How do you determine the strike price of options?
Assume that you have identified the stock on which you want to make an options trade. Your next step is to choose an options strategy, such as buying a call or writing a put. Then, the two most important considerations in determining the strike price are your risk tolerance and your desired risk-reward payoff.
How is the price of a stock option determined?
How the price you pay for that option is determined depends on a number of factors. A stock option's intrinsic value is equal to the profit you would gain by exercising the option and immediately selling the underlying stock, without regard to any transaction fees or commissions.
Is a strike price above or below the stock price?
Similarly, a put option strike price at or above the stock price is safer than a strike price below the stock price. Picking the wrong strike price may result in losses, and this risk increases when the strike price is set further out of the money.
What happens when you buy a stock option?
When you buy a stock option, you gain control over the underlying stock for a fixed period of time, but you don't actually own the stock. Instead, you pay a premium for the right to purchase the stock for a set price, called the strike price, through the expiration date.

How are option strike prices determined?
Strike prices represent stock value at the time of their sale. Though strike prices are determined when the contract is first written, changing factors, like market price fluctuations and profit per share, impact the value at the time that the strike price is exercised.
What is strike price based on?
When given employee stock options in a private or public company, your Exercise Price or Strike Price is the price at which you have the option to purchase a given number of shares. The exercise price is determined by the Fair Market Value (FMV) at the time the options are granted.
How does option price change with strike price?
The strike price determines whether an option has intrinsic value. An option's premium (intrinsic value plus time value) generally increases as the option becomes further in-the-money. It decreases as the option becomes more deeply out-of-the-money.
Can you negotiate strike price?
There are cases where your strike price may be higher, but you should only accept this if there is clear evidence of a higher current share value, such as a signed term sheet from a new investor with a higher valuation.
What happens when a call option goes above the strike price?
Call options are “in the money” when the stock price is above the strike price at expiration. The call owner can exercise the option, putting up cash to buy the stock at the strike price. Or the owner can simply sell the option at its fair market value to another buyer before it expires.
Which strike price is best for option buying?
A relatively conservative investor might opt for a call option strike price at or below the stock price, while a trader with a high tolerance for risk may prefer a strike price above the stock price. Similarly, a put option strike price at or above the stock price is safer than a strike price below the stock price.
Why is the strike price lower than current price?
In the case of a call option, if the strike price is below the spot price (current market value), that option is in the money because the holder could exercise the option by buying the underlying asset for less than its market value.
What happens if I buy a call option below current price?
A call option, or call, is a derivative contract that gives the holder the right to buy a security at a set price at a certain date. If this price is lower than the cost of buying the security on the open market, the owner of the call can pocket the difference as profit.
What is strike price in stock options?
Stock option strike prices. Remember: stock options are the right to buy a set number of company shares at a fixed price, typically called a strike price, grant price, or exercise price. In this example, your stock option strike price is $1 per share. To come up with that $1 price, Meetly (our example company) had to determine its fair market value ...
What happens when a company offers you stock options?
When a company offers you stock options, the hope is you’ll be able to sell them for more than you paid for them. If you’ve ever wondered what determines these prices and how to figure out how much your options could be worth, we’ve got you covered. Here, we’ll cover:
What is FMV in stock options?
For private companies, FMV is essentially what the price would be if the stock were traded publicly on the open market. Your stock option strike price is usually equal to the FMV of the company’s stock on the day the option is granted.
What is the difference between FMV and strike price?
When the stock’s value increases, the difference between the FMV and your strike price is called “the spread .” This is the underlying value of the stock. When the spread is positive, your options are considered “in-the-money.”
Why doesn't the strike price change?
The strike price doesn’t change at all over time because it’s a fixed price. The yellow line is Meetly’s stock price (or FMV). Right now, those prices are the same. If you decide to exercise your options and buy your shares, you would have to pay $1 to get $1 in return.
What is stock dilution?
Stock dilution is when a company issues additional shares and subsequently reduces how much of the company you (and the other shareholders) own. It usually happens when a company raises money. When you received your options from Meetly, they had 5,000 shares outstanding.
What is strike price?
Strike price is the price at which a derivative contract can be bought or sold (exercised). Derivatives are financial products whose value is based (derived) on the underlying asset, usually another financial instrument. The strike price, also known as the exercise price, is the most important determinant of option value.
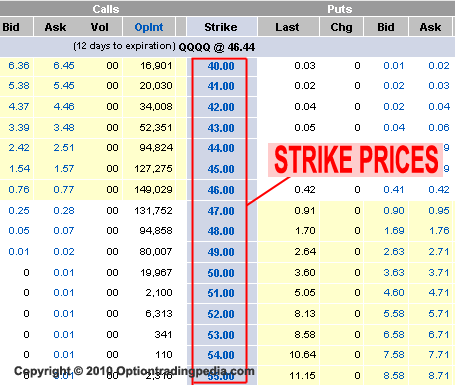
Why is the $40 put option no value?
This is because the underlying stock is below the strike price of the put. The $40 put option has no value because the underlying stock is above the strike price. Recall that put options allow the option buyer to sell at the strike price.
How much is the first contract worth at expiration?
At expiration, the first contract is worth $45. That is, it is in the money by $45 . This is because the stock is trading $45 higher than the strike price. The second contract is out of the money by $5. If the price of the underlying asset is below the call's strike price at expiration, the option expires worthless.
What is the meaning of "out of the money"?
If exercising the option would not generate profit , then the option is referred to as “out of the money.”.
Is strike price the same as exercise price?
Yes, the terms strike price and exercise price are synonymous. Some traders will use one term over the other, and may use the terms interchangeably, but their meanings are the same. Both terms are widely used in derivatives trading.
What is strike price?
The strike price of an option is the price at which the contract can be exercised. The strike price of a stock and an index option is fixed in the contract. Depending on the amount of premium you want to spend, you may want to set the strike price higher or lower.
How much to strike for ABC call options?
Since you want to purchase at the money call options, you would set a strike price of $20. This indicates that if the stock stays above $20 before the expiration date of your call options, you could exercise your options and buy shares of ABC for $20.
Can you buy call options with a higher strike price?
Generally, if you are buying call options, a higher strike price results in a cheaper option and vice versa for put options. Setting a strike price depends on the amount of risk you want to take and how much you are willing to spend on purchasing the options. If you buy or hold a call option, you have the right to purchase stock shares at ...
What is strike price?
What is the Strike Price? The strike price is the price at which the holder of the option can exercise the option to buy or sell an underlying security, depending on whether they hold a call option. Call Option A call option, commonly referred to as a "call," is a form of a derivatives contract that gives the call option buyer the right, ...
What is option trading?
or put option. An option is a contract where the option buyer purchases the right to exercise the contract at a specific price, which is known as the strike price. Buying or selling options is a popular trading strategy. Options trading is not complex, but as with any other investment, having good information is important.
What happens to the seller of a put option if it expires?
The seller will profit from selling the option if the option expires out of the money, which in the case of a put option means the stock price remains higher than the strike price up to the date of the option’s expiration. CFI is a global provider of financial modeling and valuation courses and on a mission to help you advance your career.
How long are options good for?
Options are only good for a set period of time, after which the option expires. The buyer of the option can exercise the option at any time before the specified expiration date. If the call option expires “out-of-the-money,” that is, with the underlying stock price still below the option strike price, then the option seller will profit by ...
What does it mean to buy on margin?
Buying on Margin Margin trading or buying on margin means offering collateral, usually with your broker, to borrow funds to purchase securities. In stocks, this can also mean purchasing on margin by using a portion of profits on open positions in your portfolio to purchase additional stocks.
What is a long and short position?
Long and Short Positions In investing, long and short positions represent directional bets by investors that a security will either go up (when long) or down (when short). In the trading of assets, an investor can take two types of positions: long and short. An investor can either buy an asset (going long), or sell it (going short).
Is option trading complex?
Options trading is not complex, but as with any other investment, having good information is important. In the image below, we can see the strike price for a call option, which confers the right to buy at the strike price and the break-even point where the option seller starts losing money.
What factors determine the value of an option?
These include the current stock price, the intrinsic value, time to expiration or the time value, volatility, interest rates, and cash dividends paid.
What are the drivers of the price of an option?
Let's start with the primary drivers of the price of an option: current stock price, intrinsic value, time to expiration or time value, and volatility. The current stock price is fairly straightforward. The movement of the price of the stock up or down has a direct, though not equal, effect on the price of the option.
Why do I get a higher premium on an AMZN option?
On the one hand, the seller of an AMZN option can expect to receive a higher premium due to the volatile nature of the AMZN stock. Basically, when the market believes a stock will be very volatile, the time value of the option rises.
How does time value relate to options?
It is directly related to how much time an option has until it expires, as well as the volatility, or fluctuations, in the stock's price.
What is the most widely used model of options?
Of these, the Black-Scholes model is the most widely known. 1 In many ways, options are just like any other investment—you need to understand what determines their price to use them effectively. Other models are also commonly used, such as the binomial model and trinomial model .
How does time decay in an option?
The time component of an option decays exponentially. The actual derivation of the time value of an option is a fairly complex equation. As a general rule, an option will lose one-third of its value during the first half of its life and two-thirds during the second half of its life.
What is intrinsic value?
Basically, the intrinsic value is the amount by which the strike price of an option is profitable or in-the-money as compared to the stock's price in the market . If the strike price of the option is not profitable as compared to the price of the stock, the option is said to be out-of-the-money. If the strike price is equal to the stock's price in the market, the option is said to be "at-the-money."
What happens when you buy a stock option?
Instead, you pay a premium for the right to purchase the stock for a set price, called the strike price, through the expiration date.
How many shares does each stock option control?
Each stock option controls 100 shares of the underlying stock. A call option gives the owner the right, but not the obligation, to buy the stock for a set price, while a put option gives the holder the right, but not the obligation to sell the stock for a set price.
What is intrinsic value of a call option?
A call option's intrinsic value is always either $0 or the amount by which the underlying stock price exceeds the option's strike price.
How to calculate time value of an option?
You can calculate an option's time value by subtracting the option's intrinsic value from its market price. Whatever is left is its time value. An option's time value fluctuates based on such factors as time remaining to expiration, volatility of the underlying stock, price difference between the option's strike price and ...
Is an option in the money or out of the money?
Time Value. An option that has intrinsic value is said to be in-the-money, while an option with no intrinsic value is said to be out-of-the-money. The market price of all stock options is a combination of the option's intrinsic value and its time value.
Do stock options move in the same way as out of the money?
Price movements of stock options tend to be less volatile than price movements of the underlying stock. The market price of an in-the-money stock option typically moves in tandem with movements in the market price of the underlying stock, while price movements for out-of-the-money options will be less pronounced.
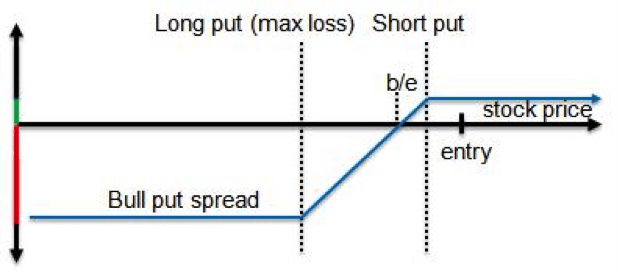
Strike Price and Dilution
Stock Option Strike Prices
- Remember: stock options are the right to buy a set number of company shares at a fixed price, typically called a strike price, grant price, or exercise price. In this example, your stock option strike price is $1 per share. To come up with that $1 price, Meetly (our example company) had to determine its fair market value (FMV). For private companie...
How Stock Options Gain Value
- “At-the-money” stock options In the graph above, the blue line represents your strike price. The strike price doesn’t change at all over time because it’s a fixed price. The yellow line is Meetly’s stock price (or FMV). Right now, those prices are the same. If you decide to exercise your options and buy your shares, you would have to pay $1 to get $1 in return. In this situation, your options …
Stock Dilution
- Stock dilutionis when a company issues additional shares and subsequently reduces how much of the company you (and the other shareholders) own. It usually happens when a company raises money. When you received your options from Meetly, they had 5,000 shares outstanding. In other words, they’ve issued 5,000 shares in total to all of their shareholders. This means your 100 shar…