Is a reverse stock split good or bad?
May 03, 2020 · How to Calculate a Reverse Stock Split Totaling Your Stocks. Total the number of stocks you own in the company. The reverse split trades a specific number of... Checking the Exchange Rate. Look up the exchange rate. The rate is normally a ratio such as 1:10 or 1 for 10. When a... Dividing Number of ...
How to find stocks that are going to split?
1 ÷ 10 = 0.10 (or 10%) Suppose that you are a shareholder with 200 shares before the reverse split – under a 1-for-10 reverse split, you would own 20 shares afterward. Shares Owned Post-Reverse Split = 10% × 200 = 20. Next, let’s assume that …
How to calculate the basis for multiple stock splits?
The typical math in a reverse stock split is performed by a company’s brokerage firm. Let’s do a quick example. But first let’s provide the simple formula: Shares after the split=shares * A/B. Stock price after the split=stock price * B/A. Let’s say for instance a company were to execute a 1 to 5 reverse stock split.
Are reverse stock splits a signal to sell?
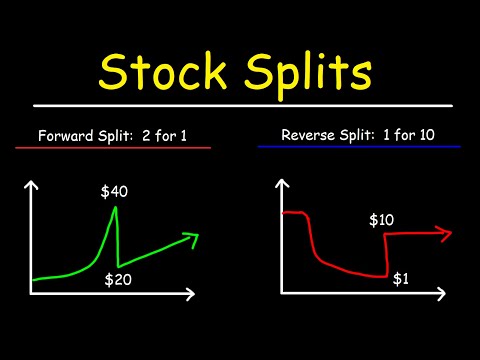
When a company completes a reverse stock split, each outstanding share of the company is converted into a fraction of a share. For example, if a company declares a one for ten reverse stock split, every ten shares that you own will be converted into a single share. If you owned 10,000 shares of the company before the reverse stock split, you will own a total of 1,000 …

What is a 1 for 500 reverse split?
What is a 1 to 1000 reverse split?
How are forward and reverse splits calculated?
What is a 50 to 1 reverse stock split?
Do you lose money on a reverse split?
Should I sell my stock before a reverse split?
How do you calculate a forward stock split?
What does a 1 for 4 reverse stock split mean?
What happens if I buy a stock after the split record date?
What is an 8 to 1 reverse stock split?
What is a 1/10 reverse stock split?
Are reverse splits ever good?
What is reverse stock split?
To put it simply a reverse stock split reduces the overall number of outstanding shares without changing the value of the underlying total securities. The math is quite simple, but can sometimes end in fraction shares. The typical math in a reverse stock split is performed by a company’s brokerage firm. Let’s do a quick example.
Who is Nate Nead?
Nate Nead is a licensed investment banker and Principal at Deal Capital Partners, LLC, a middle-marketing M&A and capital advisory firm. Nate works with corporate clients looking to acquire, sell, divest or raise growth capital from qualified buyers and institutional investors. He holds Series 79, 82 & 63 FINRA licenses and has facilitated numerous successful engagements across various verticals. Four Points Capital Partners, LLC a member of FINRA and SIPC. Nate resides in Seattle, Washington. Check the background of this Broker-Dealer and its registered investment professionals on FINRA's BrokerCheck.
What is reverse stock split?
Reverse stock splits occur when the company reduces the number of outstanding shares by converting a specified number of old shares into one new share. For example, a company might exchange three old shares for one new share. As a result, the price per share will go up. A reverse stock split isn't a taxable event because the value ...
Is a reverse stock split taxable?
A reverse stock split isn't a taxable event because the value of what you own doesn't change. For example, if you own 10 percent of the shares of the company before the reverse split, you'll still own 10 percent of the shares of the company after. However, knowing your average basis per share will help you determine whether you're making ...
What is reverse stock split?
Reverse stock split refers to the process of boosting a company’s stock price by reducing the number of its outstanding shares. It is attained by combining some of the existing shares in the market and simultaneously raising their value in the same ratio.
Why do companies reverse split?
On the other hand, companies use reverse stock split to inflate the per-share value when their stock price is constantly falling. In a 1-for-4 split, a shareholder of four shares will end up with one share.
What is stock exchange?
Stock Exchange Stock exchange refers to a market that facilitates the buying and selling of listed securities such as public company stocks, exchange-traded funds, debt instruments, options, etc., as per the standard regulations and guidelines—for instance, NYSE and NASDAQ. read more. .
What is shareholder in stock?
Shareholders A shareholder is an individual or an institution that owns one or more shares of stock in a public or a private corporation and, therefore , are the legal owners of the company . The ownership percentage depends on the number of shares they hold against the company's total shares. read more. better.
What is dividend distribution?
Dividend Dividend is that portion of profit which is distributed to the shareholders of the company as the reward for their investment in the company and its distribution amount is decided by the board of the company and thereafter approved by the shareholders of the company. read more. .
Where is Matt from Motley Fool?
Matt is a Certified Financial Planner based in South Carolina who has been writing for The Motley Fool since 2012. Matt specializes in writing about bank stocks, REITs, and personal finance, but he loves any investment at the right price. Follow him on Twitter to keep up with his latest work!
What is reverse stock split?
What is a reverse stock split? A reverse stock split is a situation where a corporation's board of directors decides to reduce the outstanding share count by replacing a certain number of outstanding shares with a smaller number. Reverse stock splits work the same way as regular stock splits but in reverse. A reverse split takes multiple shares ...
Is a reverse split good or bad?
A reverse split isn't necessarily good or bad all by itself. It is simply a change in the stock structure of a business and doesn't change anything related to the business itself. That said, a reverse split is usually taken as a sign of trouble by the market. In rare cases, a reverse split buys a company the time it needs to get back on track.
Can a company do a reverse stock split?
It's also possible for a company to complete a reverse stock split, which works in the exact opposite way. Unlike forward splits, reverse stock splits leave shareholders with fewer shares, and they often result from situations in which a stock has lost a substantial amount of its value. Here's a quick overview of what a reverse stock split is, ...
What is a stock split?
Stock splits are most commonly associated with positive news, as they typically happen when a stock has performed quite well, and they generally result in an increased number of shares owned by each investor . But those splits, officially called forward stock splits, are only one variety. It's also possible for a company to complete ...
What was the hardest hit bank in 2008?
Citigroup ( NYSE:C) was one of the hardest-hit bank stocks among the financial institutions that survived the 2008 financial crisis. As a result, the bank's shares were trading for just a few dollars -- more than 90% lower than their pre-crisis high.
Why do companies reverse split?
A company does a reverse split to get its share price up . The most common reason for doing so is to meet a requirement from a stock exchange to avoid having its shares delisted. For example, the New York Stock Exchange has rules that allow it to delist a stock that trades below $1 per share for an extended period.
How to calculate reverse stock split?
To calculate a reverse stock split, divide the current number of shares you own in the company by the number of shares that are being converted into each new share. For example, in a 1-for-3 reverse stock split, you would end up with only one new share for every three shares you previously owned. So, if you owned 300 shares ...
Why do stock splits increase liquidity?
In addition, stock splits increase the liquidity of the stock because there are more shares outstanding after a split. 00:00.
Where is Mike from The Motley Fool?
Based in the Kansas City area , Mike specializes in personal finance and business topics. He has been writing since 2009 and has been published by "Quicken," "TurboTax," and "The Motley Fool.".