Stocks are treated as equity instruments whereas bonds are debt instruments Debt Instruments Debt instruments provide finance for the company's growth, investments, and future planning and agree to repay the same within the stipulated time. Long-term instruments include debentures, bonds, GDRs from foreign investors.
What is the difference between stocks and bonds?
· Stocks are equity instruments and can be considered as taking ownership of a company. While bonds are issued by all types of entities – including governments, corporations, nonprofit organizations, etc. – stocks, on the other hand, are issued by sole proprietors , partnerships, and corporations.
Where to buy stocks and bonds?
Stocks are equity shares issued by corporations. In exchange for buying shares, investors receive some ownership in a company. Stocks offer investors the ability to participate in profits but also...
What is the use of stocks and bonds in the economy?
· Convertible bonds are a type of corporate bond that can be converted into common stock in the company that issued them. U.S. Treasury Bonds US Treasury bonds are issued with the full faith of the U.S. government. Government bonds issued by the Treasury pay a fixed interest rate every six months until maturation.
What is the difference between debt and bond financing?

What type of financing are bonds?
A bond is a debt security, similar to an IOU. Borrowers issue bonds to raise money from investors willing to lend them money for a certain amount of time. When you buy a bond, you are lending to the issuer, which may be a government, municipality, or corporation.
What type of financing is stocks?
Equity FinancingWhat Is Equity Financing? Equity financing is the process of raising capital through the sale of shares. Companies raise money because they might have a short-term need to pay bills or have a long-term goal and require funds to invest in their growth.
Are bonds equity or debt financing?
Debt financing is the opposite of equity financing, which entails issuing stock to raise money. Debt financing occurs when a firm sells fixed income products, such as bonds, bills, or notes. Unlike equity financing where the lenders receive stock, debt financing must be paid back.
Is bonds a short-term financing?
Short-term financing bonds refer to the bond financing instrument issued by the non-financial enterprises with legal person qualification in the inter-bank bond market who promise to repay the principal and pay the interest within one year.
What is debt financing examples?
Examples of debt financing include traditional bank loans, personal loans, loans from family or friends, credit cards, government loans, lines of credit, and more. The main advantage of debt financing over equity financing is that the lender does not take an equity position in your business.
What are the three types of financing?
A: There are only three types of financing available to a small business owner: debt financing, equity financing, or a combination of the two. Debt financing comes from banks, government loan programs, or anyone you can convince to lend you money, to be repaid over a period of time with interest.
What are stocks and bonds?
Stocks give you partial ownership in a corporation, while bonds are a loan from you to a company or government. The biggest difference between them is how they generate profit: stocks must appreciate in value and be sold later on the stock market, while most bonds pay fixed interest over time.
What are the four types of debt financing?
Debt Financing OptionsBank loan. A common form of debt financing is a bank loan. ... Bond issues. Another form of debt financing is bond issues. ... Family and credit card loans. Other means of debt financing include taking loans from family and friends and borrowing through a credit card.
What is traditional debt financing?
In a traditional sense, debt financing involves a business selling bonds, bills, or notes to individual or institutional investors in return for debt capital. In return, the investors become creditors to the business and can expect to receive payment based on the debt financing agreement.
What is an example of long term financing?
Car loans, home loans and certain personal loans are examples of long-term loans. Long term loans can be availed to meet any business need like buying of machinery or any personal need like owning a house. Long-term loans are the most popular form of credit in the financial industry.
What is medium term financing?
What Are Medium-Term Loans? Medium-term loans are loans with a repayment period between two and five years. Usually, these loans offer up to $500,000 in financing, a monthly or bimonthly payment schedule, and mid-market interest rates. It typically takes two to three weeks to get funding with a medium-term loan.
What is long term financing?
Long-term finance can be defined as any financial instrument with maturity exceeding one year (such as bank loans, bonds, leasing and other forms of debt finance), and public and private equity instruments.
What are the 4 types of finance?
Types of FinancePublic Finance,Personal Finance,Corporate Finance and.Private Finance.
What type of activity is common stock?
It would appear as financing activity because sale of common stock impacts owners' equity. It would appear as investing activity because purchase of equipment impacts noncurrent assets. It would appear as operating activity because sales activity impacts net income as revenue.
What are the types of stock?
What Are The Different Types Of Stock?Common Stock. When investment professionals talk about stock, they almost always mean common stock. ... Preferred Stock. ... Class A Stock and Class B Stock. ... Large-Cap Stocks. ... Mid-Cap Stocks. ... Small-Cap Stocks. ... Growth Stocks. ... Value Stocks.More items...•
What are the 5 sources of finance?
5 Main Sources of FinanceSource # 1. Commercial Banks:Source # 2. Indigenous Bankers:Source # 3. Trade Credit:Source # 4. Installment Credit:Source # 5. Advances:
How do bonds work?
Bonds are also a common way to fund projects for public use, such as libraries, stadiums, or bridges. Let's say that a city wants to install a top-of-the-line recreational center with a pool, tennis courts, and a fitness center for its residents. The city could fund the center using money it has saved; it could increase taxes and wait to build it; or the city might choose to issue a bond. The city would receive the money needed to build the recreational center and repay the money to the bondholders, with interest, over a specified period of time. (See the boxed insert "The Bond Report Card" to learn about bond ratings.)
Who gets the money from a bond issue?
The entity issuing the bond (the issuer) gets the money for the project from the bond issue. After the issuer gets the money, the bonds may be traded among people and institutions in the secondary bond market, and the issuer gets no additional money.
What is the primary market?
The primary market is the market in which new stocks and bonds are issued. The primary market consists of businesses and their initial investors. This is where new stocks are born. Although businesses have other options, their initial investors are usually acquired through an IPO issued by an investment banker. An investment banker is someone who works with a business to determine how much money should be raised to accomplish the goals of the business and the price and number of shares that should be sold to reach those goals. The investment banker also assesses a business's potential for growth and profit, as well as its risks.
How does an investment banker work?
The investment banker works for an investment bank that will purchase the IPO shares or advise other investors to purchase shares of the new stock, including large institutional investors such as mutual funds or commercial banks. 4 A mutual fund is a company that pools investors' money and then issues shares to its investors. Commercial banks are businesses that accept deposits and make loans. The buyers of the stock provide the business with the money it needs to grow. So companies raise money by issuing an IPO with the assistance of an investment banker. If the company wants to raise money in the future, it can talk with an investment banker about issuing a secondary public offering. Companies aren't limited to a single public offering.
Why do people buy stocks in the Dow?
Because people rely on the money they may gain from stocks in the Dow, as well as the tens of thousands of other stocks sold across the world, to fund their homes, educations, and retirements. When people buy stock, they are buying a share of ownership in a company.
Why is it good to buy stock?
Actually, there are at least three very good reasons. First, a higher stock price is good for the company's employees who may own the company stock. Second, the company is seen as having a higher value (one measure of value is the price of its stock multiplied by the number of shares in the hands of the public).
Why do companies buy and sell their own stock?
Companies often buy and sell their own stock in the secondary market. They might buy their stock to decrease the number of shares that are available in the market. Such a purchase will often have the effect of increasing the price per share. So why would a company care about its price per share if it doesn't get the money when its stock is sold? Actually, there are at least three very good reasons. First, a higher stock price is good for the company's employees who may own the company stock. Second, the company is seen as having a higher value (one measure of value is the price of its stock multiplied by the number of shares in the hands of the public). So, if the company would want to issue more stock through the primary market in a secondary public offering, the price it could ask would be higher. A higher value also would help if the company were to seek a loan from a bank.
What is the difference between stock and bond?
Stocks and bonds are two different ways for an entity to raise money to fund or expand its operations. Stocks are simply ownership shares of corporations. When a company issues stock, it is selling a piece of itself in exchange for cash. 1
Why do people invest in stocks and bonds?
Many people invest in both stocks and bonds to diversify. Deciding on the appropriate mix of stocks and bonds in your portfolio is a function of your time horizon, tolerance for risk, and investment objectives. Typically, stocks and bonds do not fluctuate at the same time. 4 5
How much does a $1,000 bond pay?
Each bond has a certain par value (say, $1,000) and pays a coupon to investors. For instance, a $1,000 bond with a 4% coupon would pay $20 to the investor twice per year ($40 annually) until it matures.
What happens to a bond after it matures?
After it matures, the investor is returned the full amount of their original principal. If, for some reason, the issuer is not able to make the payment, the bond will default. This rarely happens.
What is stock in business?
Stocks are simply ownership shares of corporations. When a company issues stock, it is selling a piece of itself in exchange for cash. 1
What to do if stock price falls?
If seeing a stock price fall quickly would cause you to panic or if you are close to retiring and may need the money soon, then a mix with more bonds could be the better option for you.
What does it mean when someone buys stock?
A person who buys a stock is buying an actual share of the company, which makes them a partial owner. That is why stock is also referred to as "equity. " This applies to both established companies and IPOs that are new to the market.
What is the difference between a stock and a bond?
Key Differences. A stock is a financial instrument issued by a company depicting the right of ownership in return for funds provided as equity. A bond is a financial instrument issued for raising an additional amount of capital.
What is bond loan?
Bonds are actually loans that are secured by a specific physical asset. It highlights the amount of debt taken with a promise to pay the principal amount in the future and periodically offering them the yields at a pre-decided percentage. In this article, we shall understand the importance of Stocks vs Bonds and the differences between them.
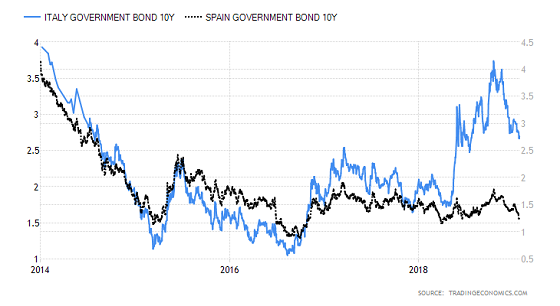
Why are bonds more risky than stocks?
The risk factor is high in stocks since the returns are not fixed or proportional whereas bonds have fixed returns making it less risky. Bonds are also rated by credit rating agencies which make it more structured before considering the investment opportunity.
Why are bonds issued by the government?
Bonds issued by the government are extensively used and also depicts the financial stability of the country. If the yields offered are less it means the nation is in a good position to pay off its debt and does not need everyone to lend to them and vice-versa.
What is secondary market?
Secondary Market A secondary market is where securities are offered to the general public after being offered in the primary market. Such securities are usually listed on the stock exchange. A significant portion of trading happens in such a market and are of two types – equities and debt markets. read more
Do bonds have fixed returns?
On the other hand, bonds have fixed returns that have to be paid irrespective of the performance of the borrower since it is a debt amount.
Is a stock an equity or debt?
Stocks are treated as equity instruments whereas bonds are debt instruments. Debt Instruments Debt instruments provide finance for the company's growth, investments, and future planning and agree to repay the same within the stipulated time. Long-term instruments include debentures, bonds, GDRs from foreign investors.
When investors buy a corporate bond or the bank loans to a small business, must they have faith that the company
When investors buy a corporate bond or the bank loans to a small business, they must have faith that the company will have the means to repay them. Riskier investments will require compensation for the lender in the form of higher interest rates.
What is debt in banking?
debt: Money that the borrowing entity owes or is required to pay to a lender.
What is EFN in finance?
In the first stage, a new company’s external financing needs (EFN) are high, since it needs money to develop its idea but lacks retained earnings. They are usually financed through debt, but may find investors who are willing to take on risk if projected growth is high.
What does it mean to fund a start up company?
By agreeing to fund a start-up company, the VC firm gets the potentials of high future returns, significant control over company decisions, and a portion of the company’s ownership.
How is venture capital different from debt?
Obtaining venture capital is different from raising debt or a loan from a lender. Lenders have a legal right to interest on a loan and repayment of the capital, irrespective of the success or failure of a business. In contrast, the venture capitalist’s return is dependent on the growth and profitability of the business.
Why do young companies with high growth potential turn to venture capitalists for funding?
Young companies with high growth potential turn to venture capitalists for funding because they cannot issue debt or raise capital in public markets.
Do corporations pay taxes on dividends?
Under a majority of taxation systems around the world, firms are subject to corporate tax and individuals to income tax, leading to double taxation of dividends, if the firm is financed through issuing stock. For example, a firm that earns 100 dollars in profits in the U.S. would have to pay around 30 dollars in taxes.
What is the difference between a stock and a bond?
Stocks give you partial ownership in a corporation, while bonds are a loan from you to a company or government. The biggest difference between them is how they generate profit: stocks must appreciate in value and be sold later on the stock market, while most bonds pay fixed interest over time.
What is corporate bond?
A company’s ability to pay back debt is reflected in its credit rating, which is assigned by credit rating agencies like Moody’s and Standard & Poor’s. Corporate bonds can be grouped into two categories: investment-grade bonds and high-yield bonds. Investment grade. Higher credit rating, lower risk, lower returns.
Why are bonds more valuable?
For example, if you buy a bond with a 2% yield, it could become more valuable if interest rates drop, because newly issued bonds would have a lower yield than yours . On the other hand, higher interest rates could mean newly issued bonds have a higher yield than yours, lowering demand for your bond, and in turn, its value.
Why do companies issue stock?
Companies may issue shares to the public for several reasons, but the most common is to raise cash that can be used to fuel future growth.
What does it mean to own stock?
Stocks represent partial ownership, or equity, in a company. When you buy stock, you’re actually purchasing a tiny slice of the company — one or more "shares." And the more shares you buy, the more of the company you own. Let’s say a company has a stock price of $50 per share, and you invest $2,500 (that's 50 shares for $50 each).
How long does a bond last?
The durations of bonds depend on the type you buy, but commonly range from a few days to 30 years. Likewise, the interest rate — known as yield — will vary depending on the type and duration of the bond.
What index is used for stock market returns?
Data is from a Vanguard study that analyzed theoretical portfolios of the above asset allocations between 1926 and 2019, using the Standard and Poor’s 90 Index (1926-1957) and the S&P 500 (1957-2019) for stock market returns, the Standard & Poor’s High Grade Corporate Index (1926-1968), the Salomon High Grade Index (1969-1972) and the Barclays U.S. Long Credit Aa Index (1973-2019) for bond market returns and the Ibbotson U.S. 30-Day Treasury Bill Index (1926-1977) and FTSE 3-Month U.S. Treasury Bill Index (1978-2019) for U.S. short-term reserves.
What is a bond loan?
Bonds and loans are financing instruments used at one moment or other by companies during the course of their existence. These are two conceptually different credit products that are sometimes confused. It is important to differentiate between both means of financing and understand their characteristics in order to know their true essence.
What is the difference between a bank loan and a bond?
A bank loan is a financial operation in which a banking entity ( lender ), through a contract or agreement between the parties involved, grants a sum of money to a third party ( borrower) in exchange for the payment of interest, known as the cost of money. A bond by contrast is defined as a debt instrument issued by a company or public administration and sold to investors in the financial markets with the aim of securing resources to fund itself. The issuer of the bond promises to return the money plus previously agreed interest payments ( coupon) to the purchaser of the bond.
What is BBVA in finance?
BBVA has the capability, knowledge and experience to provide its customers with top-quality advice on sustainable finance solutions in both bonds and loans, and is playing a key role in developing both markets.
What is the European Commission's strategy for sustainable finance?
The European Commission has published its Action Plan to boost the contribution of the financial industry to the aim of achieving a more sustainable global economy.
What is social bond?
Social bonds: the profitability of the common good. In today's society, there is an increasing demand for sustainable growth and development. To respond to that demand, there are financial instruments such as social bonds, whose resources are by definition destined for projects that improve the social environment.
Is BBVA a green loan?
In the green loans business, in which BBVA has been a pioneer and is a fundamental driving force , the bank closed 2017 as the most active entity worldwide, with a total of 11 operations in Europe and Latin America for clients from various sectors and is the undisputed leader in Spain.
What is a bond issued by?
When companies or government agencies need to raise funds, they issue bonds, which are securities issued with the backing of the issuing entity. They can be bought on the primary bond market directly from the issuer or traded on the secondary market.
What are the different types of bonds?
Bonds are issued with terms that include the coupon rate and face value. Zero-coupon bonds are one type of bond, while other different types include U.S. Treasuries, agency and municipal bonds, investment-grade and junk bonds, foreign bonds, and convertible bonds. There are government bonds, corporate bonds, and savings bonds.
Why are bonds important to investors?
One good thing about bonds is that their returns are consistent, so they offer income that investors can count on. For this reason, investors may be more interested in long-term rather than short-term securities.
What is agency bond?
Agency bonds are those issued to raise money by government-sponsored enterprises (GSEs) like the Federal National Mortgage Association (better known as Fannie Mae). Agency bonds are also issued by a federal U.S. government department other than the U.S. Treasury Department, such as the Small Business Administration or the Government National Mortgage Association (Ginnie Mae).
What is the initial price of a bond?
The initial price of a bond is usually par or a face value of $100 or $1,000. The market price after it starts trading depends on a variety of factors, such as the issuer’s credit quality, the amount of time left before it matures, and the coupon rate compared to other interest rates. Since they have an inverse correlation with interest rates, bonds tend to increase in price with lower interest rates and decrease in price with higher interest rates.
Why are bonds important?
Bonds are an important part of the financial and investment market. Depending on market conditions, bond prices may move up or down. Prices usually differ from the face value of the bond, and they are negatively correlated with yields, which is important for an investor to understand when it comes to buying bonds.
What is convertible bond?
Convertible bonds are a type of corporate bond that can be converted into common stock in the company that issued them.
What is funding in business?
Companies always seek sources of funding to grow the business. Funding, also called financing, represents an act of contributing resources to finance a program, project, or a need. Funding can be initiated for either short-term or long-term purposes. The different sources of funding include:
How do companies obtain debt financing?
Debt Capital. Companies obtain debt financing privately through bank loans. They can also source new funds by issuing debt to the public. In debt financing, the issuer (borrower) issues debt securities, such as corporate bonds or promissory notes.
What are the sources of funding for a company?
Summary. The main sources of funding are retained earnings, debt capital, and equity capital. Companies use retained earnings from business operations to expand or distribute dividends to their shareholders. Businesses raise funds by borrowing debt privately from a bank or by going public (issuing debt securities).
What is equity capital?
Equity Capital. Companies can raise funds from the public in exchange for a proportionate ownership stake in the company in the form of shares issued to investors who become shareholders after purchasing the shares.
Why are companies borrowers?
Companies that initiate debt issues are borrowers because they exchange securities for cash needed to perform certain activities. The companies will be then repaying the debt (principal and interest) according to the specified debt repayment schedule and contracts underlying the issued debt securities.
What is a debenture?
Debenture A Debenture is an unsecured debt or bonds that repay a specified amount of money plus interest to the bondholders at maturity. A debenture is a long-term debt instrument issued by corporations and governments to secure fresh funds or capital. Coupons or interest rates are offered as compensation to the lender.
What is venture capital funding?
Funding sources also include private equity, venture capital, donations, grants, and subsidies that do not have a direct requirement for return on investment (ROI), except for private equity and venture capital#N#Venture Capital Venture capital is a form of financing that provides funds to early stage, emerging companies with high growth potential, in exchange for equity or an ownership stake. Venture capitalists take the risk of investing in startup companies, with the hope that they will earn significant returns when the companies become a success.#N#. They are also called “crowdfunding” or “soft funding.”