainly, as interest rates move higher, stock prices tend to move lower.
Why might rising interest rates depress stock prices?
Rising interest rates might depress stock prices if investors move their money from stocks to the fixed rate instruments with higher interest rates. This movement reduces the demand for stocks, causing their prices to go down. Consumers usually pay a price for the goods and services they buy.
What makes stocks go up and down?
If more people want to buy a stock (demand) than sell it (supply), then the price moves up. Conversely, if more people wanted to sell a stock than buy it, there would be greater supply than demand, and the price would fall. Understanding supply and demand is easy.
How are stocks affected by interest rates?
There are two main ways in which stocks are affected by interest rates: directly and indirectly. Here is a summary of how businesses, and therefore stocks, are affected by changes to interest rates: 1. Businesses are directly affected by bank rates because they affect the amount a company can afford to borrow. ...
What happens to stock prices when interest rates decrease?
When interest rates decrease, it’s cheaper for companies to borrow capital with the aim of achieving growth, and this may encourage stock prices to rise. 2.
Why are stocks attractive when interest rates fall?
It may seem easier to find attractive stocks when interest rates fall because lower rates can lead to higher disposable income in an economy, along with potentially lower borrowing costs for companies. Some stocks that may embark on an bullish theme around these scenarios include:
Why do central banks have volatility?
When central banks are due to announce changes in interest rates, this in and of itself can cause volatility around the markets. As mentioned previously, the stock market is quick to react to changes in interest rates, so traders will often be making their projections ahead of major central bank announcements.
Why is borrowing more expensive?
Borrowing becomes more expensive and there is more incentive to save money, so people may be encouraged to spend less. Lower interest rates may boost economic growth. Borrowing becomes cheaper and there is less incentive to save money, so people may be encouraged to spend or invest.
How long does it take for the stock market to catch up to interest rate changes?
The stock market often reacts quickly to interest rate changes – certainly more quickly than many other areas of the economy, which may take up to 12 months to catch up. This can mean many opportunities for traders who analyze stock markets, both when buying and holding or employing a shorter-term speculative approach.
What are the different types of interest rates?
There are different types of interest rates that will affect the stock market – the main distinction is: Bank rates: This is the rate at which banks lend to each other. It’s also the rate that directly influences the stock market. In the US, this is called the Fed Funds rate. Consumer interest rates: These are the rates charged on loans ...
Interest rates are going up
Super-easy pandemic monetary policy gave strong support to asset prices. The prices of bonds in the secondary markets increased as new bonds could be issued at lower rates (and thus lower current yields - see example on how interest rates affect bonds).
How do stocks perform when interest rates rise?
Historically, when rates increase it's actually good for stocks overall. Again, the implications are that rates are going up to slow (not stop) the rate of economic growth. A strong economy can be very good for companies.
Diversification, my old friend
The purpose of diversification is because like broad-based market moves, there’s no way to know when certain sectors, styles, or factors are going to outperform or underperform, for how long, and to what extent.
How Do Interest Rates Affect The Stock Market?
Interest rates affect the stock market in two ways. A long-term prime interest rate below 5% encourages economic expansion, which is seen in stock market growth. A high-interest rate stifles investment and causes the economy and stock market to contract. Equally important is the direction and speed of interest rate changes.
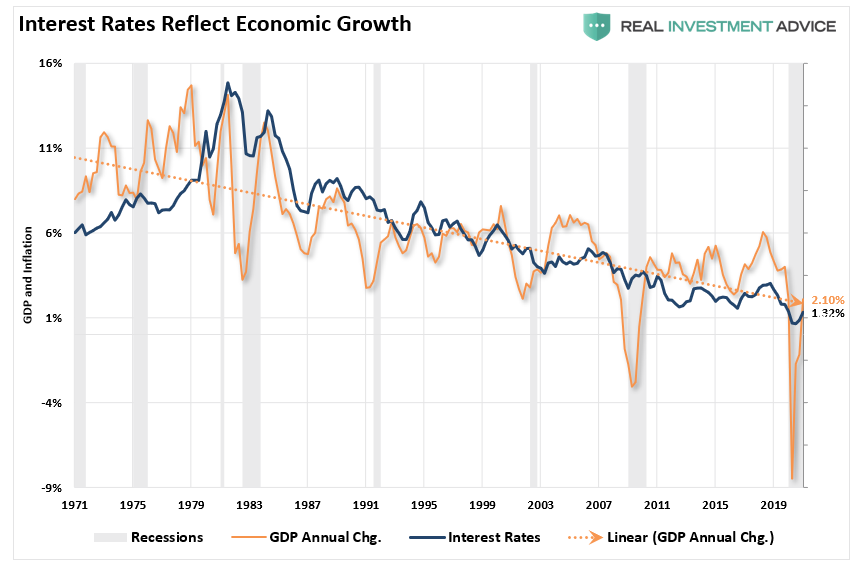
60 Years of Interest Rates vs. The S&P Composite Index
Figure 1 shows you exactly how monetary policy affects the stock market by overlaying the U.S. Prime Interest Rate on the S&P500 returns from 1954 through October 2009.
S&P500 Index vs. the Federal Reserve Prime Rate Example
We can see clearly in this chart what the biggest influence over the stock market direction is.
What Is A Good Interest Rate For Stocks?
60 years of research shows that interest rates below 10% are good for stock market returns, below 5% produces strong stock market performance, and close to 0% produces economic crisis recovery and stock market booms.
Will Stocks Fall When Interest Rates Rise?
My analysis shows that slow increases in interest rates over multiple years, that remain below 5% will not cause stocks to fall dramatically. Any large increases in interest rates will immediately affect property prices and cause the balance sheets of companies to contract, affecting stocks.
Live Chart: Federal Funds Prime Rate
Here is a live chart of the Federal Reserve Prime Rate. Remember, rapidly increasing interest rates, especially above 5% will cause stock market declines.
Bank Stocks for Interest Raises: JPMorgan Chase (JPM)
JPMorgan Chase easily tops this list of bank stocks. The bank is a well-run colossus that has become a bellwether for the broader economy. While it’s fair to note that many banks performed well during the pandemic, it’s hard to see how the bank would not benefit from rising interest rates.
Bank of America (BAC)
Rising interest rates are generally problematic for banks. While depositors may appreciate the higher rates, it’s a cost that banks have to account for. However, among the bank stocks, Bank of America has the highest percentage of non-interest bearing accounts.
Bank Stocks for Interest Raises: Wells Fargo (WFC)
It may not be a great time to be a customer at Wells Fargo, but it’s not a bad time to be an investor. Wells Fargo has been a stalwart performer this year. WFC stock is up 54% in 2021. And the bank recently increased its dividend by 10 cents per share.
Citigroup (C)
Yet another big bank to consider is Citigroup. And there is an oddly specific reason for that. Rising interest rates are a risk-reward proposition for banks. On the one hand, rising interest rates drive more revenue to the top line. However, they also have a historical link to rising consumer defaults.
Bank Stocks for Interest Raises: US Bancorp (USB)
While it’s logical that many investors would pay attention to the big banks, US Bancorp is one of the stronger regional banks to consider. The bank reported a double beat in its recent earnings report. That hasn’t had much effect on the stock.
Goldman Sachs (GS)
I read a statement that caught my attention. Many analysts believe the stock market is overvalued. Yet those same analysts believe the market will continue to climb. If the second of those statements is true it would be a bullish sign for Goldman Sachs.
Bank Stocks for Interest Raises: SPDR S&P Bank ETF (KBE)
If you want to invest in bank stocks without investing in specific names, an exchange-traded fund (ETF) is typically a good option. In the case of bank stocks, one that stands out is the SPDR S&P Bank ETF. The fund is up 18% in 2021 as of Aug. 2. By way of comparison, JPMorgan Chase is up 20% in that same time frame.
