
What is the worst stock market crash?
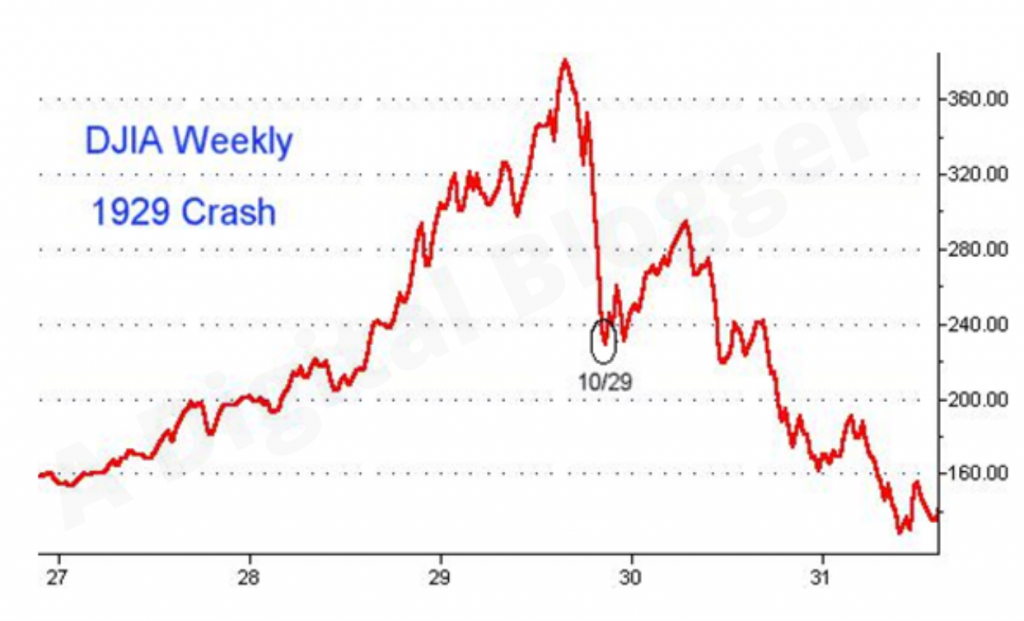
The worst stock market crash in history started in 1929 and was one of the catalysts of the Great Depression. The crash abruptly ended a period known as the Roaring Twenties, during which the economy expanded significantly and the stock market boomed.
What actually happens during a stock market crash?
The stock market crash of 1987 was a steep decline in U.S. stock prices over a few days in October of 1987; in addition to impacting the U.S. stock market, its repercussions were also observed in other major world stock markets.
What was the exact date the stock market crashed?
The stock market crash of 1929—considered the worst economic event in world history—began on Thursday, October 24, 1929, with skittish investors trading a record 12.9 million shares.
When was the last market crash?
Though the market was ’saved’ from a disastrous month during the last two trading days in January 2022, the results were nonetheless atrocious. Market crashes don’t necessarily have to happen in a day, week, or month. After the mid-month holiday ...
When did the stock market crash happen in 2008?
On October 24, 2008, many of the world's stock exchanges experienced the worst declines in their history, with drops of around 10% in most indices. In the U.S., the DJIA fell 3.6%, although not as much as other markets.
What caused the stock market crash of 2008?
The stock market and housing crash of 2008 had its origins in the unprecedented growth of the subprime mortgage market beginning in 1999. U.S. government-sponsored mortgage lenders Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac made home loans accessible to borrowers who had low credit scores and a higher risk of defaulting on loans.
How long did the 2008 market crash last?
The US bear market of 2007–2009 was a 17-month bear market that lasted from October 9, 2007 to March 9, 2009, during the financial crisis of 2007–2009.
How much did the stock market drop in 2008 and 2009?
From its local peak of 1,300.68 on August 28, 2008, the S&P 500 fell 48 percent in a little over six months to its low on March 9, 2009. This drop is similar to the decrease in much of the rest of the world (Bartram and Bodnar 2009).
Who got rich during the 2008 financial crisis?
Hedge fund manager John Paulson reached fame during the credit crisis for a spectacular bet against the U.S. housing market. This timely bet made his firm, Paulson & Co., an estimated $2.5 billion during the crisis.
How long did it take to recover from 2008?
In October 2008, the U.S. government approved a bailout package in an effort to protect the U.S. financial system and promote economic growth. By mid-2009, the economy had finally begun to recover.
Who is to blame for the Great Recession of 2008?
The Biggest Culprit: The Lenders Most of the blame is on the mortgage originators or the lenders. That's because they were responsible for creating these problems. After all, the lenders were the ones who advanced loans to people with poor credit and a high risk of default. 7 Here's why that happened.
What was the worst day in stock market history?
The largest point drop in history occurred on March 16, 2020, when concerns over the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic engulfed the market, dropping the Dow Jones Industrial Average 2,997 points.
What was the biggest stock market crash?
stock market crash of 1929, also called the Great Crash, a sharp decline in U.S. stock market values in 1929 that contributed to the Great Depression of the 1930s. The Great Depression lasted approximately 10 years and affected both industrialized and nonindustrialized countries in many parts of the world.
Will there be recession in 2021?
Unfortunately, a global economic recession in 2021 seems highly likely. The coronavirus has already delivered a major blow to businesses and economies around the world – and top experts expect the damage to continue.
What caused the 2007 to 2009 financial crisis?
The Great Recession, one of the worst economic declines in US history, officially lasted from December 2007 to June 2009. The collapse of the housing market — fueled by low interest rates, easy credit, insufficient regulation, and toxic subprime mortgages — led to the economic crisis.
How long did it take for the housing market to recover after 2008?
3.5 yearsIt took 3.5 years for the recovery to begin after the recession began. A lot of buyers who bought in 2008, 2009 or 2010 saw their home prices decrease before the recovery started in 2011. Condos deprecated by only 12%, while single-family homes depreciated by 19% after the recession.
Why did the stock market crash in 2008?
In all, the stock market crash 2008 as a result of a series of events that eventually led to the failure of some of the largest companies in the US.
What was the impact of the 2008 stock market crash?
There is no doubt behind the saying, that the crash pushed the banking system towards the edge of collapse.
Why did the Dow Jones crash?
The major crash occurred due to the major fall of Dow Jones to 777.8 in single-day trading and the rejection of bank bail-out bill by the Congress. But the signs were visible from the time before the crash hit the market.
What was the Dow value in September 2008?
The day was ended at the Dow value of 11,388.44. On September 20, 2008, the bank bailout bill was sent to Congress by Secretary Paulson and Federal Reserve Chair. The Dow fell to 777.68 points during the intraday trading that increased panic in the Global Market.
How many points did the Dow drop in 2008?
By September 17, 2008, the Dow fell by 446.92 points. By the end of the week on September 19, 2008, the Fed established the Asset-Backed Commercial Paper Money Market Mutual Fund Liquidity Facility that committed to offer loans to banks to buy Commerical paper from the money market funds.
How much did the Fed lose from Lehman Brothers?
By making $85 billion loans for 79.9% equity the Fed took ownership of the AIG. With the collapse of Lehman Brothers, there was a loss of $196 billion that increased the panic among many businesses. Bank has driven up the rates as they were afraid to lend money. By September 17, 2008, the Dow fell by 446.92 points.
How much GDP growth was there in 2007?
As per the study in 2007 by the BEA, the GDP growth estimation reveals that there was only 0.6% growth in the fourth quarter of 2007 with the loss of 17,000 jobs since 2004.
What was the financial crisis of 2008?
The 2008 financial crisis had its origins in the housing market, for generations the symbolic cornerstone of American prosperity. Federal policy conspicuously supported the American dream of homeownership since at least the 1930s, when the U.S. government began to back the mortgage market. It went further after WWII, offering veterans cheap home loans through the G.I. Bill. Policymakers reasoned they could avoid a return to prewar slump conditions so long as the undeveloped lands around cities could fill up with new houses, and the new houses with new appliances, and the new driveways with new cars. All this new buying meant new jobs, and security for generations to come.
When did the mortgage market explode?
According to the Final Report of the National Commission on the Causes of the Financial and Economic Crisis of the United States, between 2001 and 2007, mortgage debt rose nearly as much as it had in the whole rest of the nation's history. At about the same time, home prices doubled. Around the country, armies of mortgage salesmen hustled to get Americans to borrow more money for houses—or even just prospective houses. Many salesmen didn’t ask borrowers for proof of income, job or assets. Then the salesmen were gone, leaving behind a new debtor holding new keys and perhaps a faint suspicion that the deal was too good to be true.
Why did the financial sector develop mortgages?
To meet this demand for higher returns, the U.S. financial sector developed securities backed by mortgage payments. Ratings agencies, like Moody's or Standard and Poor's, gave high marks to the processed mortgage products, grading them AAA, or as good as U.S. Treasury bonds. And financiers regarded them as reliable, pointing to data and trends dating back decades. Americans almost always made their mortgage payments. The only problem with relying on those data and trends was that American laws and regulations had recently changed. The financial environment of the early 21st century looked more like the United States before the Depression than after: a country on the brink of a crash.
Why did the Federal Reserve put low interest rates on mortgages?
After the Federal Reserve System imposed low interest rates to avert a recession after the September 11, 2001 terrorist attacks, ordinary investments weren’t yielding much. So savers sought superior yields.
When did the Dow Jones Industrial Average fall?
A trader works on the floor of the New York Stock Exchange on September 15, 2008 in New York City. In afternoon trading the Dow Jones Industrial Average fell over 500 points as U.S. stocks suffered a steep loss after news of the financial firm Lehman Brothers Holdings Inc. filing for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection.
Who cut Lehman loose?
The Bush administration, criticized for earlier bailouts, cut Lehman loose
Was Lehman too big to fail?
Lehman, they thought, was not too big to fail.
Why did the stock market crash in 2008?
The stock market crashed in 2008 because too many had people had taken on loans they couldn’t afford. Lenders relaxed their strict lending standards to extend credit to people who were less than qualified. This drove up housing prices to levels that many could not otherwise afford.
What happened to the housing market in 2007?
A crisis was virtually inevtiable. Once the housing market slowed down in 2007, the housing bubble was ready to burst.
What banks were involved in the bailout?
The build-up of bad debt resulted in a series of government bailouts starting with Bear Stearns, a failing investment bank. Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac (the nickname given the Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation) were next on the government-sponsored bailout train.
What was the unemployment rate in 2007?
The economy continued to lose hundreds of thousands of jobs, and the unemployment rate peaked at 10 percent, double the December 2007 national unemployment rate of 5 percent. Three of the biggest automakers (known as the Big Three) were in trouble and asked the government for help.
How did the relaxed lending standards affect the housing market?
The relaxed lending standards fueled the housing growth and corresponding rise in home values. People with bad credit and little-to-no savings were offered loans they could not afford. Meanwhile, banks were repackaging these mortgages and selling them to investors on the secondary market.
What caused the real estate bubble?
Easy credit and raising home prices resulted in a speculative real estate bubble. While the market crashed in 2008, the problem started years earlier.
When did the Dow Jones go down?
The Dow Jones hit bottom in the first quarter of 2009 as the bad financial news continued. The widespread panic fueled steady economic decline. Only weeks after taking office, President Barack Obama outlined an economic stimulus package to boost consumer spending.
What happened in 2008?
By the fall of 2008, borrowers were defaulting on subprime mortgages in high numbers, causing turmoil in the financial markets, the collapse of the stock market, and the ensuing global Great Recession.
When did the housing market crash?
The stock market and housing crash of 2008 had its origins in the unprecedented growth of the subprime mortgage market beginning in 1999.
Why did the government take over Fannie Mae?
2007 peaks, the government announced its takeover of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac as a result of losses from heavy exposure to the collapsing subprime mortgage market. 6 One week later, on Sept. 14, major investment firm Lehman Brothers succumbed to its own overexposure to the subprime mortgage market and announced the largest bankruptcy filing in U.S. history at that time. 7 The next day, markets plummeted and the Dow closed down 499 points at 10,917. 8
Why did Bear Stearns fail in 2007?
By March 2007, with the failure of Bear Stearns due to huge losses resulting from its underwriting many of the investment vehicles linked to the subprime mortgage market, it became evident that the entire subprime lending market was in trouble. Homeowners were defaulting at high rates as all of the creative variations of subprime mortgages were resetting to higher payments while home prices declined.
How much credit did Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac extend in 2002?
As of 2002, government-sponsored mortgage lenders Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac had extended more than $3 trillion worth of mortgage credit. In his 2002 book Conquer the Crash, Prechter stated, "confidence is the only thing holding up this giant house of cards.". 2 .
How much did the Dow drop in 2008?
The Dow would plummet 3,600 points from its Sept. 19, 2008 intraday high of 11,483 to the Oct. 10, 2008 intraday low of 7,882. The following is a recap of the major U.S. events that unfolded during this historic three-week period.
How much was consumer debt in 2004?
To compound the potential mortgage risk, total consumer debt, in general, continued to grow at an astonishing rate. In 2004, consumer debt hit $2 trillion for the first time.
When did the subprime crisis hit the economy?
The subprime crisis reached the entire economy by the third quarter of 2008 when GDP fell by 0.3%. 7
Why did the subprime mortgage crisis in 2006 signal the beginning of the Great Recession?
The subprime mortgage crisis in 2006 signaled the beginning of the Great Recession. Because they were confident that home mortgages were sound collateral for MBS, banks and other financial corporations invested in these in the form of derivatives.
Why did the financial crisis spread?
The bottom line? Banks relied too much on derivatives. They sold too many bad mortgages to keep the supply of derivatives flowing. That was the underlying cause of the recession. This financial catastrophe quickly spilled out of the confines of the housing scene and spread throughout the banking industry, bringing down financial behemoths with it. Among those deemed “too big to fail” were Lehman Brothers and Merrill Lynch. Because of this, the crisis spread globally.
Why did banks feel safe buying CDS?
But they felt safe because they also bought credit default swaps (CDS), which insured against the risk of defaults. But when the MBS market caved in, insurers did not have the capital to cover the CDS holders.
When did the Great Recession start?
The Great Recession began well before 2008. The first signs came in 2006 when housing prices began falling. By August 2007, the Federal Reserve responded to the subprime mortgage crisis by adding $24 billion in liquidity to the banking system. 1 By September 2008, Congress approved a $700 billion bank bailout, now known as ...
What was the unemployment rate in 2009?
In October 2009, unemployment peaked at 10% , the worst level since the 1982 recession. Almost 6 million jobs were lost in the 12 months prior to that. Employers were adding temporary workers as they grew too wary of the economy to add full-time employees.
When did the Bank of America increase lending?
In December of 2009, Bank of America pledged to President Obama that it would increase lending to small and medium-sized businesses by $5 billion in 2010. But that was only after drastically slashing lending in 2009. 24
What happened to 401(k) in 2008?
These 401 (k) funds took a beating in 2008 — and it could happen again 1 Target-date funds whose investors were on the verge of retirement experienced losses exceeding 20 percent during the 2008 crisis. 2 Market corrections happen, but investors must maintain a long-term focus and save consistently.
What happens to the target date fund as retirement approaches?
As your retirement date approaches, your target-date fund would gradually reduce the equity allocation and increase the bond portion in order to lower market risk.
Do target date funds hold short term bonds?
Where some target-date funds held short-term bond funds within their fixed income allocations, others held riskier high-yield bond funds, which can move in the same direction as equities, he said.

2007
2008
- At the end of January, the BEA revised its fourth-quarter 2007 GDP growth estimate down.9 It said growth was only 0.6%. The economy lost 17,000 jobs, the first time since 2004.10 The Dow shrugged off the news and hovered between 12,000 and 13,000 until March.2 On March 17, the Federal Reserve intervened to save the failing investment bank, Bear Stearns. The Dow dropped …
September 2008
- The month started with chilling news. On Monday, September 15, 2008, Lehman Brothers declared bankruptcy. The Dow dropped more than 200 points.2 On Tuesday, September 16, 2008, the Fed announced it was bailing out insurance giant American International Group Inc. It made an $85 billion loan in return for 79.9% equity, effectively taking ownership. AIG had run out of cash. It wa…
October 2008
- Congress finally passed the bailout bill in early October, but the damage had already been done.24 The Labor Department reported that the economy had lost a whopping 159,000 jobs in the prior month.25 On Monday, October 6, 2008, the Dow dropped by 800 points, closing below 10,000 for the first time since 2004.26 The Fed tried to prop up banks by lending $540 billion to money mar…
November 2008
- The month began with more bad news. The Labor Department reported that the economy had lost a staggering 240,000 jobs in October.34 The AIG bailout grew to $150 billion.35 The Bush administration announced it was using part of the $700 billion bailouts to buy preferred stocks in the nations' banks.36 The Big Three automakers asked for a federal bailout. By November 20, 20…
December 2008
- The Fed dropped the fed funds rate to 0%, its lowest level in history.29 The Dow ended the year at a sickening 8,776.39, down almost 34% for the year.2
2009
- On January 2, 2009, the Dow climbed to 9,034.69.2 Investors believed the new Obama administration could tackle the recession with its team of economic advisers. But the bad economic news continued. On March 5, 2009, the Dow plummeted to its bottom of 6,594.44.37 Soon afterward, President Barack Obama's economic stimulus plan instilled the confidence nee…
Aftermath
- Investors bore the emotional scars from the crash for the next four years. On June 1, 2012, they panicked over a poor May jobs report and the eurozone debt crisis. The Dow dropped 275 points.39 The 10-year benchmark Treasury yield dropped to 1.47.40 This yield was the lowest rate in more than 200 years.41It signaled that the confidence that evaporated during 2008 had not q…