
Which companies offer preferred stock?
None of the heavyweights – Apple Inc. ( AAPL ), Exxon Mobil Corp. ( XOM ), Microsoft Corp. ( MSFT ), etc., offer preferred stock.
What are pre-preferred stocks?
Preferred stocks are equity securities that share many characteristics with debt instruments. Preferred stock is attractive as it offers higher fixed-income payments than bonds with a lower investment per share. Preferred stock often has a callable feature which allows the issuing corporation to forcibly cancel the outstanding shares for cash.
Do preferred stockholders get preferential treatment when electing board members?
Just from the name, you’d figure preferred stockholders would receive, well, preferential treatment. But when a company elects board members, it’s the common stockholders who do the electing while the preferred stockholders sit on the sidelines, disenfranchised. (For more, see: Know Your Rights as a Shareholder .)
What is a perpetual preferred stock?
A perpetual preferred stock is a type of preferred stock that pays a fixed dividend to the investor for as long as the company is in business. Short for "par value," par can refer to bonds, preferred stock, common stock or currencies, with different meanings depending on the context.
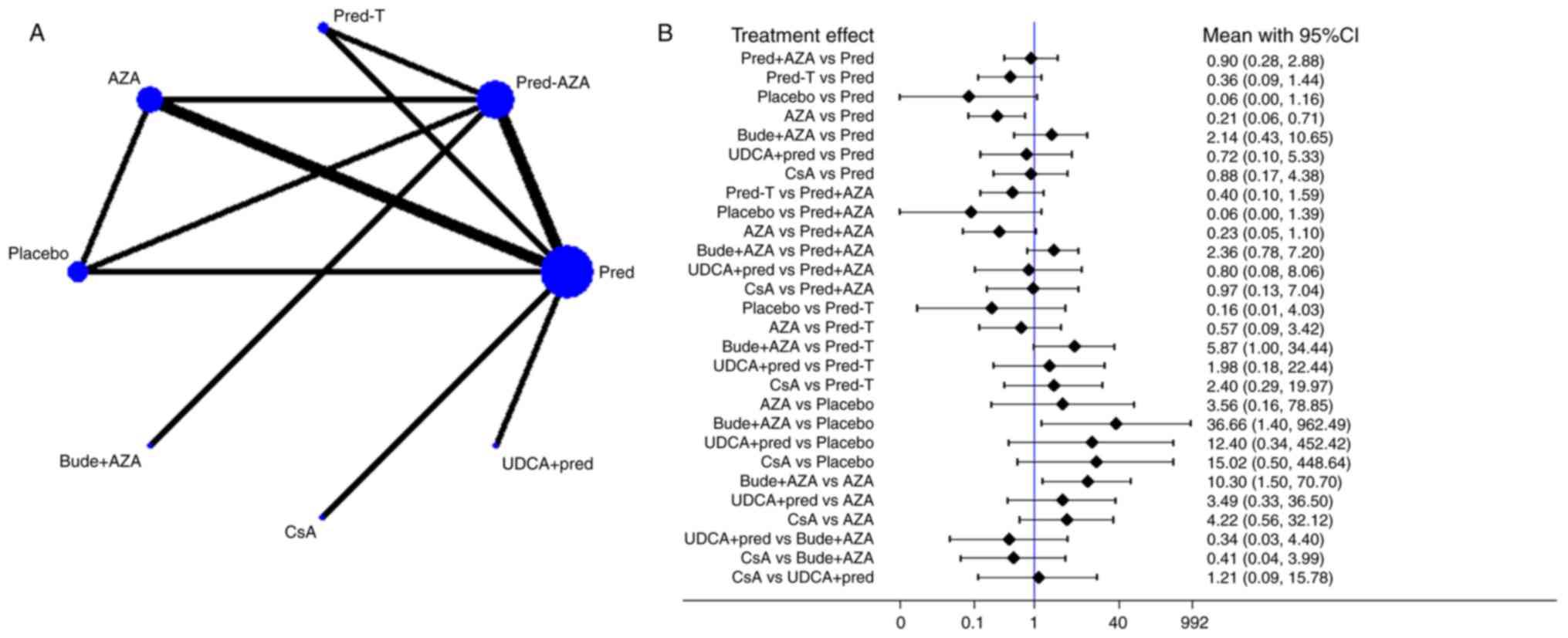
Who gets preferred stock?
Preferred shareholders have priority over a company's income, meaning they are paid dividends before common shareholders. Common stockholders are last in line when it comes to company assets, which means they will be paid out after creditors, bondholders, and preferred shareholders.
Which share has preferential rights?
Preference shares also commonly known as preferred stock, is a special type of share where dividends are paid to shareholders prior to the issuance of common stock dividends. Ergo, preference share holders hold preferential rights over common shareholders when it comes to sharing profits.
What are the example of preferred stock?
What Is an Example of a Preferred Stock? Consider a company is issuing a 7% preferred stock at a $1,000 par value. In turn, the investor would receive a $70 annual dividend, or $17.50 quarterly. Typically, this preferred stock will trade around its par value, behaving more similarly to a bond.
How is preferred stock treated?
Preferred Stock vs Bonds Unlike bonds, preferred stock is not debt that must be repaid. Income from preferred stock gets preferential tax treatment, since qualified dividends may be taxed at a lower rate than bond interest. Preferred stock dividends are not guaranteed, unlike most bond interest payments.
What are the four types of preference shares?
The four main types of preference shares are callable shares, convertible shares, cumulative shares, and participatory shares.
Why do companies issue preference shares?
Preferred shares are an asset class somewhere between common stocks and bonds, so they can offer companies and their investors the best of both worlds. Companies can get more funding with preferred shares because some investors want more consistent dividends and stronger bankruptcy protections than common shares offer.
How many preferred stocks are there?
two typesIn the United States there are two types of preferred stocks: straight preferreds and convertible preferreds. Straight preferreds are issued in perpetuity (although some are subject to call by the issuer, under certain conditions) and pay a stipulated dividend rate to the holder.
What is a most preferred stock?
Most preferred stock is cumulative, meaning if the company withholds part or all of the expected dividends, they are considered dividends in arrears and must be paid before any other dividends. Preferred stock that doesn't carry the cumulative feature is called straight, or noncumulative preferred.
What is the example of preferred?
Preferred sentence example. The house was quiet, the way he preferred it. He preferred the direct approach over any form of subtlety. In the case of a lawsuit the plaintiff preferred his own plea.
What is Series S preferred stock?
Series S Preferred Stock means the shares of the Company's Series S Contingent Convertible Perpetual Non-Cumulative Preferred Stock, no par value and liquidation preference $100,000 per share.
How preferred are volatile stocks?
Furthermore, like common stock, preferred shares are generally more volatile than bonds in terms of how much their prices fluctuate. However, because of their fixed dividends and higher position in the capital stack, preferred shares generally aren't as volatile as common shares.
What is Series C preferred stock?
Similar to previous stages of financing, the series C round primarily relies on raising capital through the sale of preferred shares. The shares are likely to be convertible shares. They offer holders the right to exchange them for common stock in the company at some date in the future.
What is preferred stock?
Preferred stock that earns no more than its stated dividend is the norm and it is known as nonparticipating preferred stock. Occasionally a corporation issues participating preferred stock. Participating preferred stock allows for dividends greater than the stated dividend.
How much does a 9% preferred stock sell for?
In other words, a 9% preferred stock with a par value of $50 being issued or traded in a market demanding 9% would sell for $50. On the other hand, if the market demands 8.9% and the stock is a 9% preferred stock with a par value of $50, then the stock will sell for slightly more than $50 as investors see an advantage in these shares.
What is the par value of preferred stock?
Par Value of Preferred Stock. The dividend on preferred stock is usually stated as a percentage of its par value. Hence, the par value of preferred stock has some economic significance. For example, if a corporation issues 9% preferred stock with a par value of $100, the preferred stockholder will receive a dividend of $9 (9% times $100) ...
Why is par value important?
In each of these examples the par value is meaningful because it is a factor in determining the dividend amounts. If the dividend percentage on the preferred stock is close to the rate demanded by the financial markets, the preferred stock will sell at a price that is close to its par value.
How much dividend do preferred shareholders get?
The holders of these preferred shares must receive the $9 per share dividend each year before the common stockholders can receive a penny in dividends. But the preferred shareholders will get no more than the $9 dividend, even if the corporation's net income increases a hundredfold.
What happens if a corporation has 10% preferred stock?
If a corporation has 10% preferred stock outstanding and market rates decline to 8%, it makes sense that the corporation would like to eliminate the 10% preferred stock and replace it with 8% preferred stock . On the other hand, the holders of the 10% preferred stock bought it with the assumption of getting the 10% indefinitely.
What is the purpose of a preferred stock indenture?
Corporations are able to offer a variety of features in their preferred stock, with the goal of making the stock more attractive to potential investors. All of the characteristics of each preferred stock issue are contained in a document called an indenture.
What is preferred stock?
Preferred stock becomes an additional asset on the balance sheet, something that banks need more than oil companies and semiconductor manufacturers do. (For more, see: Preferred Stock Features .)
What are the disadvantages of preferred stock?
Just from the name, you’d figure preferred stockholders would receive, well, preferential treatment. But when a company elects board members, it’s the common stockholders who do the electing while the preferred stockholders sit on the sidelines, disenfranchised. (For more, see: Know Your Rights as a Shareholder .)
Do preferred shareholders receive dividends?
Preferred shareholders indeed receive dividend payments: the dividends are a selling feature, intrinsic to the security. Whereas with common stock, corporations are under no obligation to offer dividends.
Who gets paid first when a company liquidates?
When the company liquidates, the bondholders get paid first. Which makes sense; they’re the creditors, the ones who lent their money to the company to help it stay afloat. Should there be anything left once the bondholders get made whole, the preferred shareholders get paid next.
Do blue chip companies have preferred stock?
In practice, the blue-chip companies that offer dividends on their common stock don’t issue preferred stock, at all. Seldom do the companies that don’t offer dividends on their common stock, either. Preferred stock is a dying class of share. According to some estimates, there’s $80 of common stock circulating in the United States for every dollar of preferred stock. None of the heavyweights – Apple Inc. ( AAPL ), Exxon Mobil Corp. ( XOM ), Microsoft Corp. ( MSFT ), etc., offer preferred stock. Among the 30 largest corporations in America by market capitalization, the only ones that do offer preferred stocks are the Big Four banks – Wells Fargo & Co. ( WFC ), Bank of America Corp. ( BAC ), Citigroup Inc. ( C) and JPMorgan Chase & Co. ( JPM ). In fact, about 88% of preferred stock is issued by banks. As to why, it’s the continuation of the aftermath of the financial crisis and corresponding bailouts of 2008-09. Preferred stock becomes an additional asset on the balance sheet, something that banks need more than oil companies and semiconductor manufacturers do. (For more, see: Preferred Stock Features .)
What is preferred stock?
Preferred stock is a special type of stock that pays a set schedule of dividends and does not come with voting rights. Read more, Preferred stock is a special type of stock that pays a set schedule of dividends and does not come with voting rights. Preferred stock combines aspects of both common stock and bonds in one security, ...
Why are preferred stocks more stable than common stocks?
With preferred stock, your gains are more limited. That’s because like bond prices, preferred stock prices change slowly and are tied to market interest rates. Preferred stocks do provide more stability and less risk than common stocks, though.
What is preferred stock par value?
Like bonds, shares of preferred stock are issued with a set face value, referred to as par value. Par value is used to calculate dividend payments and is unrelated to preferred stock’s trading share price. Unlike bonds, preferred stock is not debt that must be repaid. Income from preferred stock gets preferential tax treatment, ...
How many shares of common stock do you get if you trade in preferred stock?
If you decided to trade in a share of preferred stock, you’d get 5.5 shares of common stock. Just because you can convert a preferred stock into common stock doesn’t mean it’ll be profitable, though. Before converting your preferred stock, you need to check the conversion price.
What happens if a preferred stock has a low premium?
If preferred stock has a low premium (or no premium), its value may rise like its related common stock. If it has a high conversion premium, meaning it is not profitable to convert its shares, it may trade with pricing consistency similar to a bond.
Can you trade preferred stock on the secondary market?
Preferred stocks can be traded on the secondary market just like common stock. However, just because it can be sold doesn’t mean you’ll receive the same amount you paid for it. While preferred stock prices are more stable than common stock prices, they don’t always match par values.
Is common stock dividend lowered?
Common stock dividends are reduced or eliminated before preferred stock dividends, although even preferred stock dividends may be lowered or eliminated in certain cases. Preferred stock’s priority ahead of common stock also extends to bankruptcy.
What is preferred stock?
Preferred stocks are equity securities that share many characteristics with debt instruments. Preferred stock is attractive as it offers higher fixed-income payments than bonds with a lower investment per share. Preferred stock often has a callable feature which allows the issuing corporation to forcibly cancel the outstanding shares for cash.
What is a participating preferred stock?
Participating. This is preferred stock that has a fixed dividend rate. If the company issues participating preferreds, those stocks gain the potential to earn more than their stated rate. The exact formula for participation will be found in the prospectus. Most preferreds are non-participating.
Why do companies issue preferred stock?
A company may choose to issue preferreds for a couple of reasons: 1 Flexibility of payments. Preferred dividends may be suspended in case of corporate cash problems. 2 Easier to market. Preferred stock is typically bought and held by institutional investors, which may make it easier to market during an initial public offering.
How much can you deduct from preferred stock?
Corporations that receive dividends on preferred stock can deduct 50% to 65% of the income from their corporate taxes. 1 .
Why are preferred stocks considered hybrid securities?
Because of their characteristics, they straddle the line between stocks and bonds. Technically, they are securities, but they share many characteristics with debt instruments . Preferred stocks are sometimes called hybrid securities.
Why are preferred dividends suspended?
Preferred dividends may be suspended in case of corporate cash problems. Easier to market. Preferred stock is typically bought and held by institutional investors, which may make it easier to market during an initial public offering.
What happens to preferred shares when interest rates rise?
If interest rates rise, the value of the preferred shares falls. If rates decline, the opposite would hold true.
What is a fully convertible preference share?
A fully and mandatorily convertible preference share is considered an equity instrument under FEMA. Therefore a fully and mandatorily convertible preference share will be taken into consideration for calculating the total Foreign Direct Investment in a company for the purposes of the sectoral caps.
What is preference share?
In other words, preference shares are the shares that carry or would carry a preferential right with respect to: Repayment of the amount of paid-up capital share capital paid up or deemed to have been paid up, in the scenario of winding up of the company or repayment of capital. Preference shares generally pay a higher rate ...
Do preference shares pay dividends?
Preference shares generally pay a higher rate of dividend however at a fixed rate or a fixed amount as a dividend. The preference shareholders are also privileged and entitled to receive all dividends i.e. current as well as an accrued dividends at priority before equity shareholders.
Do you have to make an open offer for convertible preference shares?
In case of acquisition of convertible preference shares, although the acquirer is not required to comply with the requirements of the Takeover Code at the time of acquisition the acquirer will have to make an open offer if the limits envisaged under the Takeover Code are breached upon conversion.
Can you redeem preference shares?
Only Fully paid-up preference shares can only be redeemed. Preference shares can be redeemed only out of the profits available for distribution to its shareholders or out of fresh proceeds of shares issued solely for the purpose of funding the redemption of the preference shares.
Preferred Stock
Investors who are looking for dividends find preferred stock attractive, as it gives owners a set rate of return instead of returns that increase and decrease with the stock market. This means it acts more like a bond with a fixed payout.
Par Value of Preferred Stock
A preferred stock dividend is often stated as a percentage of the par value. That means the par value holds slight economic significance. If a corporation gives out 9 percent preferred stock that has a par value of $100, the stockholder will get a dividend of $9 per share every year, which is 9 percent multiplied by $100.
Preferred Stock Features
Corporations have varying features they can offer in their preferred stock, and the goal is to make their stock look attractive to possible investors. The following are characteristics of preferred stock issue:
