Key Takeaways
- Bonds affect the stock market because when bonds go down, stock prices go up. ...
- Bonds are loans you make to a corporation or government; stocks are shares of ownership in a company.
- Whether bonds or stocks are better for you depends on your investment goals, but it's smart to have a diversified portfolio with a mix of both.
What are the factors that influence bond in the market?
Factors that influence the performance of bonds
- Market conditions Broader market conditions can have an impact on bonds. ...
- Ratings Bonds are assigned credit ratings by ratings agencies, such as Moody’s and Standard & Poor’s. ...
- The age of a bond The age of a bond relative to its maturity date can affect pricing. ...
What factors determine the market price of a bond?
Factors That Affect Bond Prices
- Interest Rates. A change in market interest rates will have the most direct effect to change a bond's market price. ...
- Issuer Credit Rating. Bond issuers, governments and corporations receive credit ratings from the rating agencies, Moody's, Standard & Poors and Fitch Ratings.
- Prepayment or Call Features. ...
What are the effects of inflation on the bond market?
What to Know About Inflation in the U.S.
- Inflation, Explained: What is inflation, why is it up and whom does it hurt? ...
- The Fed’s Pivot: Jerome Powell’s abrupt change of course moved the central bank into inflation-fighting mode.
- Fastest Inflation in Decades: The Consumer Price Index rose 6.8 percent in November from a year earlier, its sharpest increase since 1982.
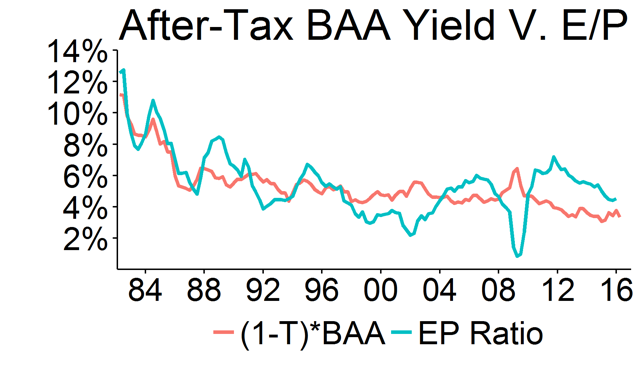
Is the bond market smarter than the stock market?
The market value of the bond markets are MUCH BIGGER than the stock markets. 2016 Values from the SIFMA Fact Book: It is often said that the Bond Market is smarter than the Stock Market (with good reason).
Does the bond market predict the stock market?
Bond investors, as a group, are seen as being "smart money" and less prone to the type of guessing seen in stocks or commodities. As a result, bonds have a fairly strong track record as a way to predict what the economy will look like in the near future.
What is the relationship between bonds and stocks?
Bond prices and stocks are generally correlated to one another. When bond prices begin to fall, stocks will eventually follow suit and head down as well. The rationale stems from the fact that bonds are generally considered less risky investments than stocks.
What are bond yields and how do they affect the stock market?
Selling in the stock market leads to higher bond prices and lower yields as money moves into the bond market. Stock market rallies tend to raise yields as money moves from the relative safety of the bond market to riskier stocks.
Why do stocks fall when bonds Rise?
As interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing becomes more expensive for them, resulting in higher-yielding debt issuances. Simultaneously, market demand for existing, lower-coupon bonds will fall (causing their prices to drop and yields to rise).
Are bonds safe in a stock market crash?
While it's always possible to see a company's credit rating fall, blue-chip companies almost never see their rating fall, even in tumultuous economic times. Thus, their bonds remain safe-haven investments even when the market crashes. Investment-grade corporate bonds are second only to U.S. Treasuries in safety.
What happens when bond yields go up?
Rising yields can create capital losses in the short-term, but can set the stage for higher future returns. When interest rates are rising, you can purchase new bonds at higher yields. Over time the portfolio earns more income than it would have if interest rates had remained lower.
Are bonds a good investment in 2022?
Sign up for stock news with our Invested newsletter. ] The U.S. Department of the Treasury recently announced that I bonds will pay a 9.62% interest rate through October 2022, their highest yield since they were first introduced back in 1998.
What stocks do well when interest rates rise?
Industrials, consumer names, and retailers can also outperform when the economy improves and interest rates move higher. Some sectors, such as real estate, can cool down during interest rate hikes.
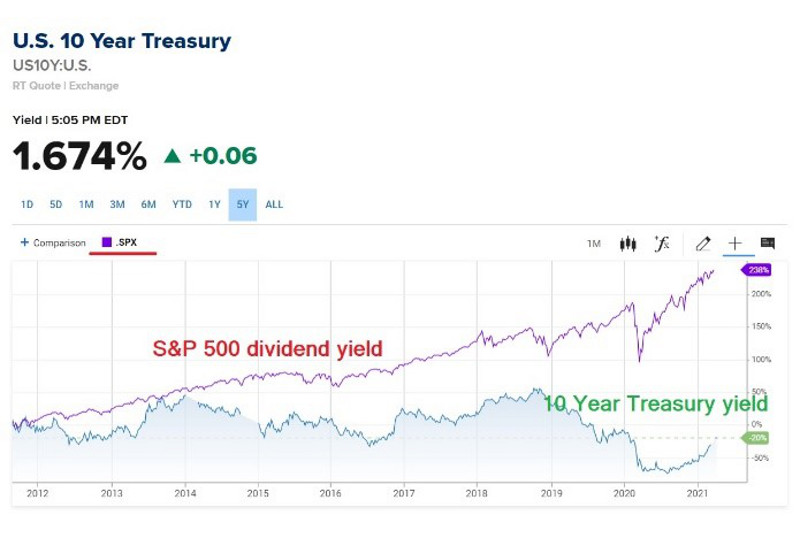
How does the 10 year Treasury affect stocks?
Because they are backed by the U.S. government, Treasury securities are seen as a safer investment relative to stocks. Bond prices and yields move in opposite directions—falling prices boost yields, while rising prices lower yields. The 10-year yield is used as a proxy for mortgage rates.
How do stock and bond prices affect each other?
To understand how stock and bond prices can affect each other, it is essential to understand that stocks and bonds are competing for investors’ money. Stocks are considered more risky than bonds, since they can lose value rapidly depending on a company’s fortunes and the stock market is typically much more volatile than the bond market.
How do interest rates affect bond prices?
Interest rates have the strongest effect on bond prices. The effective yield of a bond is reduced when investors could achieve close to the same profit without paying for a bond as interest rates rise. Thus, bond prices fall when interest rates rise, and rise when interest rates fall. At the same time, interest rate changes may or may not have ...
Why do stock prices fall?
Rising interest rates constrict the economy, causing stock prices to fall. If interest rates have a strong effect on the stock market, then lower interest rates will cause both stock and bond prices to rise, while higher interest rates will cause both stock and bond prices to fall. However, the stock market does not always respond strongly ...
Why are stocks less risky in a bull market?
In a bull market, investors are likely to see stocks as less risky because the stock market as a whole is performing well. That means that stocks potentially offer a greater reward-risk ratio, so investors will move their money from bonds to stocks, increasing the price of stocks and decreasing the price of bonds.
Why does the stock market not respond to interest rate changes?
However, the stock market does not always respond strongly to interest rate changes because of investor sentiment, a strong or poor earnings season, or a multitude of other factors. In that case, it can be difficult to predict whether the bond and stock markets will move in the same direction in response to an interest rate change.
Why do bonds exist?
The bond market exists because once a bond is issued to an investor, that investor can then turn around and trade it for a profit or loss. The bond market is not a single market, but rather a catch-all term for the collection of different bond markets.
What is a bond?
A bond is essentially a receipt for a loan made by an investor to a company or government, indicating that the loan is to be repaid in the future. Companies and governments typically issue bonds to finance a specific project, receiving money in the short term in exchange for a promise to pay back the loan with interest.
How does a bull market affect bonds?
How Does a Bull Market in Stocks Affect Bonds? Bonds and stocks compete for investment money at a fundamental level and that suggests that a strengthening equity market would attract funds away from bonds. Facing decreased demand for bonds, sellers would have to lower prices to attract buyers. Based on this theory, the price ...
What are the factors that affect the direction of a stock?
However, there are other factors that also impact the direction of stocks and bonds, including interest rates, monetary policy, inflation, government action, and broader investor sentiment.
What happens in a bull market?
In a bull market, equity prices move higher overall, boosting investor confidence, and making investors less risk-averse. In this environment, low-risk bonds are less appealing than riskier stocks, and stocks surge in response. However, there are other factors that also impact the direction of stocks and bonds, including interest rates, ...
How does Fed intervention affect stocks?
It may be possible for bond prices to rise while stocks are enjoying a bull market.
What is the Fed's interest rate policy?
The interest rate policy of the Federal Reserve (and other central banks for markets outside of the U.S.) must also be considered. The Fed sets short-term interest rates in an effort to affect economic conditions.
Do bonds and stocks compete for investment money?
Bonds and stocks compete for investment money at a fundamental level and that suggests that a strengthen ing equity market would attract funds away from bonds. Facing decreased demand for bonds, sellers would have to lower prices to attract buyers.
Is it safe to invest in bonds?
Most bonds ( not junk bonds) are a safer investment than most stocks, which means that stocks have to offer a higher return as a premium for the increased risk. This is why money leaves equities and goes into the bond market during times of uncertainty. The opposite is often true during a bull market as stocks begin to receive funds at ...
A rally in the stock market tends to raise bond yields as money moves from the relative safer investment bet to riskier equity stock markets
Note: Subscription will be auto renewed, you may cancel any time in the future without any questions asked.
Dear Reader,
Business Standard has always strived hard to provide up-to-date information and commentary on developments that are of interest to you and have wider political and economic implications for the country and the world.
Why do investors demand higher rates on high yield bonds?
High yield bonds are generally issued by corporations or municipalities that carry greater risk of default, which is why investors demand higher rates on these bonds. During a recession, the weaker corporations are at more risk of default than in more favorable economic environments.
Why are bonds good for bear market?
Bonds can be a good investment during a bear market because their prices generally rise when stock prices fall. The primary reason for this inverse relationship is that bonds, especially U.S. Treasury bonds, are considered a safe haven, which makes them more attractive to investors than volatile stocks in such times.
What is credit risk in ETFs?
Be careful when investing in high yield bonds and the mutual funds and ETFs that are based on them during bear markets and recessions. The exposure inherent with this type of bond is called credit risk, which is the threat of the underlying bond issuer defaulting on its own debt.
What does it mean when the stock market is in a bear market?
Generally, a bear market occurs when a broad market index falls by 20% or more over at least a two-month period. Stocks briefly entered a bear market in March 2020.
What is a TIPS bond?
Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS) and municipal bonds may provide protection in some bear markets, but results could be mixed. Performance of these bond types depends on the cause for, and magnitude of, the bear market sell-off.
Can bonds be profitable during a bear market?
While bonds and bond funds can remain stable or produce gains during a bear market, they are not guaranteed profitable investments. Also, when the Fed ends monetary stimulus, bond yields may begin to rise as bond prices begin to fall.
Can bond mutual funds turn in a positive performance?
During a stock bear market, bond mutual funds could turn in a positive performance. Amid a bear market, and especially after a recession, bond funds also could decline in price in line with the stock market.
What are the risks of investing in bonds?
Investing in the bond market is subject to risks, including market, interest rate, issuer, credit, inflation risk, and liquidity risk. The value of most bonds and bond strategies are impacted by changes in interest rates. Bonds and bond strategies with longer durations tend to be more sensitive and volatile than those with shorter durations; bond prices generally fall as interest rates rise, and the current low interest rate environment increases this risk. Current reductions in bond counterparty capacity may contribute to decreased market liquidity and increased price volatility. Bond investments may be worth more or less than the original cost when redeemed. Corporate debt securities are subject to the risk of the issuer's inability to meet principal and interest payments on the obligation and may also be subject to price volatility due to factors such as interest rate sensitivity, market perception of the creditworthiness of the issuer and general market liquidity. Sovereign securities are generally backed by the issuing government. Obligations of U.S. government agencies and authorities are supported by varying degrees, but are generally not backed by the full faith of the U.S. government. Portfolios that invest in such securities are not guaranteed and will fluctuate in value. Equities may decline in value due to both real and perceived general market, economic and industry conditions. Diversification does not ensure against loss. It is not possible to invest directly in an unmanaged index.
What are the factors that affect bond performance?
Apart from interest rate movements, there are three other key factors that can affect the performance of a bond: market conditions, the age of a bond and its rating. Let’s look at each in turn. Market conditions. Broader market conditions can have an impact on bonds.
What happens to a bond when it is downgraded?
If a bond’s credit rating is downgraded, the bond becomes less attractive to investors and its price will likely fall. The age of a bond. The age of a bond relative to its maturity date can affect pricing. This is because the bondholder is paid the full face value of the bond when the bond reaches maturity.
How does the price of a bond relate to yield?
The price of a bond relative to yield is key to understanding how a bond is valued. Essentially, the price of a bond goes up and down depending on the value of the income provided by its coupon payments relative to broader interest rates.
Why are corporate debt securities subject to price volatility?
Corporate debt securities are subject to the risk of the issuer's inability to meet principal and interest payments on the obligation and may also be subject to price volatility due to factors such as interest rate sensitivity, market perception of the creditworthiness of the issuer and general market liquidity.
What is the first value of a bond?
The first is the initial price of the bond – or its face value – which is set when the bond is first issued to the market. This is also the amount of capital that will be returned to the investor at maturity barring a default. The second relates to the price of the bond as it trades in the secondary market.
What is covered bond?
Covered bonds. Debt securities issued by banks that are secured against a pool of assets (generally mortgages), which are held on the bank’s balance sheet. Credit market. The market whereby companies and governments can raise funds by allowing investors to purchase their debt securities.
What is the interest rate that impacts the stock market?
The interest rate that impacts the stock market is the federal funds rate. Also known as the discount rate, the federal funds rate is the rate at which depository institutions borrow from and lend to each other overnight.
How do higher interest rates affect stock prices?
Higher interest rates tend to negatively affect earnings and stock prices (with the exception of the financial sector). Understanding the relationship between interest rates and the stock market can help investors understand how changes may impact their investments.
What happens to the market as interest rates fall?
Conversely, as interest rates fall, it becomes easier for entities to borrow money, resulting in lower-yielding debt issuances.
How does the business cycle affect the market?
At the onset of a weakening economy, a modest boost provided by lower interest rates is not enough to offset the loss of economic activity; stocks may continue to decline.
What is the measure of the sensitivity of a bond's price to a change in interest rates called?
The measure of the sensitivity of a bond's price to a change in interest rates is called the duration . One way governments and businesses raise money is through the sale of bonds. As interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing becomes more expensive for them, resulting in higher-yielding debt issuances.
Why did the Dow drop?
The number of points the Dow dropped on Oct. 10, 2018, due to the fear of higher interest rates. That said, the Dow also dropped even more significantly in March 2020 as the Fed cut rates to near zero amidst the global coronavirus pandemic.
What is the opposite effect of a rate hike?
A decrease in interest rates by the Federal Reserve has the opposite effect of a rate hike. Investors and economists alike view lower interest rates as catalysts for growth—a benefit to personal and corporate borrowing. This, in turn, leads to greater profits and a robust economy.