The tax code typically allows a deduction for the full amount of a dividend received from a company owned 80 percent or more. A corporate shareholder owning between 20 percent and 79 percent of a company may deduct 80 percent of a dividend received.
Does a company pay tax if it receives a dividend?
Additionally, in contrast to S corps that lets shareholders report profit and losses on their personal tax returns, shareholders receive dividends (i.e. a share of company profits). Shareholders must pay personal ... or an S corp does.
Are dividends considered a company expense?
The dividend is that part of profits of the company which is distributed to the shareholders of the company and is not considered to be an expense as it is the portion of company’s profit which is returned to the shareholders of the company as a return on their investment done in the company and is deducted from the retained earnings of the company.
Do companies pay taxes on dividends in US?
Most publicly traded Canadian companies pay dividends that are eligible for the dividend tax credit. U.S. dividends, on the other hand, do not qualify for the DTC and are therefore taxed at the same rate as interest or other income. This article was published more than 6 years ago.
Are Dividends subject to withholding tax?
Dividend distributions to non-PRC tax resident enterprises are subject to 10% withholding tax, unless reduced under the terms of a relevant income tax treaty. Enterprise income tax is imposed on gains realised from the disposal of shares.
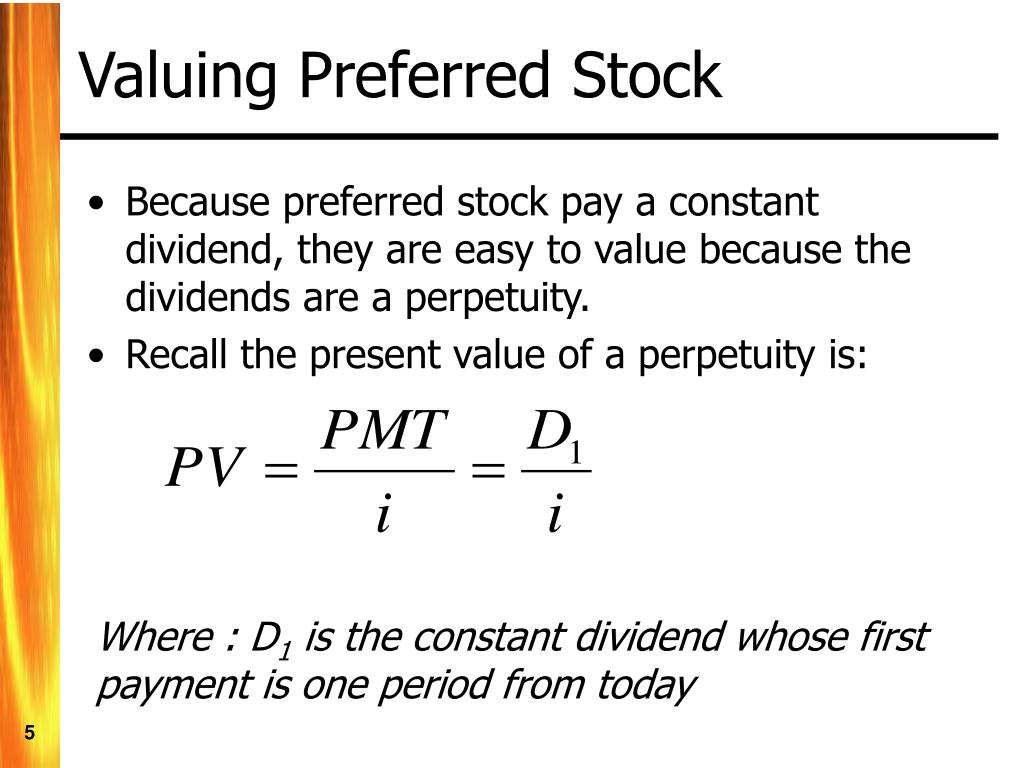
Are common stock dividends tax-deductible for corporations?
If dividends are paid out, it is always using after-tax dollars—and thus does not offer a current tax deduction. Preferred shares are considered to be like debt in that they pay a fixed rate like a bond (a debt investment).
What dividends qualify for dividends received deduction?
Dividend income A US corporation generally may deduct 50% of dividends received from other US corporations in determining taxable income. The dividends received deduction (DRD) is increased from 50% to 65% if the recipient of the dividend distribution owns at least 20% but less than 80% of the distributing corporation.
Which dividends are exempt from tax?
As a shareholder or investor, you have to pay tax on dividends only when your income by way of the dividend exceeds ₹ 1 Lakh. So, if your dividend income is less than ₹ 10 Lakh in a financial year, then you won't have to pay tax on dividend.
Are interest and preferred stock dividends tax-deductible?
Preferred stock dividends are not tax deductible to the company who issues them. Preferred stock dividends are paid out of after-tax cash flows so there is no tax adjustment for the issuing company. When investors buy preferred stock they expect to earn a certain return.
Can a corporation receive qualified dividends?
Dividends are the most common type of distribution from a corporation. They're paid out of the earnings and profits of the corporation. Dividends can be classified either as ordinary or qualified.
What are qualified and nonqualified dividends?
There are two types of ordinary dividends: qualified and nonqualified. The most significant difference between the two is that nonqualified dividends are taxed at ordinary income rates, while qualified dividends receive more favorable tax treatment by being taxed at capital gains rates.
How do I avoid tax on stock dividends?
One way to avoid paying capital gains taxes is to divert your dividends. Instead of taking your dividends out as income to yourself, you could direct them to pay into the money market portion of your investment account. Then, you could use the cash in your money market account to purchase under-performing positions.
Are all dividends taxable?
All dividends are taxable and all dividend income must be reported. This includes dividends reinvested to purchase stock. If you received dividends totaling $10 or more from any entity, then you should receive a Form 1099-DIV stating the amount you received.
Is dividend from equity shares taxable?
Thus, if shares are held for trading purposes then the dividend income shall be taxable under the head income from business or profession. Whereas, if shares are held as an investment then income arising in the nature of dividend shall be taxable under the head of income from other sources.
Why are dividends not tax-deductible?
Corporate Income Taxes Profit is simply the company's revenue minus its expenses. Dividends, however, are not a business expense, meaning you can't deduct them on your corporate income tax return.
Are preferred stock dividends qualified dividends?
Most preferred stock dividends are treated as qualified dividends, meaning they are taxed at the more favorable rate of long-term capital gains. Some preferred stock dividends are not qualified, however.
Are preference shares dividends taxable?
(2) Where the stipulated dividend in respect of preference share of a company issued and subscribed for after the 31st March, 1959, and before the 1st of April, 1960, is free of income-tax, and the company, besides paying the stipulated dividend to the holder of such share, pays to Government on his behalf any sum on ...
How much of a dividend can be deducted from a company?
The tax code typically allows a deduction for the full amount of a dividend received from a company owned 80 percent or more. A corporate shareholder owning between 20 percent and 79 percent of a company may deduct 80 percent of a dividend received.
What is dividend tax?
The United States' federal income tax system characterizes dividends as something distinct from other types of payments or receipts. Special rules within the Internal Revenue Code govern the tax implications for corporations distributing dividend payments, as well as shareholders receiving dividend income.
How long do you have to hold stock to qualify for dividends?
In order for dividends to qualify for the reduced tax rate, the underlying corporate stock generally must be held for more than 60 days. Advertisement.
Do dividends count as income?
Shareholders receiving dividends take them into account as a form of taxable income. As a general rule, the Internal Revenue Service taxes citizens on all income from whatever source derived. Some notable exceptions to the rule exist, however. Namely, individual shareholders receiving qualifying dividends treat the income similar to a capital gain. A lower rate of tax (usually 15 percent for most taxpayers) applies to capital gains. In order for dividends to qualify for the reduced tax rate, the underlying corporate stock generally must be held for more than 60 days.
Do corporations pay dividends?
Corporations provide a return to their investors by paying dividend distributions. These payment amounts represent earnings that have accumulated in prior periods. Accumulated earnings reside in the equity section of a company's balance sheet. A reduction to equity by virtue of a dividend distribution does not generally constitute a taxable event for federal income tax purposes. Taking another perspective on the matter, note that a corporation figures its accumulated earnings every year on a net basis. This means that all deductible expenses have already been applied against gross income in determining net earnings. Therefore, when a corporation pays a dividend, it does not get another tax deduction because it has previously deducted all allowable expenses in calculating the underlying earnings amount.
Can dividends be offset from corporate income tax?
However, dividends received from controlled foreign corporations may qualify for a foreign tax credit offset to corporate income tax liability. The amount of the credit is proportional to the amount of foreign taxes actually paid by the controlled foreign corporation on the underlying earnings.
Can you take a dividend from a controlled foreign corporation?
Controlled Foreign Corporations. Note that corporate shareholders may not take a dividend received deduction for any dividend received from a controlled foreign corporation. The law deems control to exist with a greater than 50 percent ownership stake in the foreign corporation.
What is a 1099 dividend?
Dividend payments received on an account are tallied and a Form 1099-DIV is mailed by the brokerage firm to report the total for each tax year. 5 These payments are subject to tax whether cash is received or dividends are reinvested to purchase more shares. Form 1099-DIV shows a breakdown for qualified dividends and ordinary dividends. 6 Qualified dividends are those paid by U.S. companies or by foreign companies whose countries of domicile have special tax treaties with the United States. If the dividends are from a foreign company without such a treaty, the payments are called ordinary dividends, which are taxed as ordinary income. 7 8 For example, if a shareholder of ABC, a U.S. company, receives $250 in dividends for the year, these are classified as qualified dividends, so the tax owed (for most taxpayers) is 15 percent, or $37.50.
How are stock splits different from dividends?
Stock splits are quite different from dividends, as they are not distributions of business profits. When trying to understand stock splits or reverse splits, realize they are merely a restructuring of shares outstanding and price per share; no tax is incurred. For example, an investor owns 100 shares of ABC at $80 per share for a total cost of $8,000. If the company issues a 2-for-1 split, the investor then owns 200 shares at $40 per share but his total cost remains the same, so no gain or loss is incurred. The stock split affects only the cost basis per share. If no further investments are made into ABC, figuring the cost basis when the shares are sold is not difficult. Figuring cost basis can be tricky when additional purchases are made after a stock split. 4
How long do you have to hold a stock to receive qualified dividends?
Investors must also hold shares for more than 60 days during the 120-day holding period.
Is dividend income taxable?
In summary, dividends and other income to a nonretirement account are taxable, while the effects of a stock split are not calculated for tax purposes until the stock is sold. Once sold, the investor adjusts the cost basis to account for the shares that experienced the split. 4 It is important for investors to work with their financial advisors and tax professionals to determine how dividends and stock splits affect their tax situations. For example, since 2013, qualified dividends have taxed at a rate of 20 percent for higher earners. 9
Does Investopedia include all offers?
This compensation may impact how and where listings appear. Investopedia does not include all offers available in the marketplace.
Is a stock split taxable?
Stock splits are generally not taxable, as the cost basis per share is updated to reflect the new stock structure and price so that the total market value is the same. Since you did not make any gains on the stock split, no taxes are owed.
Is stock dividend taxed in 2021?
Updated Mar 28, 2021. If shares are held in a retirement account, stock dividends and stock splits are not taxed as they are earned. 1 Generally, in a nonretirement brokerage account, any income is taxable in the year it is received.
What is the FMV of a dividend?
When property (rather than cash) is distributed, the amount of the dividend equals the fair market value (FMV) of the property on the date of the distribution, reduced by any liabilities assumed by the recipient or to which the property is subject (Sec. 301 (b)). In addition, as is the case with cash dividends, the distribution must be from current or accumulated E&P to be classified as a dividend. The recipient shareholder's basis in appreciated property received in a distribution equals the property's FMV (Sec. 301 (d)). The shareholder's holding period begins on the date of distribution.
What happens if the new stock is identical to the old stock?
If the new stock is identical to the old stock, the basis of the old stock is reallocated to both the old and new stock (Regs. Sec. 1.307-1). If the new stock is not identical to the old stock (e.g., preferred stock distributed for shares of common stock), the basis of the old stock is allocated between the old and new stock based on their respective share of the total FMV of both types of stock. In either case, the new stock takes the same holding period as the old stock (Sec. 1223 (4)).
What is the FMV of a stock?
If a shareholder receives a taxable stock dividend, the amount of the dividend is the FMV of the stock (Regs. Sec. 1.305-1 (b)). This FMV becomes the basis of the new stock to the shareholder.
What is the difference between federal and state corporate law?
Federal income tax law governs how corporate payments to or for the benefit of shareholders are taxed for federal income tax purposes. However, state corporation statutes govern the property rights of a corporation's shareholders and creditors.
Is cash distribution taxable?
A cash distribution to a shareholder is a taxable dividend to the extent of the corporation's current or accumulated E&P. If the current E&P equals or exceeds the amount of the distribution, it is a fully taxable dividend to the shareholder even if the corporation has negative accumulated E&P (Regs. Sec. 1.316-1 (a)).
Is a dividend taxable?
Shareholders recognize a taxable dividend to the extent a distribution is paid out of corporate earnings and profits (E&P). If the distribution exceeds E&P, the excess reduces the shareholder's stock basis. Any amount in excess of the shareholder's stock basis is capital gain (Secs. 301 (b) (1) and (c)). The amount of the distribution is decreased (but not below zero) by liabilities assumed by the shareholder (e.g., a mortgage on a distributed piece of real estate).
Is a C corporation a dividend?
Distributions by C corporations are treated as dividends to the extent of the corporation's current or accumulated earnings and profits (AE&P). However, a special rule provides relief to the shareholders of a corporation that has terminated its S corporation status.
How are dividends taxed?
How dividends are taxed depends on how they have been held by the recipient. There are two types of dividends - ordinary dividends and qualified dividends. Qualified dividends are eligible for a lower tax rate than other ordinary income. 2 . Ordinary dividends are taxable as ordinary income. That means they are added to your other tax return ...
What is ordinary dividend tax?
Ordinary (non-qualified) dividends are taxed at your normal tax rate, along with your other income.
What form do you report dividends on?
The dividends must have been held a minimum amount of time. 4 . Dividends are reported to individuals and the IRS on Form 1099-DIV. This information is included on the individual's Form 1040. Qualified dividends are taxed at a lower rate than ordinary income, at the capital gains tax rate. Ordinary (non-qualified) dividends are taxed ...
What is a 1099 dividend?
Companies paying dividends must provide shareholders receiving those dividends a report showing the amount of the dividends paid to that shareholder for the year. The report is made, on payments over $10 for the year, to recipients on Form 1099-DIV .
What is dividends in stock?
Dividends are a portion of a company's profits paid to shareholders. Public companies (that sell stock to the public) pay dividends on a schedule, but they can pay these dividends at any time. A company can also pay a special or extra dividend in addition to regular dividends. 1 .
How long do you have to hold a dividend to pay capital gains tax?
The capital gains tax rate you pay depends on how long you kept the dividend and on your income level. if you hold an asset like a dividend for more than one year before you dispose of it, your capital gain or loss is long term. 5
Where to enter qualified dividends on 1099?
Qualified Dividends. Enter the total of all qualified dividends from all 1099-DIV forms on line 3b of your Form 1040. 8
What percentage of dividends can be deducted from a C corporation?
C-corporations with 20% or more ownership, but less than 80% ownership stake can deduct 80% of dividend income received — report 20% of received dividends as taxable income. C-corporations with 80% or more ownership can deduct the full amount of dividend received and have no income tax liability on that portion of their income. ...
Why is the dividend received deduction exempt from tax?
Therefore, the current tax code has the dividends received deduction exemption, to alleviate taxing the same income multiple times. This multiple taxation can occur when a corporate entity distributes dividends to its parent company or another C-corporation that has an ownership stake.
Why do you need to file a received dividend deduction?
The main purpose of the received dividends deduction is to prevent potential triple taxation of certain dividend distributions.
What is the most common type of dividend income distribution?
The most frequent type of dividend income distributions are cash payouts. Cash dividends are easy to distribute for the equity making the payouts and easy to manage for the investors receiving the income.
What is dividend payout?
Dividends are just distributions of a company’s assets or earnings to shareholders. Depending on the source of the payout — earnings, assets, interest, etc. — a dividend might technically be called a “distribution.”
Where is the dividend tax liability on a 1099?
Generally, the total amount of ordinary dividends will be listed in the 1a box at the top of the form. Alternatively, the amount of qualified dividend taxable at capital gains rates will appear in box 1b of the same form.
When is dividend income taxed?
The first level of taxation occurs when the company distributing the dividend pays taxes on its earnings before distributing dividends. Subsequently, the company receiving the dividend income is responsible for paying taxes on that income. Lastly, a portion of the original dividend income is subject to taxation for the third time when the shareholders of the second company receive dividend distributions, which become taxable income for the individual shareholders.
