What were 5 causes of the stock market crash?
Equally relevant issues, such as overpriced shares, public panic, rising bank loans, an agriculture crisis, higher interest rates and a cynical press added to the disarray. Many investors and ordinary people lost their entire savings, while numerous banks and companies went bankrupt.Apr 27, 2021
What are the 3 main causes of the stock market crash?
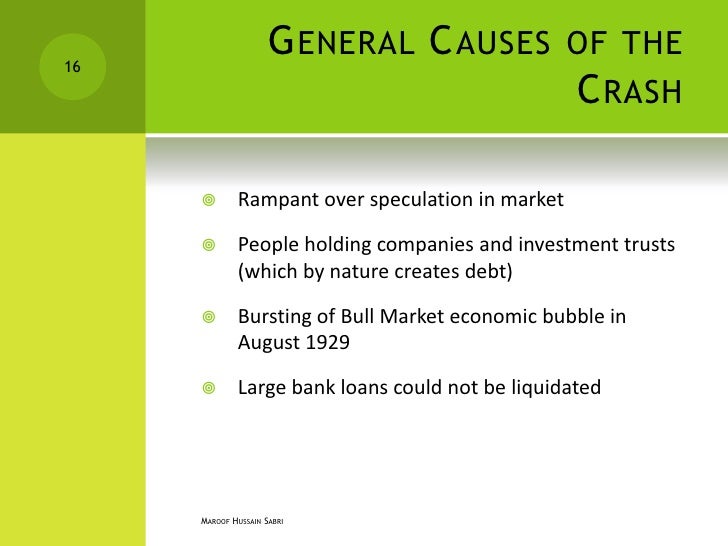
By then, production had already declined and unemployment had risen, leaving stocks in great excess of their real value. Among the other causes of the stock market crash of 1929 were low wages, the proliferation of debt, a struggling agricultural sector and an excess of large bank loans that could not be liquidated.Apr 27, 2021
What caused the stock market crash of 1929 quizlet?
(1929)The steep fall in the prices of stocks due to widespread financial panic. It was caused by stock brokers who called in the loans they had made to stock investors. This caused stock prices to fall, and many people lost their entire life savings as many financial institutions went bankrupt.
What were the 4 main causes of the Great Depression?
However, many scholars agree that at least the following four factors played a role.The stock market crash of 1929. During the 1920s the U.S. stock market underwent a historic expansion. ... Banking panics and monetary contraction. ... The gold standard. ... Decreased international lending and tariffs.
What are the effects of stock market crash?
The stock market crash crippled the American economy because not only had individual investors put their money into stocks, so did businesses. When the stock market crashed, businesses lost their money. Consumers also lost their money because many banks had invested their money without their permission or knowledge.
What were three major reasons that led to the stock market crash quizlet?
Terms in this set (7)Uneven Distribution of Wealth. ... People were buying less. ... overproduction of goods and agriculture. ... Massive Speculation Based on Ignorance. ... Many stocks were bought on margin. ... Market Manipulation by a Small Group of Investors. ... Very Little Government Regulation.
What is the main cause of stock market crashes of 1929 and 1987?
Well-known U.S. stock market crashes include the market crash of 1929, which resulted from economic decline and panic selling and sparked the Great Depression, and Black Monday (1987), which was also largely caused by investor panic.
What caused Wall Street crash of 1929?
The 1929 stock market crash was a result of an unsustainable boom in share prices in the preceding years. The boom in share prices was caused by the irrational exuberance of investors, buying shares on the margin, and over-confidence in the sustainability of economic growth.Jul 5, 2017
What caused the 1929 Wall Street crash?
The Stock Market Crash of 1929 was caused by over-speculation in the 1920s, which included investors using borrowed money to buy stocks.
What happened in the Stock Market Crash of 1929?
In October of 1929, the Wall Street stock experienced a massive sell-off of stocks, which caused the market to crash after eight years of massive g...
How could the Stock Market Crash of 1929 been prevented?
Had the Federal Reserve and other governing bodies established a separation of banks and investment firms, the stock market would likely not have b...
Stock Market 1929 Facts
Below is an outline of the events surrounding the Stock Market Crash of 1929:
The Roaring Twenties
The Roaring Twenties were a time of great prosperity for many, but especially for large corporations. The development of new technology and refined industrial methods inspired hope for many who had suffered through the first World War.
Market Saturation
In hindsight, it was clear the stock market was saturated in early 1929. The small market slide in the spring of that year, coupled with the response from the Federal Reserve, indicated that boundless confidence in Wall Street was likely unfounded.
What are the conditions that cause stock market crashes?
Generally speaking, crashes usually occur under the following conditions: a prolonged period of rising stock prices (a bull market) and excessive economic optimism, a market where price–earnings ratios exceed long-term averages, and extensive use of margin debt and leverage by market participants.
What is a stock market crash?
A stock market crash is a sudden dramatic decline of stock prices across a major cross-section of a stock market, resulting in a significant loss of paper wealth. Crashes are driven by panic selling and underlying economic factors. They often follow speculation and economic bubbles. A stock market crash is a social phenomenon where external ...
How much did the DJIA fall in 1929?
Across the two days, the DJIA fell 23%. By the end of the weekend of November 11, 1929, the index stood at 228, a cumulative drop of 40% from the September high. The markets rallied in succeeding months, but it was a temporary recovery that led unsuspecting investors into further losses.
What caused the Indonesian stock market to close?
The economic crisis caused countries to close their markets temporarily. On October 8, the Indonesian stock market halted trading, after a 10% drop in one day. The Times of London reported that the meltdown was being called the Crash of 2008, and older traders were comparing it with Black Monday in 1987.
What were the consequences of the 1987 crash?
One of the consequences of the 1987 Crash was the introduction of the circuit breaker or trading curb on the NYSE. Based upon the idea that a cooling off period would help dissipate panic selling, these mandatory market shutdowns are triggered whenever a large pre-defined market decline occurs during the trading day .
How many shares were traded in the 1987 stock market crash?
The average number of shares traded on the New York Stock Exchange rose from 65 million shares to 181 million shares. The crash on October 19, 1987, Black Monday, was the climatic culmination of a market decline that had begun five days before on October 14.
What caused the stock market to crash in 1907?
In 1907 and in 1908, stock prices fell by nearly 50% due to a variety of factors, led by the manipulation of copper stocks by the Knickerbocker Trust Company. Shares of United Copper rose gradually up to October, and thereafter crashed, leading to panic. Several investment trusts and banks that had invested their money in the stock market fell and started to close down. Further bank runs were prevented due to the intervention of J. P. Morgan. The panic continued to 1908 and led to the formation of the Federal Reserve in 1913.
What caused the 1929 stock market crash?
The stock market crash of 1929 was largely caused by bad stock market investments, low wages, a crumbling agricultural sector and high amounts of debt that could not be liquidated.
Why did people panic when they sold their stocks?
People were panicking to sell their stocks in a hurry to avoid being left with worthless stock. Stock prices continued to drop for two years, and many people lost their entire life savings. The Great Depression followed, resulting in the worst economic period in the history of the United States.. ADVERTISEMENT.
What is buying on margin?
Buying on margin refers to the act of putting a small amount of money down on a stock and allowing the broker to "lend" the rest to the investor. When stocks rose, the investor made money and was able to make up the difference. When prices fell, the investor had to pay back the money that was owed. In October 1929, stock prices began to fall, ...
How did the stock market crash affect people?
Although only a small percentage of Americans had invested in the stock market, the crash affected everyone. Banks lost millions and, in response, foreclosed on business and personal loans, which in turn pressured customers to pay back their loans, whether or not they had the cash.
How to explain the stock market crash?
By the end of this section, you will be able to: 1 Identify the causes of the stock market crash of 1929 2 Assess the underlying weaknesses in the economy that resulted in America’s spiraling from prosperity to depression so quickly 3 Explain how a stock market crash might contribute to a nationwide economic disaster
What happened to the stock market on September 20th?
Even the collapse of the London Stock Exchange on September 20 failed to fully curtail the optimism of American investors. However, when the New York Stock Exchange lost 11 percent of its value on October 24—often referred to as “Black Thursday”—key American investors sat up and took notice.
What happened on October 29, 1929?
October 29, 1929, or Black Tuesday, witnessed thousands of people racing to Wall Street discount brokerages and markets to sell their stocks. Prices plummeted throughout the day, eventually leading to a complete stock market crash. The financial outcome of the crash was devastating.
How much did the stock market lose in 1929?
Between September 1 and November 30, 1929, the stock market lost over one-half its value, dropping from $64 billion to approximately $30 billion. Any effort to stem the tide was, as one historian noted, tantamount to bailing Niagara Falls with a bucket.
What were the advertisements selling in the 1920s?
In the 1920s, advertisers were selling opportunity and euphoria, further feeding the notions of many Americans that prosperity would never end. In the decade before the Great Depression, the optimism of the American public was seemingly boundless.
How many shares were traded on Black Tuesday?
On Black Tuesday, October 29, stock holders traded over sixteen million shares and lost over $14 billion in wealth in a single day. To put this in context, a trading day of three million shares was considered a busy day on the stock market. People unloaded their stock as quickly as they could, never minding the loss.
What were the causes of the 1929 stock market crash?
Among the other causes of the stock market crash of 1929 were low wages, the proliferation of debt, a struggling agricultural sector and an excess of large bank loans that could not be liquidated.
What was the stock market crash of 1929?
The stock market crash of 1929 was not the sole cause of the Great Depression, but it did act to accelerate the global economic collapse ...
What happened to stock market in 1929?
Stock prices began to decline in September and early October 1929, and on October 18 the fall began. Panic set in, and on October 24, Black Thursday, a record 12,894,650 shares were traded. Investment companies and leading bankers attempted to stabilize the market by buying up great blocks of stock, producing a moderate rally on Friday. On Monday, however, the storm broke anew, and the market went into free fall. Black Monday was followed by Black Tuesday (October 29, 1929), in which stock prices collapsed completely and 16,410,030 shares were traded on the New York Stock Exchange in a single day. Billions of dollars were lost, wiping out thousands of investors, and stock tickers ran hours behind because the machinery could not handle the tremendous volume of trading.
What happened after Black Tuesday?
In the aftermath of Black Tuesday, America and the rest of the industrialized world spiraled downward into the Great Depression (1929-39), the deepest and longest-lasting economic downturn in the history of the Western industrialized world up to that time .
When did stock prices drop in 1929?
Stock prices began to decline in September and early October 1929 , and on October 18 the fall began. Panic set in, and on October 24, Black Thursday, a record 12,894,650 shares were traded.
When did the stock market peak?
During the 1920s, the U.S. stock market underwent rapid expansion, reaching its peak in August 1929 after a period of wild speculation during the roaring twenties. By then, production had already declined and unemployment had risen, leaving stocks in great excess of their real value.
When was the New York Stock Exchange founded?
The New York Stock Exchange was founded in 1817, although its origins date back to 1792 when a group of stockbrokers and merchants signed an agreement under a buttonwood tree on Wall Street.
What was the Black Tuesday stock market crash?
Remembered today as "Black Tuesday," the stock market crash of October 29, 1929 was neither the sole cause of the Great Depression nor the first crash that month, but it's typically remembered as the most obvious marker of the Depression beginning. The market, which had reached record highs that very summer, had begun to decline in September.
How much money did the stock market lose in 1930?
By two months later, stockholders had lost more than $40 billion dollars. Even though the stock market regained some of its losses by the end of 1930, the economy was devastated. America truly entered what is called the Great Depression. 02. of 05.
What was the Great Depression made worse by?
The economic devastation of the Great Depression was made worse by environmental destruction. A years-long drought coupled with farming practices which did not use soil-preservation techniques created a vast region from southeast Colorado to the Texas panhandle that came to be called the Dust Bowl.
What was the cause of the economic downturn in Europe?
The economic downturn wasn't just confined to the United States; it affected much of the developed world. One cause of the depression in Europe, was that the Nazis came to power in Germany, sowing the seeds of World War II . 1:44.
What was the Great Depression?
The Great Depression lasted from 1929 to 1939 and was the worst economic depression in the history of the United States. Economists and historians point to the stock market crash of October 24, 1929, as the start of the downturn.
How many banks failed in 1929?
Nearly 700 banks failed in waning months of 1929 and more than 3,000 collapsed in 1930. Federal deposit insurance was as-yet unheard of, so when the banks failed, people lost all their money. Some people panicked, causing bank runs as people desperately withdrew their money, which in turned forced more banks to close.
Who fought against the Hawley-Smoot Tariff?
D. Baker Rails Against the Hawley-Smoot Tariff. Bettmann / Getty Images. As the Great Depression tightened its grip on the nation, the government was forced to act. Vowing to protect U.S. industry from overseas competitors, Congress passed the Tariff Act of 1930, better known as the Smoot-Hawley Tariff.