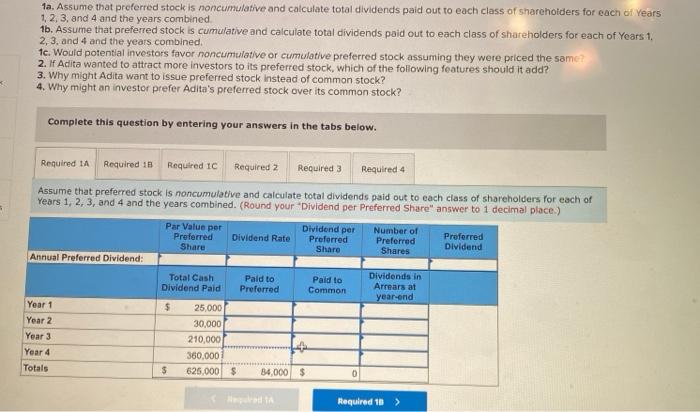
What does it mean if preferred stock is noncumulative?
The term "noncumulative" describes a type of preferred stock that does not pay stockholders any unpaid or omitted dividends. Preferred stock shares are issued with pre-established dividend rates, which may either be stated as a dollar amount or as a percentage of the par value.
Why would an investor buy preferred stock?
Most shareholders are attracted to preferred stocks because they offer more consistent dividends than common shares and higher payments than bonds. However, these dividend payments can be deferred by the company if it falls into a period of tight cash flow or other financial hardship.
What is the difference between cumulative and noncumulative preferred stock?
Cumulative Preferred Stock Straight, noncumulative preferred does not accumulate unpaid dividends, but its dividends are paid ahead of common stock, after any accumulated dividend obligations have been paid to holders of the cumulative preferred. Common stock dividends get paid last.
Are preferred stocks a good investment now?
Preferred stock has long appealed to retail investors because of the relatively high and secure dividend yields....Investors can buy preferred stock from corporate issuers to closed-end funds.Preferred Issue / TickerNuveen Preferred Income Opportunities / JPCRecent Price7.87YTD Change-19.4Yield8.089 more columns•May 7, 2022
What is the downside of preferred stock?
Disadvantages of preferred shares include limited upside potential, interest rate sensitivity, lack of dividend growth, dividend income risk, principal risk and lack of voting rights for shareholders.
Who buys preferred stock?
Institutions are usually the most common purchasers of preferred stock. This is due to certain tax advantages that are available to them, but which are not available to individual investors. 3 Because these institutions buy in bulk, preferred issues are a relatively simple way to raise large amounts of capital.
Would the company be better off with a noncumulative feature?
Advantages of Noncumulative Stock Issuing noncumulative stock assists corporations in times of financial distress. By canceling the company's obligation to pay unpaid dividends, noncumulative stock frees up cash flow and allows companies to utilize it when required.
How do you calculate noncumulative preferred stock?
0:282:43Cumulative & Noncumulative Preferred Stock - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd again the calculation is based on the dollar amount of each. Share times the number of sharesMoreAnd again the calculation is based on the dollar amount of each. Share times the number of shares out there in total times the dividends rate.
What is the difference between cumulative preferred shares and non cumulative preferred shares which situation could have dividends in arrears?
Missed Payments and Cumulative Preferred Stock These standard preferred shares are sometimes referred to as non-cumulative preferred stock. In contrast, holders of the cumulative preferred stock shares will receive all dividend payments in arrears before preferred stockholders receive a payment.
Can you lose money on preferred stock?
Like with common stock, preferred stocks also have liquidation risks. If a company is bankrupt and must be liquidated, for example, it must pay all of its creditors first, and then bondholders, before preferred stockholders claim any assets.
Should I buy preferred or common stock?
Preferred stock may be a better investment for short-term investors who can't hold common stock long enough to overcome dips in the share price. This is because preferred stock tends to fluctuate a lot less, though it also has less potential for long-term growth than common stock.
Can preferred stock lose value?
Preferreds are issued with a fixed par value and pay dividends based on a percentage of that par, usually at a fixed rate. Just like bonds, which also make fixed payments, the market value of preferred shares is sensitive to changes in interest rates. If interest rates rise, the value of the preferred shares falls.
What is non cumulative preference?
Non-cumulative preference shares are those shares that provide the shareholder fixed dividend amount each year from the company’s net profit but in case the company fails to pay the dividend on such preference share to the shareholder in any year then such dividend cannot be claimed by the shareholder in future.
Why do companies issue non-cumulative preference shares?
A company issues cumulative preference shares so that it can pay out lower dividends as they trade rich in the market as they are placed above the non-cumulative preference shares and leads to a higher credit rating for the companies. But having issued non-cumulative preference shares provides flexibility to companies, ...
What is dividends in arrears?
Dividends In Arrears Dividends in Arrears is the cumulative dividend amount that has not been paid to the cumulative preferred stockholders by the presumed date.
What is dividend in accounting?
Dividend Dividend is that portion of profit which is distributed to the shareholders of the company as the reward for their investment in the company and its distribution amount is decided by the board of the company and thereafter approved by the shareholders of the company . read more. for a $500 dividend.
What does "arrears" mean in dividends?
Definition. As the name suggests, any arrears in dividends get accumulated and are paid when the company decides to pay out dividends. Any arrear in dividends does get accumulated, and they have no right to claim it any time in the future if skipped. Rank. Placed above the non-cumulative preference shares and are paid before them.
Why should companies maintain a balanced capital structure?
This helps them to manage a balanced investment with a satisfying return to investors and , at the same time managing with lower cash flows.
Do preference shares get paid before common shareholders?
Preference over Common Shareholders – Being in the nature of preference share, these non-cumulative preference stocks also have preferential rights over equity/ common shares holders. They get paid before the common shareholders when it comes to the dividend, thus getting an assuming that the equity shareholders will not be getting paid before them.
What is noncumulative stock?
What Is Noncumulative? The term "noncumulative" describes a type of preferred stock that does not pay stockholders any unpaid or omitted dividends. Preferred stock shares are issued with pre-established dividend rates, which may either be stated as a dollar amount or as a percentage of the par value.
Why do preferred stocks rank ahead of common shares?
Preferred stock ranks ahead of common shares in getting something back if the company declares bankruptcy and sells off its assets. More importantly, preferred stocks are issued with stated dividend rates. If a company is profitable, preferred shareholders collect dividends before common stockholders.
Why are companies reluctant to issue noncumulative stocks?
Most companies are reluctant to issue noncumulative stocks because shrewd investors are unlikely to buy this class of shares —unless they're offered at significant discounts.
What happens if ABC fails to pay dividends?
For example, if ABC Company fails to pay the $1.10 annual dividend to its cumulative preferred stockholders, those investors have the right to collect that income at some future date. This essentially means cumulative preferred stockholders will receive all of their missed dividends before holders of common stock receive any dividends, should the company begin paying dividends again.
Can corporate bonds be converted into preferred stock?
Corporate bonds may be issued with a conversion feature, enabling those bonds to be converted into a specific number of shares of either common stock or preferred stock. This conversion option lets bondholders convert a debt investment into stock. For example, let's assume an investor owns a $1,000 par amount corporate bond that can be converted into 20 shares of preferred stock.
Who is Will Wills?
He developed Investopedia's Anxiety Index and its performance marketing initiative. He is an expert on the economy and investing laws and regulations. Will holds a Bachelor of Arts in literature and political science from Ohio University. He received his Master of Arts in economics at The New School for Social Research.
What Does Noncumulative Preferred Stock Mean?
Unlike cumulative preferred stock, noncumulative preferred stock does not utilize the dividend in arrears account for unpaid dividends. Noncumulative preferred stockholders have priority over common shareholders when it comes to dividends that are declared in the current year.
Example
It might be easiest to look at an example. Assume a company with 100, 10%, $10 par value noncumulative preferred stocks outstanding issued a dividend for a $50 dividend.
What is dividend in arrears?
Any unpaid dividend on preferred stock for an year is known as ‘dividends in arrears’. The disclosure of dividends in arrears is of great importance for the investors and other users of financial statements. Such disclosure is made in the form of a balance sheet note.
What is cumulative preferred stock?
Cumulative preferred stock: In case of cumulative preferred stock, any unpaid dividends on preferred stock are carried forward to the future years and must be paid before any dividend is paid to common stockholders.
Is there a question of dividends in arrears?
If preferred stock is noncumulative and directors do not declare a dividend because of insufficient profit in a particular year, there is no question of dividends in arrears.
Why do investors use preferred stocks?
For this reason, investors can use preferred stocks to lower their overall investment portfolio volatility. Preferred dividend payout: Preferred shareholders are entitled to receive dividends after bondholders and before common shareholders.
Why are preferred shares important?
Preferred shares are a unique tool for investors looking for more secure annual dividends and lower risk of losses, which is especially important when you are retired or close to retirement.
What is preferred stock?
Preferred shares, also known as preferred stocks, are a distinct type of fixed-income security, combining characteristics of both stocks and bonds. They provide a high dividend yield and consistent dividend payments, and their prices are fairly stable. Preferred shares are a valuable instrument for passive income investors, ...
What makes preferred stocks attractive?
That makes preferred stocks attractive for investors looking to create stable passive income. Banks, insurance companies, real estate investment trusts (REITs), utilities, and other financial institutions primarily issue preferred shares. Companies use preferred shares as a debt instrument. In addition to common shares, they can issue series ...
What happens to preferred stockholders when a company becomes insolvent?
Priority for repayment: If a company becomes insolvent, preferred stockholders have a higher priority for repayment or a greater claim on the company’s assets during liquidation. The common stock shareholders will be paid out last after creditors, bondholders, and preferred shareholders.
How does growth investing work?
Growth investing increases capital through actively buying and selling common stocks at profit. Value investing in preferred shares creates a dividend cash flow with a lower risk. In addition to the lack of voting rights, preferred shares are different from common shares in many ways.
Why do companies pay higher dividends?
Companies pay higher dividends to attract investors and compensate them for giving up the right to vote and the lack of price appreciation in shares.
What is preferred stock?
Preferred stock is an important funding source for the issuing corporation and a relatively safe investment alternative to common stock for the investor. Regardless of whether it is cumulative or non-cumulative, all types of preferred shares enjoy priority over common stock. Only after preferred stockholders have been paid in full can common ...
What is cumulative dividend?
Cumulative shares incentivize investors with the promise of a minimum return on investment. If preferred shares are cumulative, all past suspended payments must be made to preferred shareholders in full before common stockholders can receive anything at all. And if a company is unable to pay cumulative dividends by their due date, it may have to pay interest on future payments.
Do common shareholders get money after preferred stock is paid?
Only after preferred stockholders have been paid in full can common shareholders receive any money . In addition, cumulative preferred stock provides additional advantages over and above the non-cumulative type.
Can you resume preferred dividends if preferred stock is non cumulative?
If the preferred stock is non-cumulative, the issuing company can resume preferred dividend payments at any time, with disregard to past, missed payments. If the preferred stock in our example is non-cumulative, the preferred stockholder will never get the missed $90 per share. Just as important, the common shareholders must not wait for ...
What is a participating preferred stock?
Participating. This is preferred stock that has a fixed dividend rate. If the company issues participating preferreds, those stocks gain the potential to earn more than their stated rate. The exact formula for participation will be found in the prospectus. Most preferreds are non-participating.
Why do companies issue preferred stock?
A company may choose to issue preferreds for a couple of reasons: 1 Flexibility of payments. Preferred dividends may be suspended in case of corporate cash problems. 2 Easier to market. Preferred stock is typically bought and held by institutional investors, which may make it easier to market during an initial public offering.
How much can you deduct from preferred stock?
Corporations that receive dividends on preferred stock can deduct 50% to 65% of the income from their corporate taxes. 1 .
What is preferred stock?
Preferred stocks are equity securities that share many characteristics with debt instruments. Preferred stock is attractive as it offers higher fixed-income payments than bonds with a lower investment per share. Preferred stock often has a callable feature which allows the issuing corporation to forcibly cancel the outstanding shares for cash.
Why are preferred stocks considered hybrid securities?
Because of their characteristics, they straddle the line between stocks and bonds. Technically, they are securities, but they share many characteristics with debt instruments . Preferred stocks are sometimes called hybrid securities.
Why are preferred dividends suspended?
Preferred dividends may be suspended in case of corporate cash problems. Easier to market. Preferred stock is typically bought and held by institutional investors, which may make it easier to market during an initial public offering.
How much can a corporation deduct from dividends?
Under what is known as the dividend received deduction, a U.S. corporation receiving dividends from a domestic company may deduct up to 50% of the income from its taxes if owns less than 20% of the dividend payer. If the corporation owns more than 20% of the dividend payer, it can deduct 65%. 1 .
How much dividend does Berkshire Hathaway pay?
Berkshire Hathaway will make the investment by purchasing 100,000 shares of preferred stock, which pays out an 8% annual dividend . Preferred shares are different from common stock, the one most people are familiar with. Both are equity in a company, but preferred stock typically pays a higher dividend.
What is the risk of investing in preferred stock?
The main risk of investing in preferred stock is that the assets are, like bonds, sensitive to changes in interest rates. There’s an inverse relationship between interest rates and the price of not only fixed income securities but also hybrids such as preferred stocks.
What is Warren Buffett famous for?
Billionaire Warren Buffett is a master when it comes to investing. The Berkshire Hathaway CEO is famous for buying and holding stock — and not giving in to the volatility of the market. He’s also well-known for taking big stakes in companies, such as the $900 million worth of shares he has in Amazon. His latest play: a $10 billion investment ...
Is preferred stock a good investment?
Earning income. If you want to get higher and more consistent dividends, then a preferred stock investment may be a good addition to your portfolio. While it tends to pay a higher dividend rate than the bond market and common stocks, it falls in the middle in terms of risk, Gerrety said.
Do preferred stockholders have priority over common shareholders?
In this case, the preferred stockholders have priority over common shareholders in receiving their back payment. If a company issues non-cumulative stock, on the other hand, it’s not required to pay missed dividends. But because of the higher risk involved, these shares tend to have higher yields than cumulative shares.
Is a preferred stock dividend guaranteed?
It’s also important to know that dividends aren’t guaranteed — they are paid out of company earnings, just like a common stock dividend. However, there are several different kinds of preferred stocks, and that could matter when it comes to collecting any dividends the company missed.
Do preferred stockholders have voting rights?
Voting rights. Preferred stockholders don’t have voting rights , so they don’t have a voice when it comes to things like electing a board of directors. Common stockholders, on the other hand, do have voting rights.