Key Takeaways
- An issuer is a legal entity that develops, registers and sells securities to finance its operations.
- Issuers may be corporations, investment trusts, or domestic or foreign governments.
- Issuers make available securities such as equity shares, bonds, and warrants.
What is an issuer and an investor?
Issuers make available securities such as equity shares, bonds, and warrants. While the entity that creates and sells a bond or another type of security is referred to as an issuer, the individual who buys the security is an investor. In some cases, the investor is also referred to as a lender.
What is a stock issue?
Stock issues are sometime referred to as on-case arguments or simply on-case or case arguments as opposed off-case arguments . Three issues must first be present in the affirmative case and are the main ideas or values to vote on for taking any action (in policy debate or in everyday life). They ask: What are we doing now (inherency stock issue)?
What do you call a person who owns stock in a company?
When a person owns stock in a company, the individual is called a shareholder and is eligible to claim part of the company’s residual assets and earnings (should the company ever have to dissolve). A shareholder may also be referred to as a stockholder.
Is the issuer considered to be a borrower?
As a result, the issuer is also considered to be a borrower, and the investor should carefully examine the borrower's risk of default before buying the security or lending funds to the issuer.

What is name of issuer?
Name of Issuer means the legal entity of the company providing the insurance, bond or guarantee, etc. Enter “self” if the owner or operator is providing a Financial Test or is using a Fund. If using a Guarantee, use the Guarantor's name.
Who is the issuer and who is the bondholder?
The bond issuer is the borrower, while the bondholder or purchaser is the lender. At the maturity of the bond, bond issuers repay the bondholder the principal value. It is a static value.
What is an example of an issuer?
An organization that registers, distributes, and sells a security on the primary market. An issuer can be a private company or a government. For example, if a company registers a stock with the SEC, makes arrangements to underwrite it, and keeps the proceeds from its sale, it is said to be the issuer of that stock.
Who is the issuer of an option?
An option is a contract between two investors: - Issuer (or seller), holder of a short position. He sells the option. - Holder (buyer), holder of a long position.
What issuer means?
An issuer is a legal entity that develops, registers and sells securities to finance its operations. Issuers may be corporations, investment trusts, or domestic or foreign governments.
Who can issue stocks?
Stocks are issued by companies to raise capital, paid-up or share, in order to grow the business or undertake new projects. There are important distinctions between whether somebody buys shares directly from the company when it issues them (in the primary market) or from another shareholder (on the secondary market).
Which of the following would not be an issuer?
An issuer is any person who issues or proposes to issue any security for sale to the public. Stock exchange specialists, company directors, and market makers do not issue securities and therefore are not issuers.
What is an issuing entity?
Issuing entity means an entity that owns a financial asset or financial assets transferred by the sponsor and issues obligations supported by such asset or assets.
What is sale to issuer?
Sale of the Issuer means any transaction or event, including without limitation, any merger, consolidation, sale of assets, tender or exchange offer, reclassification, compulsory share exchange or liquidation in which all or substantially all of outstanding shares of the Issuer's Common Stock are sold for cash.
What are issuer services?
Issuer Services is a part of Citi Institutional Clients Group that supports the issuance and administrative needs of global institutional clients through two key business segments, namely Agency and Trust and Depositary Receipt Services.
Where do stock options come from?
Stock options are a benefit often associated with startup companies, which may issue them in order to reward early employees when and if the company goes public. They are awarded by some fast-growing companies as an incentive for employees to work towards growing the value of the company's shares.
What is issuer code?
Issuer Code is the 4th, 5th, 6th & 7th characters of ISIN. For example, For ISIN INE123A01010 of a company, the issuer code is 123A, which is the 4th, 5th, 6th & 7th characters of ISIN.
What is issue stock?
Issued stock refers to the shares that the company is able to sell.
When a company reissues treasury stock, is it obliged to offer the stock to
When the company chooses to reissue treasury stock, it is not obliged to offer the stock to existing shareholders first. The company must first offer any additional stock being issued on a date after the original date of issue to existing shareholders on a pro rata basis.
Why do companies buy back their own shares?
A company can decide to buy back its own shares in order either to withdraw the shares from circulation or reissue them. In some instances, the repurchasing of shares has the effect of supporting current shareholders by boosting the company's stock price.
Why do companies repurchase their stock?
There are sometimes other motivations behind a company's decision to repurchase stock, including to prevent a takeover. Additionally, the company may feel its shares are currently undervalued on the market.
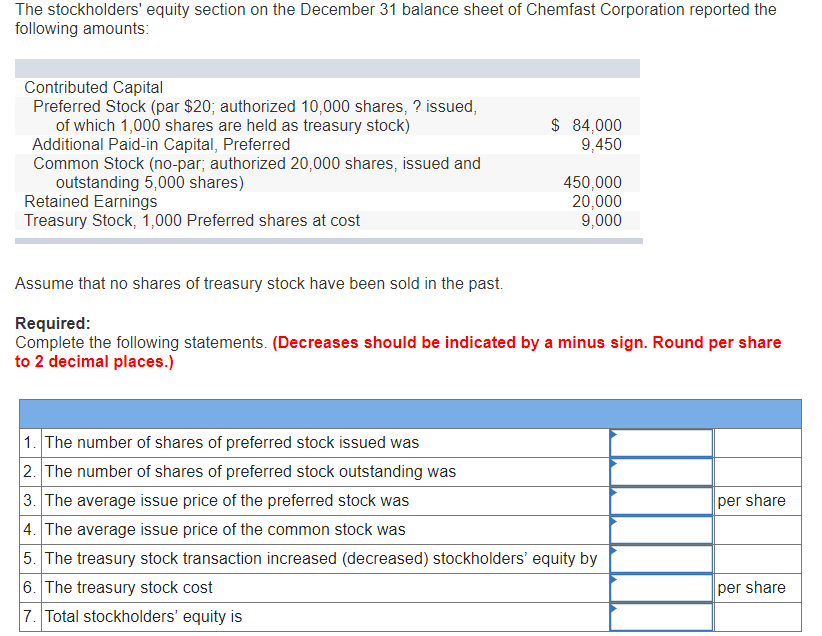
What is preferred stock?
Preferred shares: Combine features of equity and debt. Give their owners priority over common shareholders when dividends are paid. Can be converted into common stock. Whether a company issues common shares or preferred stock, it records the transaction in the stockholder's equity section of its balance sheet.
Can a company issue stock without approval?
Shares cannot be issued without the approval of the company's board. The company must then be paid something of value for the stock. When a company issues stock, it also needs to comply with securities laws at the state and federal level.
Can shareholders vote on how much capital they want to keep in reserve?
Although part of a company's authorized capital typically is not issued, shareholders can vote on how much capital they want to keep in reserve. Are seen as a riskier bet than preferred stock, but may produce better returns. Give their owners priority over common shareholders when dividends are paid.
What is an issued stock?
Issued shares refer to a company's total stock of equity shares held by investors, insiders, and held in reserve for employee compensation. Unlike outstanding shares, issued shares factor in treasury shares—stock a company buys back from shareholders. The number of shares issued must be first authorized and approved by a company's board ...
What is authorized shares?
Authorized shares are those a company’s founders or board of directors (B of D) have approved in their corporate filing paperwork. Issued shares are those that the owners have decided to sell in exchange for cash, which may be less than the number of shares actually authorized.
Why are shares of a company considered treasury shares?
When companies buy back their own shares, the shares remain listed as issued, even though they become classified as " treasury shares " because the company may resell them. For a small, closely-held corporation, the original owners may hold all of the issued shares.
Where are issued shares recorded?
The number of issued shares is recorded on a company’s balance sheet as capital stock, or owners' equity, while shares outstanding (issued shares minus any shares in the treasury) are listed on the company’s quarterly filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). The number of outstanding shares is also found in the capital section ...
How is ownership measured?
In addition, ownership may be measured by using issued and authorized stock as a forecast of the position shareholders may be in at a future date. This is called the working model calculation. All board members must use the same calculation when making decisions or plans for the business.
What is an issuer in stock market?
Issuer. An organization that registers, distributes, and sells a security on the primary market. An issuer can be a private company or a government. For example, if a company registers a stock with the SEC, makes arrangements to underwrite it, and keeps the proceeds from its sale, it is said to be the issuer of that stock.
What is an issuer in financial terms?
An issuer is a corporation, government, agency, or investment trust that sells securities, such as stocks and bonds, to investors. Issuers may sell the securities through an underwriter as part of a public offering or as a private placement. Dictionary of Financial Terms. Copyright © 2008 Lightbulb Press, Inc.
What is the purpose of issuing stock?
Issuing stock is one of the two basic ways to raise funding to grow your business. If your business is new, or is growing, capital is necessary, and issuing stock involves selling pieces of ownership in your business to investors in exchange for cash.
Why do corporations issue stock?
Corporations issue shares of stock to raise money for their business. The shares that are issued represent the amount of money invested by the shareholders in the company. Shareholders have an ownership stake in the company and enjoy certain rights such as voting rights and the receipt of dividends.
What is a stock subscription agreement?
The stock subscription agreement will outline who you are selling shares to, the amount of shares, the price per share, the date of the transaction, the amount of cash being received, and the payment method. It will also outline all the various risks and responsibilities associated with being a shareholder.
How much would a preferred shareholder receive if there were five preferred shares?
If there are five preferred shares, they would receive their $25 first, after which the common shareholders would be paid. If the profits were $25 , only the preferred shareholders would be compensated. Always consult with an accountant or lawyer to decide on the ideal mix of shares to issue.
Why do new corporations hold back their shares?
New corporations will likely hold back shares so that, if necessary, it can raise capital at a later date. When you incorporate your business, you will be required to decide how many shares your business is authorized to issue. For example, the initially authorized amount may be 100 shares.
Do you have to print shareholder certificates?
After the agreement is made , you must print out hard copy shareholder certificates to provide your shareholders. This is a legal document that specifies the shareholder's name, the amount of shares held, the value the shares were purchased at, the business name, and any special rights granted to the shareholder.
Is it good to issue stock after debt is paid off?
In addition, once the debt is paid off, you get to keep all the profits that will be made from the loaned money , whereas with issuing stock it would need to be shared with shareholders. Issuing debt is a good idea if you have good credit rating, and a profitable and stable business.
What is bondholders in finance?
Bondholders are investors who purchase bonds – they “hold” the bonds until the issuing entity repays their investment . But “hold” is a relative term in today’s electronic age. Most bond issuers do not actually issue paper bonds that an investor can literally hold, but instead they issue bonds electronically, for investors to hold virtually.
Why are bonds called conduit issuers?
Some bond issuers are called “conduit issuers” because they issue bonds that benefit a third-party. For example, a city (the conduit issuer) may issue bonds for a hospital (the conduit borrower). There’s a measure of risk for investors with conduit financing because if the bond defaults, the conduit issuer is typically off the hook to guarantee ...
Is a bond more risky than a stock?
Some bonds are federally tax-exempt, and they may also be exempt from state taxes. Bonds are generally “safer” investments than stocks because bonds don’t typically experience the daily highs and lows that stocks do (an exception is “junk bonds,” which are riskier than other bond types).
Who are the big players in bond lending?
But in bond transactions, “big” players (including companies, corporations and even governments ) become the recipients of the loan and the “little guys” are the lenders.
Can bond issuers default on payments?
Bond issuers potentially can default on payments if they experience financial difficulties. Investors can check an issuer’s credit rating before purchasing bonds, although a current good credit rating is not a guarantee of continued financial health. Call risk.
What is a stockholder?
What is a Stock? When a person owns stock in a company, the individual is called a shareholder and is eligible to claim part of the company’s residual assets and earnings (should the company ever have to dissolve). A shareholder may also be referred to as a stockholder. The terms “stock”, “shares”, and “equity” are used interchangeably in modern ...
What is a shareholder in finance?
A shareholder may also be referred to as a stockholder. The terms “stock”, “shares”, and “equity” are used interchangeably in modern financial language. The stock market. Stock Market The stock market refers to public markets that exist for issuing, buying and selling stocks that trade on a stock exchange or over-the-counter.
How many years of dividends can a stockholder receive?
The company can decide the amount of dividends to be paid in one period (such as one quarter or one year), or it can decide to retain all of the earnings to expand the business further.
What are the benefits of owning a stock?
There are many potential benefits to owning stocks or shares in a company, including the following: #1 Claim on assets. A shareholder has a claim on assets of a company it has stock in. However, the claims on assets are relevant only when the company faces liquidation. In that event, all of the company’s assets ...
What is stock investing?
Stocks, also known as equities, represent fractional ownership in a company. Investing for beginners. Investing: A Beginner's Guide CFI's Investing for Beginners guide will teach you the basics of investing and how to get started.
What is a finance career?
Most finance career paths will be directly involved with stocks in one way or another, either as an advisor. Banking (Sell-Side) Careers The banks, also known as Dealers or collectively as the Sell-Side, offer a wide range of roles like investment banking, equity research, sales & trading. , an issuer,
What are the factors that affect the price of a stock?
There are many factors that affect share prices. These may include the global economy, sector performance, government policies, natural disasters, and other factors. Investor sentiment – how investors feel about the company’s future prospects – often plays a large part in dictating the price.
What Does Common Stock Mean?
Before diving into some of the reasons, let’s review exactly what does common stock mean? Common stock is often referred to as capital stock.
What Is the Purpose of Issuing Stock?
Understanding what is the purpose of stock issuing comes down to numerous variables. There is not a single reason why a company may issue stocks, but here are some of the most common:
Advantages of Issuing Common Stock
The above covered what is the purpose of stock issuing, but what are the benefits of a company issuing stock?
Disadvantages of Issuing Common Stock
Without question, issuing common stock comes with numerous disadvantages. These disadvantages include:
How to Issue Stock
Issuing stock is not easy. There is an entire legal process a company must go through, in addition to meeting various SEC requirements if the company is issuing stock on the public market.
In What Positions Would a Company Issue Common Stock?
As companies evolve, their position on needing to issue common stock changes. Some of the most common real world positions are as follows.
Common Stock vs Preferred Stock
The main difference between common stock and preferred stock is the fact that preferred stockholders receive their dividend payments as a priority. If the company only has enough money to pay dividends to preferred shareholders, they will.
What is the term for the argument that a resolution affirmative is supported by a stock issue?
Stock issues are sometime referred to as on-case arguments or simply on-case or case arguments as opposed off-case ...
What is not inherent in a case?
A case is "not inherent" when the status quo is already implementing the plan or solving the harms. Clearly, a solution that is new or different from the status quo is not warranted in such a case. Three common types of inherency are:
Is topicality a stock issue?
In practice, most debate strategies and debate club practice regions do not consider Topicality to be a "stock issue" per se; instead, it is a high-level debate brought up by the Negative that does not excuse the Affirmative plan or case approach from defects that are not found prima facie in the resolution.