"A lack of liquidity is a problem if an investor needs to sell an ETF and it doesn't trade enough shares to get the appropriate price," Lee says. "In this case, an ETF that lacks sufficient liquidity could be sold at a share price that's lower than it should be during a time with market volatility."
How does an ETF trade like a stock?
An ETF trades like a stock in that there is a bid price (the price an investor is offering to pay for a share) and an ask price (the share price an investor is offering to sell a share). The difference between the bid and the ask price is called the “spread,” and that can vary depending upon trading activity.
How are ETFs bought and sold?
ETFs are bought and sold through major exchanges at any time during a trading day. An ETF trades like a stock in that there is a bid price (the price an investor is offering to pay for a share) and...
How much does a 20% increase in one stock affect an ETF?
Assuming the ETF tracks the average of the 5 stock prices you bought and equal weightage was given to each stock , an increase in 20% in any one of the five stocks will cause the price of the ETF to increase by 4% also
What happens when an ETF is shunned from the market?
If an ETF is shunned, its supply of holdings will simply drop and vice versa. Since the market is in general rather efficient, the price of the ETF will most of the time reflects the prices of the underlying securities. However, there are times when ETF price deviates from its fundamental value.
What happens when you sell an ETF?
This rule, from IRS Publication 550, states that any gains or losses realized by selling these types of investments are treated as 60% long-term gains (up to 23.8% tax rate) and 40% short-term gains (up to 40.8% tax rate). This happens regardless of how long the investor has held the ETF.
Does buying and selling ETF affect price?
Because ETFs trade like shares of stocks listed on exchanges, the market price will fluctuate throughout the day as buyers and sellers interact with one another and execute trades. If more buyers than sellers arise, the price will generally rise in the market.
Does shorting an ETF affect the underlying stocks?
If market participants are actively using ETF shorting as an avenue to circumvent short- ing constraints, does ETF short selling have predictive power over the future return of the ETFs and their underlying stocks? The answer is yes.
Should you ever sell an ETF?
"A lack of liquidity is a problem if an investor needs to sell an ETF and it doesn't trade enough shares to get the appropriate price," Lee says. "In this case, an ETF that lacks sufficient liquidity could be sold at a share price that's lower than it should be during a time with market volatility."
What is the best time of day to buy ETFs?
"Middle of the day is generally best, and if there are international (European) securities in the ETF, trading in the morning will ensure you get prices closest to fair value," Nadig explains.
Can you buy and sell ETF same day?
Trading ETFs and stocks There are no restrictions on how often you can buy and sell stocks or ETFs. You can invest as little as $1 with fractional shares, there is no minimum investment and you can execute trades throughout the day, rather than waiting for the NAV to be calculated at the end of the trading day.
What is the most shorted ETF?
RankETF% Shares Short#1XRT - SPDR S&P Retail441.50%#2XOP - SPDR S P Oil Gas Exploration …57.54%#3XHB - SPDR S&P Homebuilders57.48%#4HYG - iShares iBoxx High Yield Corporate …57.23%17 more rows
Can I short sell an ETF?
ETFs (an acronym for exchange-traded funds) are treated like stock on exchanges; as such, they are also allowed to be sold short. Short selling is the process of selling shares that you don't own, but have instead borrowed, likely from a brokerage.
Does ETF increase volatility?
In this analysis, a one-standard-deviation increase in ETF ownership is associated with a statistically significant increase in daily volatility that ranges between 9% and 15% of a standard deviation, for S&P 500 stocks. The effect is, therefore, economically significant.
Can you get rich off ETF?
It's a common belief that investors get rich by picking individual stocks and beating the market. While that can be true, stock picking isn't the only path for investors to build wealth. Funds -- ETFs in particular -- can also make you a millionaire, even though many of them never beat the market.
How long do I have to hold an ETF?
Holding period: If you hold ETF shares for one year or less, then gain is short-term capital gain. If you hold ETF shares for more than one year, then gain is long-term capital gain.
Should you hold ETFs long-term?
ETFs can be great building blocks for long-term investors. They can provide broad exposure to market sectors, geographies, and industries and help investors quickly diversify their portfolios and reducing their overall risk profile. The best long-term ETFs provide this exposure for a relatively low expense ratio.
What influences the price of an ETF?
On rare occasions, an ETF's price can move away from the value of the underlying investments. This can be due to illiquid underlying assets, fees, taxes and other factors affecting the ability to price or hedge the product.
Does it matter what price you buy an ETF at?
The price you can buy and sell an ETF at should be close to the NAV per unit. But at times the price may move away from the NAV. Most ETFs also provide real-time NAV updates.
Does an ETF go up if more people buy it?
If the value of an ETF's underlying assets rise, and the number of shares remains unchanged, then the price per share will also increase. If trading demand for an ETF's shares increases, then more units are created. The increased supply of shares keeps the share price in line with the ETF's NAV.
How does ETF price change?
The traded price of an ETF changes throughout the day like any other stock, as it is bought and sold on the stock exchange. The trading value of an ETF is based on the net asset value of the underlying stocks that an ETF represents.
What is IBD 50?
IBD'S TAKE: The IBD 50 lets you track the market's leading growth stocks based on earnings, sales, price performance and other proprietary metrics. Check out the list now.
How much did FFTY gain in 2015?
FFTY, which launched in April 2015, has attracted more than $375 million in assets. It's returned 32.1% over the past year as of Feb. 16, according to Morningstar Direct, well ahead of the S&P 500's 18.7% gain.
Is an ETF a basket?
Since an ETF is a basket of stocks, it's often better to give the underlying components a chance to settle.
Is a market order better than a limit order?
If you want to execute the trade as quickly as possible, a market order is likely your better bet. However, if time isn't of the essence, industry experts say a limit order is almost always the best way to go.
What is the difference between a bid and ask price in an ETF?
An ETF trades like a stock in that there is a bid price (the price an investor is offering to pay for a share ) and an ask price (the share price an investor is offering to sell a share). The difference between the bid and the ask price is called the “spread,” and that can vary depending upon trading activity.
How does mutual fund trading work?
dollars. In other words, you buy a set dollar amount and that gets you the proportionate number of shares, including fractions of shares. With an ETF, you place an order for a specific number of shares and the total price that you pay is the share price times the number of shares. Simply put, you cannot place an ETF order for a dollar amount and you cannot place a mutual fund order for a number of shares.
Why are ETFs important?
ETFs can offer investors a great way to implement a low-cost investing strategy, but it's important to focus on keeping trading costs under control. This is especially true when trading larger amounts, where investors can unwittingly run up their costs.
How long does it take for mutual funds to settle?
Settlement time: Most mutual funds settle in one day . This means if you sell your mutual fund on one trading day you will have your cash on the next trading day. ETFs settle in three days in most cases. 5 trading tips.
When are mutual funds bought and sold?
Buying and selling: Mutual funds are bought and sold only at the end of the trading day, after all securities have been repriced. An investor selling a share of the mutual fund would receive the exact same amount as anyone else selling shares of the same mutual fund. ETFs are bought and sold through major exchanges at any time during a trading day.
Why do you need a limit order for ETFs?
For investors buying or selling ETFs, limit orders have some advantages over market orders since they offer some price control and thus protection . The limit also tends to establish a boundary around your preset transaction price. However, be aware that a limit order may not necessarily get filled.
How to avoid volatility?
Avoid volatility when possible. Avoid trading on days with higher than normal market volatility, which can result in wider bid-ask spreads. Though volatility is generally unpredictable, there are a number of events that can trigger higher volatility. For example, the stock market might experience increased volatility when a Federal Reserve Bank policy decision is announced or when key economic data is released.
Is liquidity an important factor to consider when investing in an ETF?
Yes, liquidity is an important consideration in exchange-traded fund (ETF) investing. ETFs have differing liquidity profiles for a number of reasons. Investing in an ETF with relatively low liquidity may cost you in terms of a wider bid-ask spread, reduced opportunity to trade profitably, and—in extreme cases—an inability to withdraw funds in certain situations like a big market crash.
What is an ETF tracking error?
An ETF’s tracking error is the difference between its returns and those of its underlying benchmark index. Tracking errors are generally small, and the largest, widely held ETFs have minimal tracking errors.
What are the advantages of ETFs?
Trading Fees. One of the biggest advantages of ETFs is that they trade like stocks. An ETF invests in a portfolio of separate companies, typically linked by a common sector or theme. Investors simply buy the ETF in order to reap the benefits of investing in that larger portfolio all at once. As a result of the stock-like nature ...
Why are ETFs important?
However, it is important to note that just because an ETF contains more than one underlying position doesn't mean that it can't be affected by volatility. The potential for large swings will mainly depend on the scope of the fund.
Why do people choose ETFs?
When it comes to risk considerations, many investors opt for ETFs because they feel that they are less risky than other modes of investment. We've already addressed issues of volatility above, but it's important to recognize that certain classes of ETFs are inherently significantly more risky as investments as compared with others.
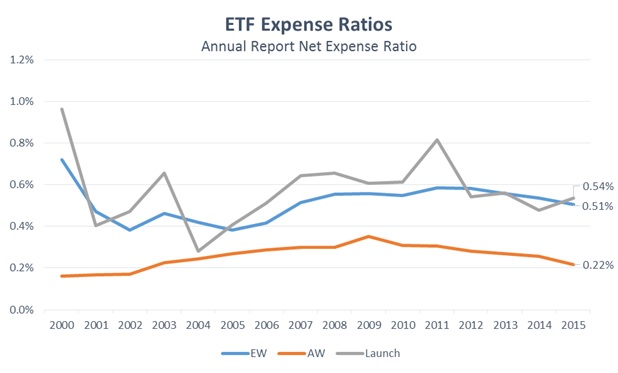
What is expense ratio?
The expense ratio is a measure of what percentage of a fund's total assets are required to cover various operating expenses each year. While this is not exactly the same as a fee that an investor pays to the fund, it has a similar effect: the higher the expense ratio, the lower the total returns will be for investors.
How to build a small investor position?
However, there is also the tried-and-true small investor's way of building a position: dollar-cost averaging. With this method, you take the same $10,000 and invest it in monthly increments of, say, $1,000. It's called dollar-cost averaging because in some months you will buy fewer shares with that $1,000 as a result of the price being higher. In other months, the share prices will be lower and you will be able to buy more shares.
What Is a Stock?
A stock represents an ownership share in a company. Publicly traded companies issue shares of stock for the first time through an initial public offering or IPO. When a company goes public, it just means its shares are available to buy and sell on an exchange like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE). Each stock that’s traded is identifiable by a ticker symbol.
Should You Invest in an ETF vs. Stock?
Whether it’s better to invest in ETFs or stocks can depend on your overall investment strategy. For example, if you’re more of a hands-off investor who’s in the market for the long term then ETFs might be the better choice. You could build a complete investment portfolio around just a handful of ETFs and watch them appreciate in value over time. On the other hand, if you like to be more hands-on with investing, then trading individual stocks might be more appealing. This is the riskier option but it also has the potential for higher rewards if you’re investing wisely.
What are the benefits of ETFs?
Exchange-traded funds mirror stocks in a lot of ways, though the biggest difference obviously is that you’re owning multiple securities vs. just one. Some of the other benefits of ETFs include: 1 Diversification across sectors with a single investment 2 Index tracking if you prefer index ETFs to other types of funds 3 Low minimum investments
What is the difference between ETFs and mutual funds?
They can be traded on an exchange just like a stock. So compared to mutual funds, ETFs can offer more flexibility. They can also be less expensive in terms of the expense ratio you pay to own them.
What are the drawbacks of the stock market?
On the con side, there are two key drawbacks to consider. The first is risk. Stocks and the stock market are susceptible to volatility. The market environment during the first part of 2020 was a great example of how quickly stock prices can dip because of things that are completely outside an investor’s control.
What is the ticker symbol on a stock?
Each stock that’s traded is identifiable by a ticker symbol. Stocks can also be referred to as equities. When you buy one or more shares of stock, what you’re getting is an equity stake in the underlying company. The value of that equity can increase or decrease over time as the stock’s share price rises or falls.
Why do people own stocks?
Financial experts tend to agree that investors who are interested in building wealth need to own some stocks. Compared to bonds, for example, stocks can produce higher returns over time. The more time you have to invest, the more your stock portfolio can grow through the power of compounding. That’s arguably the biggest pro in favor of stock investing. But other advantages include:
What does "nobody wants to buy" mean?
The "nobody wants to buy" is the part that you're missing since the arbitrage opportunity is what various firms will take advantage and move the trading price of the ETF and thus there will be those seeking to exploit these differences if possible.
How many componenets are in an ETF?
An ETF consists of two componenets : stocksand weightage of each stock.
What happens if an ETF is shunned?
If an ETF is shunned, its supply of holdings will simply drop and vice versa.
How many Q&A communities are there on Stack Exchange?
Stack Exchange network consists of 178 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
What is the creation mechanism of an ETF?
The creation mechanism for ETF's ensure s that the value of the underlying stocks do not diverge significantly from the Fund's value. Authorized participants have a strong incentive to arbitrage any pricing differences and create/redeem blocks of stock/etf until the prices are back inline.
Do you know if an ETF has a different value?
You do know the value of the stocks in the ETF can have a different value than the trading price of the ETF yes?
What is the meaning of "back up"?
Making statements based on opinion; back them up with references or personal experience.
How much will ETFs be in 2020?
In the U.S. alone, ETF assets under management are expected to total $4.2 trillion by the end of 2020, growing about 15 percent, on average, each year. [See: 7 of the Best ETFs to Own in 2017 .] The 2016 Trends in Investing Survey, by the Journal of Financial Planning and the Financial Planning Association Research and Practice Institute, ...
What is an ETF objective?
An ETF's objective is to track a specific market index, but that doesn't mean the fund consistently mirrors the index's returns. That's where tracking error comes in.
Does Pincus argue that this type of change would affect an investor's overall diversification minimally?
Pincus argues that this type of change would affect an investor's overall diversification minimally. If you're concerned about maintaining your exposure to small-cap stocks, however, you'd have to consider how well an ETF making such a change would continue to fit your larger investment strategy.
What to do if you're paying more for an ETF?
If you're paying more for a specific ETF, analyze the reasons for the higher cost.
Can an ETF change its benchmark?
Although it's uncommon, an ETF can shift its underlying strategy and even change its benchmark over time. Gabriel Pincus, president and portfolio manager of GA Pincus Funds in Dallas, Texas, says investors should consider how much that change might affect their portfolio's diversification.
Does ETF liquidity shrink?
Although it doesn't happen often, if an ETF's liquidity shrinks, so could its profitability. "A lack of liquidity is a problem if an investor needs to sell an ETF and it doesn't trade enough shares to get the appropriate price," Lee says. "In this case, an ETF that lacks sufficient liquidity could be sold at a share price that's lower ...
Can exchange traded funds stop investing?
Over time, any exchange-traded fund can stop fitting your investing strategy.