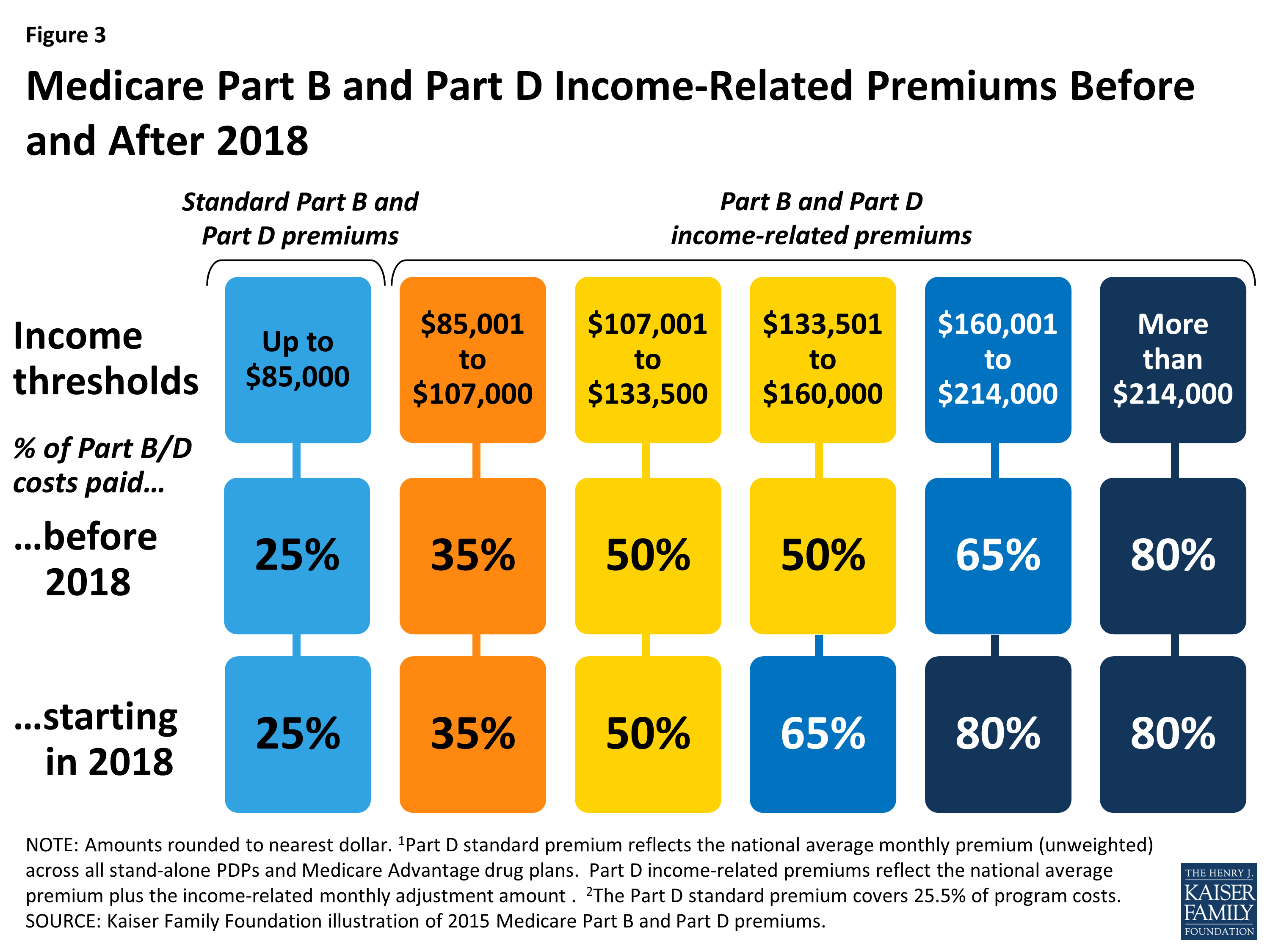
Are bonuses taxable for FICA?
All bonuses for W-2 type employees are taxable for FICA, Medicare, and withholding. FICA is 6.2% (unless the employee has maxed out for the year), Medicare is 1.45% (2.35% if the employee has made over $200,000 in taxable wages for the year), and withholding.
What are FICA taxes on stock options?
FICA taxes provide funds for Social Security and Medicare. You pay these taxes on wage income. When you receive and exercise stock options from your employer, some of their value might be treated like wages, in which case FICA taxes will apply.
How are bonuses calculated for employee taxes?
No matter how you calculate the bonus for employee taxes, you must pay the employer part of FICA taxes on bonus amounts. Form W-2, the tax report to employees and the Social Security Administration. Bonuses can be discretionary (at the discretion of the employer) or non-discretionary for certain exempt employees.
Do you have to pay taxes on signing bonuses?
For example, a bonus paid to an employee at the time of hire (sometimes called a "signing bonus") is subject to all employment taxes. The employees must pay federal and state income taxes and FICA taxes (Social Security and Medicare) on bonus pay.

Do FICA taxes apply to bonuses?
Bonuses are taxable compensation subject to income tax withholding and FICA. They're treated as supplemental wages.
Are stock grants subject to FICA?
Equity compensation, such as restricted stock, is subject to Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA) taxes. Payroll tax withholding is required at the time of vesting unless a section 83(b) election is made; in which case, withholding should be done at the time of grant.
Who pays FICA and Medicare?
An employer's federal payroll tax responsibilities include withholding from an employee's compensation and paying an employer's contribution for Social Security and Medicare taxes under the Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA).
Are bonuses exempt from Social Security tax?
Other Tax Liabilities For example, you'll likely have to pay: The 6.2% Social Security tax on all of your wages including your bonus that falls below the $142,800 Social Security cap for tax year 2021.
How is stock grant taxed?
If you're granted a restricted stock award, you have two choices: you can pay ordinary income tax on the award when it's granted and pay long-term capital gains taxes on the gain when you sell, or you can pay ordinary income tax on the whole amount when it vests.
How do I avoid paying taxes on RSU?
There are three common ways to cover the RSU tax bill:Your company “tenders” the number of shares needed to cover the withholding tax.You fund the withholding out of pocket and hold 100% of the vested shares.More items...•
Who is exempt from FICA taxes?
FICA (Social Security and Medicare) taxes do not apply to service performed by students employed by a school, college or university where the student is pursuing a course of study. Whether the organization is a school, college or university depends on the organization's primary function.
Who is exempt from paying Medicare tax?
The Code grants an exemption from Social Security and Medicare taxes to nonimmigrant scholars, teachers, researchers, and trainees (including medical interns), physicians, au pairs, summer camp workers, and other non-students temporarily present in the United States in J-1, Q-1 or Q-2 status.
Why do I pay both FICA and Medicare tax?
As you work and pay FICA taxes, you earn credits for Social Security benefits. How much is coming out of my check? An estimated 171 million workers are covered under Social Security. FICA helps fund both Social Security and Medicare programs, which provide benefits for retirees, the disabled, and children.
What bonuses are not taxed?
You may be able to reduce taxes on your bonus to zero by asking your employer to make it a non-financial bonus. Examples of non-financial bonuses could include the ability to work from home or work flexible hours. Not all non-financial bonuses are tax-free, however.
Do bonuses count towards social security?
EARNINGS -- CHRISTMAS CASH BONUS. A Christmas cash bonus from an employer to an employee is earnings and must be counted in determining whether monthly social security benefits are not payable because of excess earnings.
Are bonuses taxed twice?
The short answer: you aren't taxed any differently on your bonus income. The IRS just uses a different methodology to withhold taxes from paychecks where you only receive bonus income. If your bonus was lumped into a regular paycheck, the calculations will likely result in more federal income tax withheld, too.
What is the federal withholding rate for bonuses?
Instead of adding it to your ordinary income and taxing it at your top marginal tax rate, the IRS considers bonuses to be “supplemental wages” and levies a flat 22 percent federal withholding rate. Here’s a breakdown of how bonuses are taxed.
What is it called when you take money out of your bonus check?
These funds are sent to the IRS on your behalf. This process is known as tax withholding.
What is the federal withholding rate for supplemental wages?
The withholding rate for supplemental wages is 22 percent . If your bonus totals more than $1 million, the withholding rate for any amount above $1 million increases to 37 percent. In addition to the 22 percent federal tax, you’ll also pay Social Security tax (or FICA) and Medicare tax.
What is supplemental pay?
A supplemental wage is money paid to an employee that isn’t part of his or her regular wages, according to the IRS. In general, bonuses of any kind, including signing bonuses and severance pay, fit into the supplemental wages category. Other examples of supplemental wages include: Accumulated sick leave.
What method do you use to calculate bonus?
The aggregate method. Sometimes employers pay bonuses alongside regular wages. In this situation, your employer must use the aggregate method to calculate the initial tax withholding on your bonus.
What is the percentage method for taxes?
The percentage method, also called the flat rate method, is the easiest way for employers to calculate taxes on a bonus. It often results in more money in your pocket, at least initially. When an employer taxes your bonus using the percentage method, it must identify the bonus as separate from your regular wages.
Do you have to pay taxes on a bonus?
Even if you receive your bonus in cash, gift cards, a vacation, or some other benefit, you’ll generally have to pay taxes. The exception to this rule is if your bonus can qualify as an employee achievement award.
FICA-SS and FICA Med Taxes on Bonus Payout
No, the FICA would have been correctly withheld from your bonus even though it's been delayed for years. The nature of the payment is considered to be compensation which is subject to Social Security and Medicare taxes.
FICA-SS and FICA Med Taxes on Bonus Payout
No, the FICA would have been correctly withheld from your bonus even though it's been delayed for years. The nature of the payment is considered to be compensation which is subject to Social Security and Medicare taxes.
How much tax do you withhold on a bonus?
If you pay the employee a bonus in a separate check from their regular pay, you can calculate the federal income tax withholding in one of two different ways: You can withhold a flat 22%. You can add the bonus to the employee's regular pay and withhold as if the total were a single payment.
What is bonus pay?
How Bonuses Are Paid. A bonus is a special payment given to someone as a reward for good work or achievement. The bonus is an additional payment to an employee beyond their salary or hourly pay. It's always nice to give a bonus in a special check to make it stand out as important.
What is a non-discretionary bonus?
A non-discretionary bonus is one in which the employer sets specific criteria for the bonus and employees expect the bonus if they meet the criteria. 5 If you give an employee a performance bonus at the end end of a year one time, that's not discretionary. Holiday bonuses are considered discretionary. Another type of non-discretionary bonus is ...
What to do if you give bonuses to some employees and not others?
1 If you give bonuses to some employees and not others, make sure you have a clear rationale for this difference. For example, you may want to give performance-related bonuses tied to evaluations. In this practice, as in others pertaining to employees, you must not discriminate against certain groups. 2.
Can you use discretionary bonuses to satisfy a standard salary?
As of January 1, 2020, you can use non-discretionary bonuses to satisfy up to 10% of the standard salary level for employees, to bring them up to the minimum salary level to keep their exempt status. You may not use discretionary bonuses to satisfy any portion of the standard salary level. These bonuses are ones in which you as ...
Can you deduct a bonus for a partnership?
Bonuses are not considered deductible expenses for sole proprietorships, partnerships, and limited liability companies (LLCs) because the owners/partners/members are considered by the IRS to be self-employed. Basically, business owners can't give themselves bonuses.
Is a bonus considered supplemental pay?
Bonuses may be considered supplemental wages, which are not included in regular pay. There are rules for calculating federal income tax withholding on employee bonuses, depending on how they are paid.
What is the FICA rate for Medicare?
FICA is 6.2% (unless the employee has maxed out for the year), Medicare is 1.45% (2.35% if the employee has made over $200,000 in taxable wages for the year), and withholding. The IRS includes bonus wages in its definition of "supplemental wages" in the Pub 15 ( http://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/p15.pdf ). Their guidelines stipulate that the Federal ...
What happens if you combine bonus with regular salary?
Essentially, if you combine the bonus with the employee's regular salary (or hourly pay), the system will take the taxable wages for that check, annualize them (multiply by the number of payrolls you have in a year), and determine the employee's tax bracket accordingly. This will likely result in a higher withholding tax rate than ...
Does payroll go into a bucket?
Assuming you chose another method for determining the tax rate and the employee does file their taxes, any under- or over-withholding that occurs through payroll goes into a bucket of income earned and taxes paid, resulting in either a refund or a bill.
How much does your tax bracket affect your FICA?
Your tax bracket doesn't necessarily affect how much money you contribute to FICA. However, you'll pay an additional 0.9% of your salary toward Medicare if you earn over. $250,000 per calendar year (for joint filers). This is often called the " Additional Medicare Tax " or "Medicare Surtax.".
What does FICA go to?
FICA taxes also go to Medicare programs that fund older and certain disabled Americans' health care costs. When you're old enough, FICA funds collected from those still in the workforce will pay your benefits.
What is a tax withholding?
A tax withholding is the amount an employer takes out of an employee's wages or paycheck to pay to the government. In addition to the FICA withholdings listed above, other employer tax withholdings often include: Federal income taxes. State income taxes (in most states)
How much is the federal tax withheld from an employee's wages?
FICA mandates that three separate taxes be withheld from an employee's gross earnings: 6.2% Social Security tax, withheld from the first $137,700 an employee makes in 2020. 1.45% Medicare tax, withheld on all of an employee’s wages.
What is the Social Security tax rate for 2020?
12.4% Social Security tax: This amount is withheld from the first $137,700 an employee makes in 2020. 2.9% Medicare tax. 0.9% Medicare surtax: For single filers earning more than $200,000 per calendar year or joint filers earning more than $250,000 per calendar year.
Do self employed people pay taxes?
Self-employed workers will pay self-employment tax (SECA) based on the net income from their business, which is calculated using form Schedule SE. The Social Security Administration uses your historical Social Security earnings record to determine your benefits under the social security program.
Does the above article give tax advice?
The above article is intended to provide generalized financial information designed to educate a broad segment of the public; it does not give personalized tax, investment, legal, or other business and professional advice. Before taking any action, you should always seek the assistance of a professional who knows your particular situation for advice on taxes, your investments, the law, or any other business and professional matters that affect you and/or your business.
What is the taxable event on exercise of NQSO?
If the taxable event occurs on exercise of the NQSO, the employer is entitled to an ordinary compensation deduction equal to the amount of ordinary income recognized by the employee on the spread between the FMV of the stock on the exercise date and the option exercise price.
How long can you defer taxes on equity compensation?
83 (i), enacted as part of the TCJA, allows employees of certain privately held companies to elect to defer the payment of income taxes on certain equity compensation for up to five years. The amount of tax owed by the employee is calculated on the taxable event and compensation amount as described above, with only the remittance of the tax being delayed by the Sec. 83 (i) election. The delayed payment by the employee in turn delays the employer's tax deduction to the year in which the employee's tax is paid. Plans of qualifying employers are not automatically subject to these deferral rules.
What is restricted stock award?
Restricted stock awards. RSAs are shares of company stock that employers transfer to employees, usually at no cost, subject to a vesting schedule. When the stock vests, the fair market value (FMV) of the shares on that date is deductible by the employer and constitutes taxable W - 2 wages to the employee.
When is Sec 409A avoided?
Application of Sec. 409A is avoided when the exercise price is no less than the stock's FMV on the grant date. Because most compensatory NQSOs do not have a readily ascertainable FMV on the grant date, they are not considered "property" on the date of grant under Sec. 83 and are not eligible for an 83 (b) election.