
Taxation at Grant (1) §83 will apply to the grant of a nonstatutory stock option only if the option has a readily ascertainable fair market value at the time of its grant. Nonstatutory stock options must meet four conditions to have a readily ascertainable fair market value. The option is transferable by the optionee.
Are nonstatutory stock options taxable?
*. Nonstatutory stock options are never taxable upon grant. If the value of the stock option was readily determinable at the time of grant. If the stock option was fully vested at the time of the grant.
What are the tax consequences of nonqualified stock options?
Tax Consequences of Nonqualified (Nonstatutory) Stock Options. Internal Revenue Code Section 83 governs nonstatutory stock options. Nonstatutory stock options trigger ordinary income to you at some point in time and produce a compensation deduction to the employer. §83 contains two rules affecting all nonstatutory stock option transactions.
When are stock options not actively traded on an established market?
In the following circumstances, all stock options are considered not actively traded on an established market. Taxation at Grant (1) §83 will apply to the grant of a nonstatutory stock option only if the option has a readily ascertainable fair market value at the time of its grant.
Is statutory stock option included in gross income?
Statutory Stock Options. If your employer grants you a statutory stock option, you generally don't include any amount in your gross income when you receive or exercise the option. However, you may be subject to alternative minimum tax in the year you exercise an ISO.
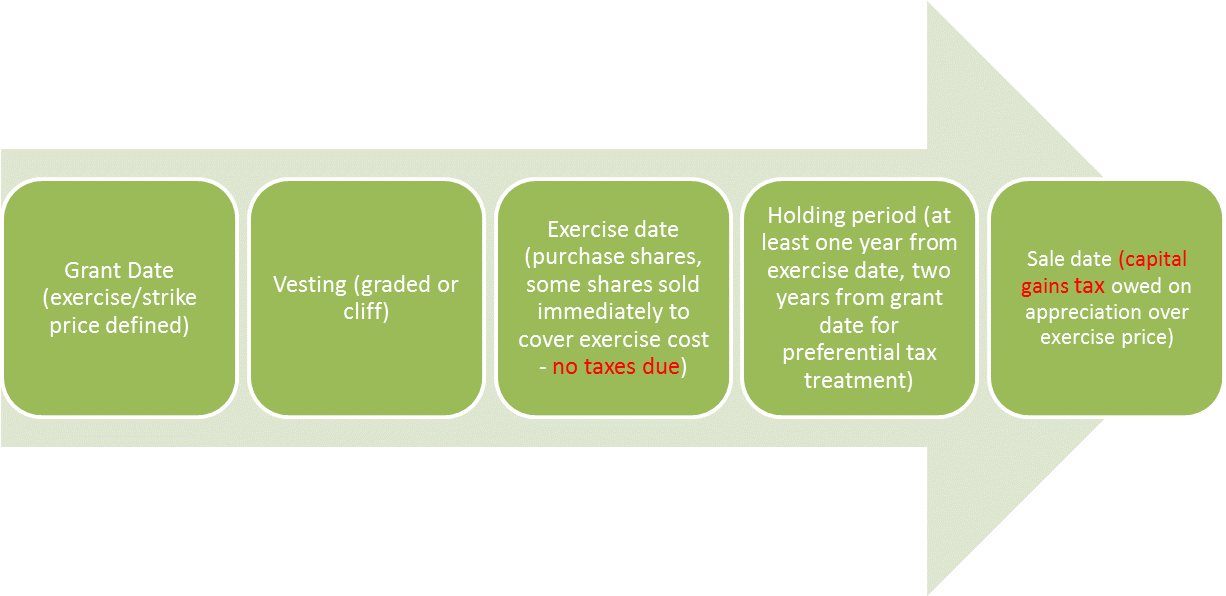
Are stock options taxable from grant date?
As long as you have held the stock for the required holding period — at least one year from the exercise date and two years from the grant date — the entire difference between the stock's selling price and your cost basis will be taxed as a long-term capital gain.
How do you report income from nonstatutory stock options?
With nonqualified stock options, for employees the spread at exercise is reported to the IRS on Form W-2 For nonemployees, it is reported on Form 1099-MISC (starting with the 2020 tax year, it will be reported on Form 1099-NEC ). It is included in your income for the year of exercise.
How are non-qualified employee stock options taxed when granted?
NSOs are taxed when you exercise them, and then later when you make money with them (when your company exits and you sell your shares). They don't get taxed either when the company first grants you them, or when they vest.
What is the difference between an incentive stock option and a nonstatutory stock option?
Incentive stock options, or “ISOs”, are options that are entitled to potentially favorable federal tax treatment. Stock options that are not ISOs are usually referred to as nonqualified stock options or “NQOs”. The acronym “NSO” is also used. These do not qualify for special tax treatment.
How are nonstatutory stock options reported on W-2?
If you exercised nonqualified stock options (NQSOs) last year, the income you recognized at exercise is reported on your W-2. It appears on the W-2 with other income in: Box 1: Wages, tips, and other compensation. Box 3: Social Security wages (up to the income ceiling)
Do stock options get taxed twice?
If you follow IRS rules when you report the sale of stock bought through an ISO, you'll avoid being taxed twice on the same income. The broker your employer uses to handle the stocks will send you a Form 1099-B.
How are stock grants taxed?
If you're granted a restricted stock award, you have two choices: you can pay ordinary income tax on the award when it's granted and pay long-term capital gains taxes on the gain when you sell, or you can pay ordinary income tax on the whole amount when it vests.
What is the difference between a qualified and nonqualified stock option?
Profits made from exercising qualified stock options (QSO) are taxed at the capital gains tax rate (typically 15%), which is lower than the rate at which ordinary income is taxed. Gains from non-qualified stock options (NQSO) are considered ordinary income and are therefore not eligible for the tax break.
When should I exercise a non-qualified stock option?
The most common expiration of NSOs is 10 years, but this does vary from company to company. Since time is often your friend when it comes to stock options, you can simply sit out the first couple of years to allow for growth and start to exercise your NSOs in a systematic way when you are nearing expiration.
Is an RSU a nonstatutory stock option?
Non-Qualified Stock Options vs. Restricted Stock Units. As you grow within an organization, equity awards can become a greater percentage of your compensation and in turn your overall net worth. Two common types of equity awards are non-qualified stock options (NQSOs) and restricted stock units (RSUs).
Are options taxed as capital gains?
Internal Revenue Code section 1256 requires options contracts on futures, commodities, currencies and broad-based equity indices to be taxed at a 60/40 split between the long and short term capital gains rates.
What is a non-statutory stock option?
An NSO, or non-statutory stock option is a type of compensatory stock that is not meant to be an ISO, or incentive stock option within the Internal Revenue Code. These are employee stock options that are offered without any restrictions. Non-statutory stock options are also known as a non-qualified stock options.
When are stock options taxed?
The recipient is taxed on the date the stock options are exercised on the difference of the stock’s market value and the grant price.
Why are NSOs important?
Benefits generally boost morale, but NSOs are extra special because they provide employees with the opportunity to make an even higher income while gaining the feeling that their overall actions will have a positive impact on their compensation.
Why are stock options called stock options?
They are named as such because the will not qualify within the strict guidelines of ISOs. They are more flexible and do not have as many restrictions when it comes to issuance.
Does Upcounsel accept NSOs?
If you need help with NSOs, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel’s marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law, and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Do NSOs have to be red taped?
They are more flexible and do not have as many restrictions when it comes to issuance. While NSOs are easier to provide, and do not require a lot of legal red tape, they still have to maintain all SEC guidelines. This is why it is crucial to work with a corporate securities attorney before you use them.
Can you buy stock for a certain price?
You can buy a stock for a certain price for a specified time period while the market value rises. The goal is to make a profit on the shares once the stock vests. The profit may be conferred immediately for NSOs.
What is nonstatutory stock option?
Nonstatutory stock options trigger ordinary income to you at some point in time and produce a compensation deduction to the employer. §83 contains two rules affecting all nonstatutory stock option transactions. In the following circumstances, all stock options are considered not actively traded on an established market.
Who transfers option?
The option is transferable by the optionee.
What is the holding period for a 83 transaction?
Under both rules above, the holding period for property acquired in a §83 transaction begins with the date on which the property becomes taxable as compensation income. The following maximum marginal tax rates are currently in effect: Holding period. Maximum marginal tax rate. 12 months or less.
How long after a restricted property is transferred can you make an 83b election?
However, you can make a §83 (b) election within 30 days after the transfer of the property. This essentially closes the taxable event at exercise and provides an opportunity to limit ordinary income ...
When do you recognize ordinary income?
Generally, you will recognize ordinary income in the year in which you exercise the nonstatutory option. The ordinary income amount will be equal to the excess of (i) the fair market value of the purchased shares on the exercise date over (ii) the exercise price paid for those shares.
When does an employer get a deduction?
The employer will receive a deduction in the year in which the employee's income inclusion ends. For example, the deduction is allowed either (1) in the employer's year that ends with the employee's year (i.e., the employer and the employee use the same taxable year); or (2) in the employer's year in which the employee's year ends (i.e., if the employee and the employer use different taxable years). Generally, the employer's deduction is the same amount included in
Is compensation income taxable at the time of a grant?
Treatment: There is no taxable event at date of the grant. If the underlying property is not restricted when you exercise the options, compensation income is computed as the difference between the fair market value at date of exercise and date of the grant. The effect of not having a taxable event at the time of grant is to treat as compensation ...
What is stock option?
Stock options are employee benefits that enable them to buy the employer’s stock at a discount to the stock’s market price. The options do not convey an ownership interest, but exercising them to acquire the stock does. There are different types of options, each with their own tax results.
How many events are there in a stock option?
For this type of stock option, there are three events, each with their own tax results: The grant of the option, the exercise of the option, and the sale of stock acquired through the exercise of the option.
What is Form 6251?
Form 6251 will help you figure out if you owe any AMT after you exercise an ISO. If you sell the stock in the same year you exercised the ISO, no AMT adjustment is required. This is because the tax treatment becomes the same for regular tax and AMT purposes. 2 .
What is included in income when you exercise an option?
When you exercise the option, you include, in income, the fair market value of the stock at the time you acquired it, less any amount you paid for the stock. This is ordinary wage income reported on your W2, therefore increasing your tax basis in the stock. 5 .
When you sell stock, do you report capital gains?
When you sell the stock, you report capital gains or losses for the difference between your tax basis and what you receive on the sale.
Do you have to report the fair market value of a stock when you sell it?
When you sell the stock, you report capital gains or losses for the difference between your tax basis and what you receive on the sale.
Do stock options have to be taxed?
Tax Rules for Statutory Stock Options. The grant of an ISO or other statutory stock option does not produce any immediate income subject to regular income taxes. Similarly, the exercise of the option to obtain the stock does not produce any immediate income as long as you hold the stock in the year you acquire it.
What Are Nonstatutory Stock Options?
Nonstatutory Stock Options (NSOs) are also known as Non-Qualified Stock Options (NQOs).
What are the two types of stock options?
We’ve discussed stock options at length on Daily Capital, but people often don’t know that there are two types of stock options: Incentive Stock Options (ISOs) and Nonstatutory Stock Options (NSOs).
When are NSOs taxed?
Typically, NSOs are taxed at the date of exercise rather than the date of grant. The amount subject to ordinary income tax is the difference between the fair market value at the time of exercise and the exercise price. If you continue to hold the stock after exercise, any gain in price is subject to capital gains rules (long-term, ...
How long can you hold a stock after exercise?
If you continue to hold the stock after exercise, any gain in price is subject to capital gains rules (long-term, if you hold for more than 12 months). For example, let’s say you are granted 300 shares of XYZ, Inc., on January 1, 2016, with an exercise price of $10 per share, with 100 shares vesting each year for the next three years.
When you sell an option, do you report the money you receive?
If you sell the option before you exercise it, report the money you receive as income. If you give it away or sell it for less than market value, you also report income when the recipient exercises the option. To figure the second amount, add the exercise price to whatever you received for the sale to get your basis.
How to calculate the value of an option?
Calculate the value of your option. If you can buy 100 shares at $10 apiece when the price is $100, for example, the option is worth $9,000 in compensation. If your stock option doesn't have a measurable value when you receive it, make this calculation when you finally exercise the option. Step 2.
Do you pay capital gains tax on stock sales?
Report the results on Schedule D. If you held the stock less than a year, you pay short-term capital gains tax on profits from the sale. If it's longer than a year, you can use long-term capital gains rates.
Do you report stock options to the IRS?
How to Report Stock Options to the IRS. If a company grants you stock options outside a stock-purchase or incentive plan, it's a nonstatutory option. The tax-reporting requirements depend on whether you can determine the value of the option. If the stock is traded on an established market and you have the right to exercise the option and sell ...
Can you set a value on an option?
If the stock is traded on an established market and you have the right to exercise the option and sell the stock immediately , you can set a value on the option. If the option doesn't meet those conditions, you can't determine the value and must report taxes differently. You pay taxes a second time when you sell your stock.
What happens if you don't exercise your options?
You don’t have total control over the stock. If you don’t exercise your options within the required time period, you’ll lose them.
Do options have a market value?
However, the option might have a readily determinable market value. If so, you’ll have to recognize income when you receive the option. Options traded in an open market have market values that are easily determined. (Ex: Traded on the New York Stock Exchange)
Can you sell NQSOs and exercise options at the same time?
You can often do a paperless transaction in which you exercise your NQSOs and sell the stock at the same time. Even though you perform only one transaction, it’s really two transactions: You exercised your options, and you sold the stock.

Non-Statutory Stock Options
- An NSO, or non-statutory stock option is a type of compensatory stock that is not meant to be an ISO, or incentive stock option within the Internal Revenue Code. These are employee stock options that are offered without any restrictions. Non-statutory stock options are also known as a non-qualified stock options. These are a stock option for employees, but also for vendors, the board …
How Non-Qualified Stock Options Work
- NQOs are among the most common stock options provided as employee benefits. You can buy a stock for a certain price for a specified time period while the market value rises. The goal is to make a profit on the shares once the stock vests. The profit may be conferred immediately for NSOs. There are no restrictions with regard to waiting periods, and you can sell the shares as so…
Nsos and Tax Considerations
- The following are tax considerationsfor NSOs: 1. NSOs are seen as a form of normal income that is received from a company. 2. The recipient is taxed on the date the stock options are exercisedon the difference of the stock’s market value and the grant price. 3. This will appear on a W-2 just like other forms of compensation. 4. NSOs are comparable ...
Advantages of Non-Statutory Stock Options
- There are three significant benefits of NSOs for both employees and companies: 1. It will increase the employee’s income without adding to the expense of the employer. An employee can make more money as the stock price rises. The expense is born not by the employer, but by the open market. 2. It will increase the morale and engagement of employees. Benefits generally boost m…
Disadvantages of Nsos
- On the flip side, there are some disadvantages of NSOs for both employees and companies to think about before exercising these options: 1. They provide a bigger tax burden. Since NSOs are treated as regular income, exercising the options is a major tax activity that can place employees into a higher tax bracket. 2. There is some risk. There will never be a guarantee that the stock pri…