
What was the biggest stock market decline in history?
On Monday, Oct. 19, 1987, the Dow Jones Industrial Average plunged by nearly 22%. Black Monday, as the day is now known, marks the biggest single-day decline in stock market history. The remainder of the month wasn't much better; by the start of November, 1987, most of the major stock market indexes had lost more than 20% of their value.
How long does a stock market drop last before a recession?
The S&P 500 tumbled by 36.8% over the course of 1.5 years, punctuated by a brief recession in the middle. 4 Stock market declines of 36.1% in the late 1960s and 48.2% in the early 1970s, lasting 1.5 years and 1.7 years, respectively, also began ahead of recessions and ended shortly before those economic contractions bottomed out. 4
How often does the stock market lose money?
How Often Does the Stock Market Lose Money? Negative stock market returns occur, on average, about one out of every four years. Historical data shows that the positive years far outweigh the negative years. Between 2000 and 2019, the average annualized return of the S&P 500 Index was about 8.87%.
Are stock market declines inevitable?
Stock market declines are the last thing most investors want to experience, but they are an inevitable part of investing. Perhaps a little historical background can help you put stock market declines in perspective. A look back at stock market history since 1951 shows that declines have varied widely in intensity, length and frequency.
How long did it take to get back into the stock market after the 1929 crash?
Why is market timing so difficult?
Is it easy to live with a market decline?
About this website
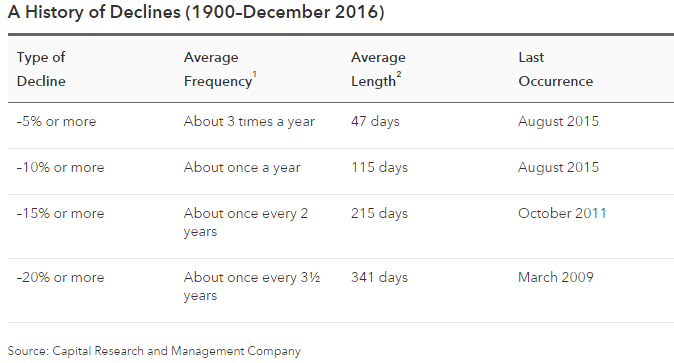
How long do stock market declines last?
A history of declines (1952–December 2021)Type of declineAverage frequency*Average length†–5% or moreAbout 3 times a year43 days–10% or moreAbout once a year110 days–15% or moreAbout once every 3 years251 days–20% or moreAbout once every 6 years370 days
What is the lost decade for stocks?
There have been only two decades since 1930 when the stock market produced negative returns: the 1930s itself, when the S&P 500 lost 0.2% because of the Great Depression, and the 2000s, when the dot-com bubble, terrorist attacks, and the collapse of the financial industry and housing market all conspired to drag down ...
How long did the 2008 bear market last?
It lasted only 33 days. A bear market that occurred during the 2008 financial crisis was a year and half. The bear market during the 2000 dot-com bubble burst went two and a half years. Frank says the average bear market lasts about 9 months, but it takes much longer to recover what was lost.
Has the S&P 500 ever lost money over a 10 year period?
10-Year Time Frames The S&P 500 Index, shown in bright red, delivered its worst ten-year return of -3% a year over the ten years ending in February 2009.
Why is 1980 the Lost Decade?
During the Latin American debt crisis of the 1980s—a period often referred to as the “lost decade”—many Latin American countries became unable to service their foreign debt.
Can stocks go to zero?
And while theoretically possible, the entire US stock market going to zero would be incredibly unlikely. It would, in fact, take a catastrophic event involving the total dissolution of the US government and economic system for this to occur.
How long did it take the S&P 500 to recover from the 2008 crash?
The S&P 500 dropped nearly 50% and took seven years to recover. 2008: In response to the housing bubble and subprime mortgage crisis, the S&P 500 lost nearly half its value and took two years to recover. 2020: As COVID-19 spread globally in February 2020, the market fell by over 30% in a little over a month.
Will the stock market crash 2022?
The Bottom Line There's no way of knowing if the stock market will crash in 2022. While there are absolutely concerning indicators, there are also signs of strength in the underlying economy. Wise investors should keep investing for the long run and stick to their overall financial plan.
Who is to blame for the Great recession of 2008?
The Biggest Culprit: The Lenders Most of the blame is on the mortgage originators or the lenders. That's because they were responsible for creating these problems. After all, the lenders were the ones who advanced loans to people with poor credit and a high risk of default. 7 Here's why that happened.
What is the KISS rule of investing?
In other words, KISS in investing is an acronym that fully means “Keep It Simple, Stupid”. The principle expresses an ideology that implies that most systems work effectively when they are made and kept simple, with no complications.
What is the average stock market return over 30 years?
10.72%Looking at the S&P 500 for the years 1991 to 2020, the average stock market return for the last 30 years is 10.72% (8.29% when adjusted for inflation). Some of this success can be attributed to the dot-com boom in the late 1990s (before the bust), which resulted in high return rates for five consecutive years.
Has the stock market ever gone down over a 10 year period?
To illustrate the volatile nature of financial markets, we took a look at intra-year stock market declines over the 20-year period from 2002–2021. As you can see in the chart below, a decline of at least 10% occurred in 10 out of 20 years, or 50% of the time, with an average pullback of 15%.
List of stock market crashes and bear markets - Wikipedia
This is a list of stock market crashes and bear markets.The difference between the two relies on speed (how fast declines occur) and length (how long they last). Stock market crashes are quick and brief, while bear markets are slow and prolonged.
How long did it take to get back into the stock market after the 1929 crash?
After the 1929 crash, it took investors 16 years to restore their investments if they invested at the market high. In 2000, it took about five years. But after the 1987 crash, it took about 23 months to get back. In 1990, it took about eight months. (In all cases, dividends were assumed to be reinvested.)
Why is market timing so difficult?
Successful market timing during a decline is extremely difficult because it requires a pair of near-perfect actions: getting out and then getting back in at the right time.
Is it easy to live with a market decline?
Living with a market decline isn’t easy, but if you understand these three key lessons, you’ll be a more intelligent investor.
Why did the stock market recover from Black Monday?
Because the Black Monday crash was caused primarily by programmatic trading rather than an economic problem, the stock market recovered relatively quickly. The Dow started rebounding in November, 1987, and recouped all its losses by September of 1989.
What was the worst stock market crash in history?
The worst stock market crash in history started in 1929 and was one of the catalysts of the Great Depression. The crash abruptly ended a period known as the Roaring Twenties, during which the economy expanded significantly and the stock market boomed.
What happened on Black Monday 1987?
Black Monday crash of 1987. On Monday, Oct. 19, 1987, the Dow Jones Industrial Average plunged by nearly 22%. Black Monday, as the day is now known, marks the biggest single-day decline in stock market history. The remainder of the month wasn't much better; by the start of November, 1987, most of the major stock market indexes had lost more ...
Why did the Dow drop in 1929?
The Dow didn't regain its pre-crash value until 1954. The primary cause of the 1929 stock market crash was excessive leverage. Many individual investors and investment trusts had begun buying stocks on margin, meaning that they paid only 10% of the value of a stock to acquire it under the terms of a margin loan.
What was the cause of the 1929 stock market crash?
The primary cause of the 1929 stock market crash was excessive leverage. Many individual investors and investment trusts had begun buying stocks on margin, meaning that they paid only 10% of the value of a stock to acquire it under the terms of a margin loan.
When did the Dow Jones Industrial Average rise?
The Dow Jones Industrial Average ( DJINDICES:^DJI) rose from 63 points in August, 1921, to 381 points by September of 1929 -- a six-fold increase. It started to descend from its peak on Sept. 3, before accelerating during a two-day crash on Monday, Oct. 28, and Tuesday, Oct. 29.
When did the Dow lose its value?
The stock market was bearish, meaning that its value had declined by more than 20%. The Dow continued to lose value until the summer of 1932, when it bottomed out at 41 points, a stomach-churning 89% below its peak. The Dow didn't regain its pre-crash value until 1954.
What happened to the stock market after the 1929 crash?
After the crash, the stock market mounted a slow comeback. By the summer of 1930, the market was up 30% from the crash low. But by July 1932, the stock market hit a low that made the 1929 crash. By the summer of 1932, the Dow had lost almost 89% of its value and traded more than 50% below the low it had reached on October 29, 1929.
How much wealth was lost in the 1929 stock market crash?
The Crash of 1929. In total, 14 billion dollars of wealth were lost during the market crash. On September 4, 1929, the stock market hit an all-time high. Banks were heavily invested in stocks, and individual investors borrowed on margin to invest in stocks.
How much wealth was lost in the 2000 crash?
The Crash of 2000. A total of 8 trillion dollars of wealth was lost in the crash of 2000. From 1992-2000, the markets and the economy experienced a period of record expansion. On September 1, 2000, the NASDAQ traded at 4234.33. From September 2000 to January 2, 2001, the NASDAQ dropped 45.9%.
How much did the Dow drop in 1987?
On October 19, 1987, the stock market crashed. The Dow dropped 508 points or 22.6% in a single trading day. This was a drop of 36.7% from its high on August 25, 1987.
What is a weak technical position on the bull side?
"A market (or a stock) is said to be in a weak technical position on the bull side when the buying power has been exhausted, either in a small or a large way. A campaign of distribution exhausts buying power in a large way because much of the floating supply of stocks is then in the hands of traders and the public. Sponsors and large operators have sold. Those of the public who still hold these stocks are potentially bearish factors because, having bought, they must sooner or later sell, and their selling will bring pressure upon the market.
What is a stock crash?
Stock Market Crash is a strong price decline across majority of stocks on the market which results in the strong decline over short period on the major market indexes (NYSE Composite, Nasdaq Composite DJIA and S&P 500).
Why are stocks bearish?
Those of the public who still hold these stocks are potentially bearish factors because, having bought, they must sooner or later sell, and their selling will bring pressure upon the market. This was the case in 1929. The whole market became saturated with stocks held by those who were looking for profit.
What happened to the stock market in March?
The stock market crashed in March, with the Dow Jones Industrial Average and the S&P 500 Index both falling more than 20% from their 52-week highs in February. For investors who sold at the bottom of these markets, the lower stock prices had a detrimental effect.
When did the S&P 500 bottom?
The S&P 500 bottomed at 676.5 on March 9, 2009, after declining 57%. 2 From there, it began a remarkable ascent, roughly doubling in the following 48 months. 3
Why do professional investors love bear markets?
Professional investors love bear markets because stock prices are considered to be "on sale.". As a rule of thumb, set your investment mixture according to your risk tolerance and re-balance your portfolio to buy low and sell high. You shouldn't cut contributions to retirement accounts during down markets.
How much have indexes gained after bear market?
In the years after the "troughs" of the bear markets throughout the stock market's history, indexes have generally gained close to half of their previous highs.
Do bear markets increase?
Bear markets tend to recover and increase to higher levels, offering higher returns for those who endured it. Bear market recoveries generally provide the most returns based on time in the market. You shouldn't cut your contributions to your retirement accounts during a bear market.
How long did the stock market decline in the late 1960s?
Stock market declines of 29.3% in the late 1960s and 42.6% in the early 1970s, lasting 1.6 years and 1.8 years, respectively, also began ahead of recessions and ended shortly before those economic contractions bottomed out.
What happened to the bear market before the recession?
Bear Markets Before Recessions. In three other bear markets, the stock market decline began before a recession officially got underway. The dotcom crash of 2000 to 2002 also was spurred by a loss of investor confidence in stock valuations that had reached new historic highs.
Why did the bear market start in 2020?
The bear market that started in March of 2020 began due to a number of factors , including shrinking corporate profits and, possibly, the sheer length of the 11-year bull market that preceded it. The immediate cause of the bear market was a combination of persistent worries about the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on the world economy and an unfortunate price war in oil markets between Saudi Arabia and Russia that sent oil prices plunging. 3
What were the bear markets in the past century?
Some of the biggest bear markets in the past century include those that coincided with the Great Depression and Great Recession.
What was the worst bear market in 1929?
The two worst bear markets of this era were roughly in sync with recessions. The Stock Market Crash of 1929 was the central event in a grinding bear market that lasted 2.8 years and sliced 83.4% off the value of the S&P 500.
How long does a bear market last?
Another definition of a bear market is when investors are more risk-averse than risk-seeking. This kind of bear market can last for months or years, as investors shun speculation in favor of boring, sure bets. Several leading stock market indexes around the globe endured bear market declines in 2018.
What is the longest time horizon for investing?
The longest time horizon for investors is usually the time between now and whenever they will need to liquidate their investments (for example, during retirement), and over the longest-possible term, bull markets have gone higher and lasted longer than bear markets.
When did the stock market get spooked?
17 May 1901. Lasting 3 years, the market was spooked by the assassination of President William McKinley in 1901, coupled with a severe drought later the same year.
What happened to the stock market in 2002?
After recovering from lows reached following the September 11 attacks, indices slid steadily starting in March 2002, with dramatic declines in July and September leading to lows last reached in 1997 and 1998.
How long did the Japanese asset bubble last?
1991. Lasting approximately twenty years, through at least the end of 2011, share and property price bubble bursts and turns into a long deflationary recession. Some of the key economic events during the collapse of the Japanese asset price bubble include the 1997 Asian financial crisis and the Dot-com bubble.
How long is Black Monday trading suspended?
Today, circuit breakers are in place to prevent a repeat of Black Monday. After a 7% drop, trading would be suspended for 15 minutes, with the same 15 minute suspension kicking in after a 13% drop. However, in the event of a 20% drop, trading would be shut down for the remainder of the day.
How long did the oil boom last?
Lasting 23 months, dramatic rise in oil prices, the miners' strike and the downfall of the Heath government.
When did the first bank of the US boom and bust?
Shares of First bank of US boom and bust in Aug and Sept 1791. Groundwork of Alexander Hamilton's cooperation with the Bank of New York to end this event would be crucial in ending the Panic of 1792 next year.
How Often Does the Stock Market Lose Money?
Negative stock market returns occur, but historical data shows that the positive years far outweigh the negative years.
When do investors withdraw from the stock market?
Most investors don't invest on January 1 and withdraw on December 31, yet market returns tend to be reported on a calendar-year basis.
What are the average returns of the stock market long term?
On average, the stock market has returned roughly 10% per year. This can vary widely each year depending on a variety of market factors. 1
What are some examples of securities with higher growth potential?
To do better than the stock market average, you have to invest in a more aggressive portfolio. International stocks, small- and mid-cap stocks, and growth stocks are examples of securities with higher growth potential, but these also bring higher risks. Discuss your investing goals with a financial advisor to help you decide the right mix for an aggressive growth strategy.
What is historical stock market returns?
Historical stock market returns provide a great way for you to see how much volatility and what return rates you can expect over time when investing in the stock market. In the table at the bottom of this article, you'll find historical stock market returns for the period of 1986 through 2019, listed on a calendar-year basis.
How does down year affect the market?
The market's down years have an impact, but the degree to which they impact you often gets determined by whether you decide to stay invested or get out. An investor with a long-term view may have great returns over time, while one with a short-term view who gets in and then gets out after a bad year may have a loss.
How is wealth built over time?
Wealth is built over the long run by staying in the market, investing in quality stocks, and adding more capital over time.
How long did it take for the stock market to normalize after 1929?
After the initial episode of the 1929-1932 stock market decline, volatility initially normalized by falling from a two-week reading of 127% to under 10% in about five months’ time. Volatility would ramp up again later, but did not exceed 100% again until almost two years later, when the worst part of the bear market drew near its conclusion.
What was the volatility of the S&P 500 during the last 10 percent of the bull market?
During the last ~10% of the bull market, two-week realized volatility rose with the S&P 500 from 8% to 15%, highlighting growing instability in the uptrend. By the time Black Monday rolled around, the SPX had already declined from the high by 16% while volatility was materially higher with a short-term reading of 25%.
What Does a Volatility Event Cycle Look Like?
In the lead-up to a volatility spike, there is often a build-up period where volatility rises gradually, indicating markets could be headed for significant dislocation and disruption. The period of subtle unrest is followed by a sudden, vertical move in volatility that reaches a climax before quickly reversing and normalizing through a gradual, but bumpy decline towards pre-event volatility levels.
How much volatility was there after the Brexit vote?
Post-Brexit vote, volatility initially cratered from 46% back to 16% in only about a month before entering the typical post-event grind towards normalization of around 7% in six weeks’ time. A few months after that there was the Pound flash-crash in October that again saw volatility spiral higher momentarily.
What do the green boxes on the gold price chart mean?
In the graph above, the green boxes mark periods when volatility rose while price appreciated , and the red boxes mark periods when it rose while the price of gold depreciated. This highlights the non-directional bias that volatility can have in commodities – the same also holds true for currency volatility.
Why is volatility high in down markets?
Because of this bias, volatility runs high in down markets when there is fear as a result of financial losses and selling, and low in up markets where fear is minimal.
What happened in 1929?
Crash of 1929. At the end of the roaring ‘20s’ bull market, the crash of 1929 kicked off the Great Depression of the 1930s. The October 28-29 crash in 1929 is particularly noteworthy and resulted in a two-day loss of 24% in the Dow Jones Industrials Average, with two-week realized volatility rocketing to 127%.
How long did it take to get back into the stock market after the 1929 crash?
After the 1929 crash, it took investors 16 years to restore their investments if they invested at the market high. In 2000, it took about five years. But after the 1987 crash, it took about 23 months to get back. In 1990, it took about eight months. (In all cases, dividends were assumed to be reinvested.)
Why is market timing so difficult?
Successful market timing during a decline is extremely difficult because it requires a pair of near-perfect actions: getting out and then getting back in at the right time.
Is it easy to live with a market decline?
Living with a market decline isn’t easy, but if you understand these three key lessons, you’ll be a more intelligent investor.
