The final problem with dividend investing is that it comes with hefty tax consequences. Even if you're holding your dividend-paying investments longer than one year (to get better tax treatment), you're still paying taxes every single year. This hurts your investment returns.
Full Answer
What happens to bonus shares when you sell them?
Selling the bonus shares will lower your percentage stake in the company, giving you less dividends and fewer shares in terms of percentage in the stock. If this is difficult to understand, imagine every other shareholder, like you, receives the same bonus shares.
Are dividend stocks worth the risk?
Here are a few reasons when investors should question the benefits of dividend investing: The company may not be doing well. The stock may not generate an income stream for shareholders. Dividend stocks are riskier than bonds.
What are the biggest misconceptions about dividends?
The biggest misconception of dividend stocks is that a high yield is always a good thing. Many dividend investors simply choose a collection of the highest dividend paying stock and hope for the best. For a number of reasons, this is not always a good idea.
What happens when a stock cuts its dividend?
A sudden cut to a dividend program often sends stock shares tumbling, as was the case with so many bank stocks in 2008. 4 5 Ultimately, investors are best served by looking beyond the dividend yield at a few key factors that can help to influence their investing decisions.

What is the downside to dividend stocks?
While the disadvantages of cash dividends are: Tax inefficiency. Investment risk. Sector concentration. Dividend policy changes.
Which is better bonus or dividend?
Dividends have a lower tax than a bonus would. But, they can also only be paid to shareholders. There is a specific process for paying dividends, which includes holding a shareholders meeting with minutes, completing vouchers and keeping records. Unlike a bonus, dividends are managed outside of payroll.
Why dividends are a bad thing?
Taxes. The final problem with dividend investing is that it comes with hefty tax consequences. Even if you're holding your dividend-paying investments longer than one year (to get better tax treatment), you're still paying taxes every single year. This hurts your investment returns.
What are the consequences of paying additional dividends?
An extra dividend is a way for a company to share a windfall of exceptional profits directly with its stockholders. An extra dividend will have the same effect as a regular dividend on a stock's price, which is, that on the ex-dividend date, the stock price will be reduced by the amount of the dividend declared.
What are the disadvantages of bonus shares?
Disadvantages of Bonus Shares 1) The company do not receive any cash while issuing bonus shares. As a result, the ability to raise money by following an offering is minimized. 2) When a company keep on issuing bonus shares instead of paying dividends, the cost of the bonus issued keeps adding up over the years.
Are bonus shares beneficial?
Bonus shares help a company to enhance its value positions in the equity market. It also helps them to gain the trust of their existing shareholders, which eventually attracts more small investors to invest. Additionally, issuing bonus shares relieves them from paying cash dividends to their shareholders.
Are dividend-paying stocks risky?
One of the first things most new investors learn is that dividend stocks are a wise option. Generally thought of as a safer option than growth stocks—or other stocks that don't pay a dividend—dividend stocks occupy a few spots in even the most novice investors' portfolios.
Can you live off dividends?
Over time, the cash flow generated by those dividend payments can supplement your Social Security and pension income. Perhaps, it can even provide all the money you need to maintain your preretirement lifestyle. It is possible to live off dividends if you do a little planning.
Is paying dividend good or bad?
Dividend-paying stocks are advantageous to shareholders. This is due to the fact that investors can get a regular income from their equity investment while continuing to retain the shares in order to profit from additional share price appreciation. Dividends are money in your pocket as the stock market rises and falls.
How do I avoid paying tax on dividends?
One way to avoid paying capital gains taxes is to divert your dividends. Instead of taking your dividends out as income to yourself, you could direct them to pay into the money market portion of your investment account. Then, you could use the cash in your money market account to purchase under-performing positions.
Why do stock prices fall after dividends?
After a stock goes ex-dividend, the share price typically drops by the amount of the dividend paid to reflect the fact that new shareholders are not entitled to that payment. Dividends paid out as stock instead of cash can dilute earnings, which can also have a negative impact on share prices in the short term.
Do dividends reduce profits?
A dividend is a distribution to shareholders of retained earnings that a company has already created through its profit-making activities. Thus, a dividend is not an expense, and so it does not reduce a company's profits.
What does it mean to pay dividends?
Essentially, by paying a dividend, growth companies are admitting that they no longer believe reinvesting profits in their own businesses is a worthwhile endeavor. They see no alternative but to return that money to shareholders. And once you receive a dividend payment, you face the same dilemma.
Is higher dividends bad for the economy?
But higher dividend payments could actually be a bad sign for the overall economy. New dividend payers. Most investors see dividend stocks as conservative, slow-growth stalwarts, and with good reason.
Do dividends increase household wealth?
And while dividends most likely increase household wealth, which in turn could increase domestic consumption, it still may not be a great sign for the overall economy. Be careful what you wish for. Clearly, it's better for a company to be able to pay a dividend than not.
What are the traits of dividend stocks?
Some of the best traits a dividend stock can have are the announcement of a new dividend, high dividend growth metrics over recent years, or the potential to commit more and raise the dividend (even if the current yield is low).
What is the dividend yield of Corpus Entertainment?
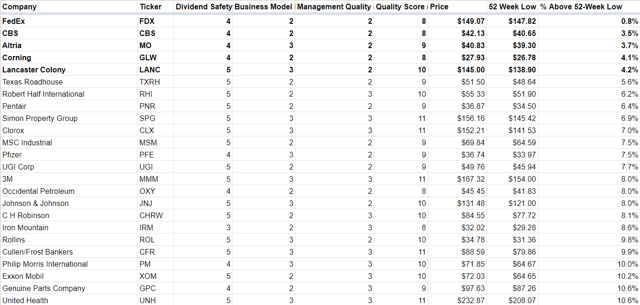
On March 17, 2018, Corpus Entertainment is the top dividend-yielding company, with a dividend yield of 26.9%. However, it has a ten-year annualized total return of -1.81% and a three-year annualized total return of -18.54%. So, while it had the "best" dividend yield, its total return was not that impressive.
What are some examples of high payout ratios?
Some sectors of the market have a standard for high payouts and its also part of the sector’s corporate structure. Real estate investment trusts (REIT) and master limited partnership (MLP) are two examples. 2 These companies have high payout ratios and high dividend yield because it is ingrained in their structure.
Is a high dividend yield good?
A high dividend yield, however, may not always be a good sign, since the company is returning so much of its profits to investors (rather than growing the company.) The dividend yield, in conjunction with total return, can be a top factor as dividends are often counted on to improve the total return of an investment.
Is dividend money reinvested?
Any money that is paid out in a dividend is not reinvested in the business. 1 If a business is paying shareholders too high a percentage of its profits, it may be a sign that management prefers not to reinvest in the company given the lack of upside.
Is it important to paint dividend stocks?
Like all investments, dividend stocks come in all shapes and colors, and it is important to not paint them with a broad brush stroke. Here are the three biggest misconceptions of dividend stocks. Understanding them should help you choose better dividend stocks.
Is low capex good for dividends?
Low capex and debt levels are also ideal. On the other hand, if a company is taking out debt to maintain its dividend, that is not a good sign. Organic growth: Earnings growth is one indicator but also keep an eye on cash flow and revenues as well.
What happens if you sell bonus shares?
Selling the bonus shares will lower your percentage stake in the company, giving you less dividends and fewer shares in terms of percentage in the stock. If this is difficult to understand, imagine every other shareholder, like you, receives the same bonus shares.
What is bonus issue?
What is a Bonus Issue? A bonus issue is an offer of free additional shares to existing shareholders. They’re basically gifts to shareholders of the company, rewarding you and me with additional shares at no cost. The bonus shares are issued and paid out of the retained profits of a company.
What happens when a stock is split?
When a stock is split, there is no change in the company’s cash reserves. In contrast, when a company declares a bonus issue of shares, the bonus shares are paid for out of the accumulated profits of the company, depleting reserves.
How to reward shareholders?
To reward shareholders. Boost investor sentiment and market confidence. Increase liquidity. Adjust the stock price to a reasonable range. As an existing shareholder, you may immediately sell the bonus shares the moment they are issued. This is why companies sometimes issue bonus shares in lieu of cash dividends.
Why do stock splits only serve one purpose?
Stock splits only serves one purpose – To increase the number of shares. Ie. To adjust the share price of the company to a lower level. Many Malaysian investors still believe a company like Nestle whose share price is RM145 per share is “expensive”. Investing RM10,000 into Nestle or a low price share is the same thing.
Do bonus shares have cash flow?
This is why companies sometimes issue bonus shares in lieu of cash dividends. Or if you’re investing in the company for the long term and do not have immediate liquidity needs, you keep your increased shareholding. It is however important to note that a share bonus issue does not involve cash flow.
Does a bonus issue affect cash flow?
It is however important to note that a share bonus issue does not involve cash flow. It increases the company’s share capital but not its net assets. It does not impact you as a shareholder materially. In addition to this, a bonus issue increases the number of outstanding shares in the market.
What is dividend investing?
If you pay attention to financial pundits and money blogs, you have probably heard at least a handful of "experts" praise dividend investing. Simply put, "dividend investing" involves investing in companies that offer cash distributions. Most dividend investors roll their distributions back into their investment to accumulate even more wealth over time.
How to become a successful investor?
Remember, there are three keys to becoming a successful investor: keeping investment costs low, diversifying your investments broadly and not chasing performance. These three key factors don't really jive with dividend investing—bringing us to the next three problems. 2. Cost. On average, keeping your investment costs low is the key to scoring ...
Is dividend investing safe?
This makes your investments riskier. So, if you think dividend investing is a safe strategy, I would cau tion you.
When investing for total return, do you look at all the money you get from your investments?
When you invest for total return, you look at all the money you get from your investments. This income can come in the form of dividends paid out in cash or as an increased investment price as the value rises. Most folks opt for the dividend-investing strategy because they want the income that comes from dividends.
Is a dividend centered investment fund more expensive than a broader, more diversified fund?
A dividend-centered investment fund (a mutual fund or exchange-traded fund) is almost always more expensive than a broader, more-diversified fund. Let's use these two examples as a basis for this argument:
Is it risky to focus on dividends?
Focusing on dividends can be very risky. Let's not forget that it was the very same euphoria for dividend-paying companies that caused a stock market bubble and poor stock market performance of the 1970s. 4. Performance Chasing. Studies continue to demonstrate the value of sticking with buy-and-hold investments.
Do dividends hurt your tax return?
The final problem with dividend investing is that it comes with hefty tax consequences. Even if you're holding your dividend-paying investments longer than one year (to get better tax treatment), you're still paying taxes every single year. This hurts your investment returns.
What is the problem with dividend focused investing?
Another major issue with a dividend-focused investor is they often become so focused on the dividend, yield, or income of an investment that they fail to pay attention to the most important metric--the total return. One need only take the situation to the extreme to see the problem with this focus. Imagine two stocks. The first has a yield of 10% and the other has a yield of 0%. Which one should you invest in? While a 10% yield sounds more attractive than a 0% yield, the correct answer is "I don't know" because the yield, by itself, does not provide enough information. Broker-sold Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) are notorious for this. They promised an "8% yield" which seemed really great until the investors realized their shares were only worth $3 each instead of the $10 per share the investors originally paid. In reality, a significant chunk of the "yield" was more like a return of their principal. Total return is the return that matters.
Is a qualified dividend good for investors?
While qualified dividends are taxed at a lower tax rate than ordinary income, distributing dividends at all isn't necessarily good for investors. This is the reason that Warren Buffett's Berkshire-Hathaway has never paid a dividend. If no dividends are distributed, the investor gets to decide when to pay the taxes on their share of the company's earnings. The investor can "declare her own dividend" any time she likes, simply by selling some shares. But in a year when no income is needed, none must be taken and no taxes need be paid. Deferring those taxes has real value given the time value of money, and thanks to the step-up in basis at death (or similar tax treatment through charitable donation of appreciated shares), might even eliminate the taxes completely.