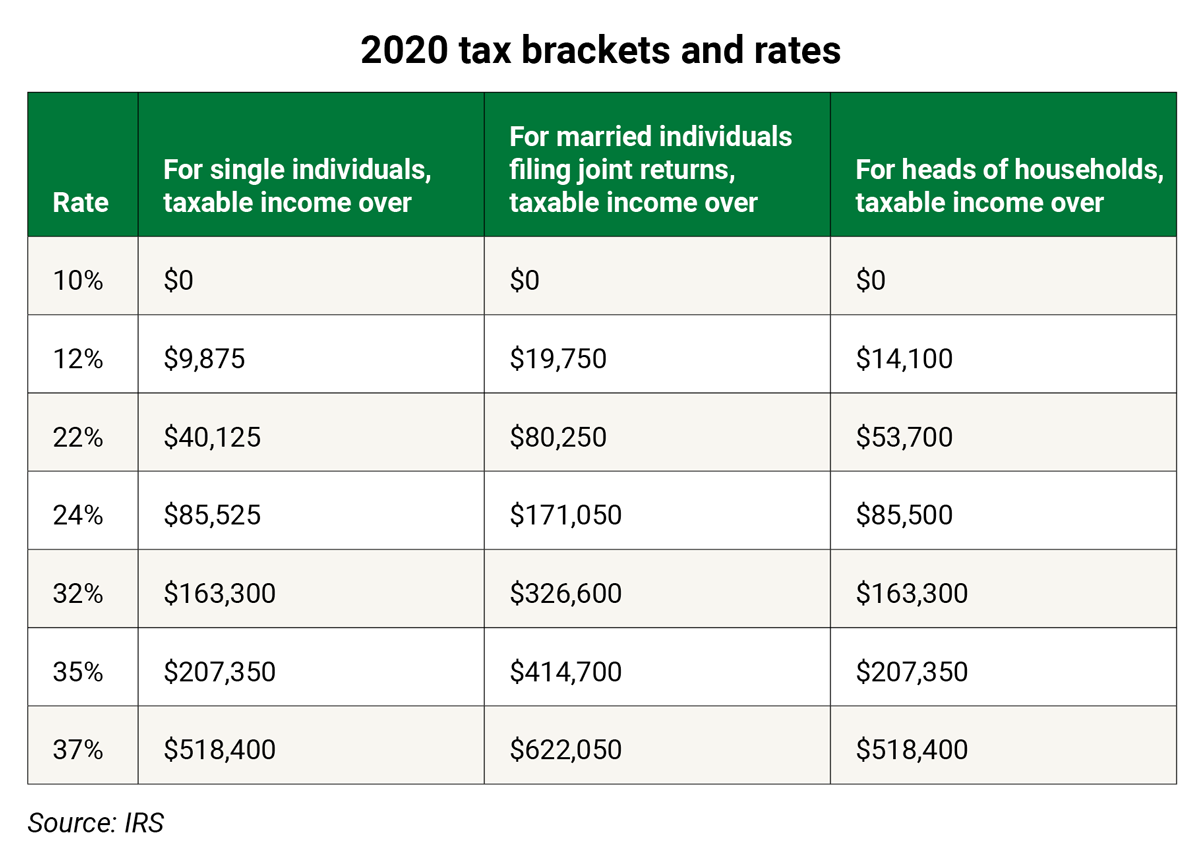
At that price, the stock can be bought in the market at $92 and sold through the exercise of the put at $95, for a profit of $3. The $3 covers the cost of the put and the trade is a wash. Profits grow at prices below $92. If the stock falls to $80, for example, the profit is $12 ($95 strike - $80 per share - the $3 premium paid for the put = $12).
Full Answer
Can you sell a put option on a stock?
For put options, you have the choice of selling the underlying stock when the contract expires. In order to conduct a put options trade, you need a strike price you can sell the stock at, option premium, and expiration that determines when the put contract settles. Put options are not the same as short selling.
How much does a put option cost on a $30 stock?
Consider two put option choices on the $30 stock. The put with the $30 strike price is quoted at $2.50. A put with a $25 strike price is priced at $0.50 for a cost of $50. The value of a put option increases by $1.00 -- $100 per contract -- for each dollar the stock price drops below a put option strike price.
What are the basics of selling in the money puts?
Basics Of Selling In The Money Puts. Selling an in-the-money put is incredibly simple. All we do is look at the current price of the stock and find the at-the-money strike (shown in green). We then look further up the chain on the put side. These are the options we sell when we sell an ITM put (shown in red).
How much does it cost to short sell a stock?
Each options contract represents 100 shares, so 1 put contract costs $500. The investor has $500 in cash, allowing either the purchase of one put contract or shorting 10 shares of the $50 XYZ stock. Here’s the payoff profile at expiration for short-sellers, put buyers and put sellers.
What is the correct price for a put option?
Put Option Pricing One put option is for 100 shares, so the cost of one contract is 100 times the quoted price. For example, a stock has a current stock price of $30. A put with a $30 strike price is quoted at $2.50. It would cost $250 plus commission to buy the put.
How are put options sold?
When you sell a put option, you agree to buy a stock at an agreed-upon price. Put sellers lose money if the stock price falls. That's because they must buy the stock at the strike price but can only sell it at a lower price. They make money if the stock price rises because the buyer won't exercise the option.
Does selling puts increase stock price?
Here are the advantages of selling puts. The payoff for put sellers is exactly the reverse of those for buyers. Sellers expect the stock to stay flat or rise above the strike price, making the put worthless. Using the same example as before, imagine that stock WXY is trading at $40 per share.
Who buys my put option?
The buyer of the put has the right, but not the obligation, to sell the asset at a specified price, within a specified time frame. The seller has the obligation to purchase the asset at the strike/offer price if the option owner exercises their put option.
When should you sell a put?
Investors should only sell put options if they're comfortable owning the underlying security at the predetermined price, because you're assuming an obligation to buy if the counterparty chooses to exercise the option.
What happens if I don't sell my put option?
The put option has no value and becomes worthless if the underlying security's price is higher than the strike price. When this happens, the put option is considered to be out of the money.
Do you need 100 shares to sell a put?
The seller sets the terms of the contract. The buyer pays the seller a pre-established fee per share (a "premium") to purchase the contract. Each contract represents 100 shares of the underlying stock. Investors don't have to own the underlying stock to buy or sell a put.
Why sell puts in the money?
Being in the money allows the holder of the contract to sell the related security at a price that is higher than where it trades when the put option contract expires.
How do puts WORK example?
Example of a put option If the ABC company's stock drops to $80 then you could exercise the option and sell 100 shares at $100 per share resulting in a total profit of $1,500. Broken out, that is the $20 profit minus the $5 premium paid for the option, multiplied by 100 shares.
How much can you make selling puts?
In general, you can earn anywhere between 1 and 5% (or more) selling weekly put options. It all depends on your trading strategy. How much you earn depends on how volatile the stock market currently is, the strike price, and the expiration date.
How do you calculate profit on a put option?
To calculate profits or losses on a put option use the following simple formula: Put Option Profit/Loss = Breakeven Point – Stock Price at Expiration.
Why do you buy put options?
Investors may buy put options when they are concerned that the stock market will fall. That's because a put—which grants the right to sell an underlying asset at a fixed price through a predetermined time frame—will typically increase in value when the price of its underlying asset goes down.
What does closing a short put mean?
Opening a position is self-explanatory, and closing a position simply means buying back puts that you had sold to open earlier. Long Put. Image by Julie Bang © Investopedia 2019.
What is the breakeven point of a $95 strike put?
The breakeven point of a $95-strike long put (bought for $3) at expiration is $92 per share ($95 strike price minus the $3 premium). At that price, the stock can be bought in the market at $92 and sold through the exercise of the put at $95, for a profit of $3. The $3 covers the cost of the put and the trade is a wash.
What is a protective put?
A protective put is used to hedge an existing position while a long put is used to speculate on a move lower in prices. The price of a long put will vary depending on the price of the stock, the volatility of the stock, and the time left to expiration. Long puts can be closed out by selling or by exercising the contract, ...
Can you buy a put option if you own a stock?
So, whether you own a portfolio of stocks, or you simply want to bet that the market will go down, you can benefit from buying a put option.
Can you buy puts on short sales?
The profit equals the sale price minus the purchase price. In some cases, an investor can buy puts on stocks that cannot be found for short sales.
What happens when you sell put options?
Selling puts generates immediate portfolio income to the seller; puts keep the premium if the sold put is not exercised by the counterparty and it expires out-of-the-money. An investor who sells put options in securities that they want to own anyway will increase their chances of being profitable. Note that the writer of a put option will lose ...
What is a put option?
Selling (also called writing) a put option allows an investor to potentially own the underlying security at a future date and at a much more favorable price. In other words, the sale of put options allows market players to gain bullish exposure, with the added benefit of potentially owning the underlying security at a future date ...
What is the difference between selling a call and a put?
Selling a call: You have an obligation to deliver the security at a predetermined price to the option buyer if they exercise the option. Buying a put: You have the right to sell a security at a predetermined price. Selling a put: You have an obligation to buy the security at a predetermined price from the option buyer if they exercise the option.
What is the difference between a call and a put option?
Buying a call option gives the holder the right to own the security at a predetermined price, known as the option exercise price . Conversely, buying a put option gives the owner the right to sell the underlying security at the option exercise price. Thus, buying a call option is a bullish bet–the owner makes money when the security goes up.
Why is the ability to generate portfolio income at the top of this list important?
The ability to generate portfolio income sits at the top of this list because the seller keeps the entire premium if the sold put expires without exercise by the counterparty. Another key benefit is the opportunity to own the underlying security at a price below the current market price.
How much is one option contract?
One option contract covers 100 shares , allowing you to collect $3,000 in options premium over time (less commission). By selling this option, you're agreeing to buy 100 shares of Company A for $250, no later than January, two years from now.
What happens if an option expires?
If the option expires worthless, you get to keep the $30 per share premium, which represents a 12% return on a $250 buy price. It can be very attractive to sell puts on securities that you want to own. If Company A declines, you'll be required to pay $25,000 in order to purchase the shares at $250.
Why do you put a put on a stock?
A stockholder can purchase a "protective" put on an underlying stock to help hedge or offset the risk of the stock price falling because the put gains from a decline in stock prices. But investors don't have to own the underlying stock to buy a put.
What happens if a stock stays at the strike price?
The seller will be put the stock and must buy it at the strike price. If the stock stays at the strike price or above it, the put is out of the money, so the put seller pockets the premium. The seller can write another put on the stock, if the seller wants to try to earn more income. Here’s an example.
What does a put seller do?
Put sellers make a bullish bet on the underlying stock and/or want to generate income. If the stock declines below the strike price before expiration, the option is in the money.
What is put option?
A put option is a contract that gives the owner the option, but not the requirement, to sell a specific underlying stock at a predetermined price (known as the “strike price”) within a certain time period (or “expiration”). For this option to sell the stock, the put buyer pays a "premium" per share to the put seller.
Why is an in the money put option considered intrinsic value?
An in-the-money put option has "intrinsic value" because the market price of the stock is lower than the strike price. The buyer has two choices: First, if the buyer owns the stock, the put option contract can be exercised, putting the stock to the put seller at the strike price.
Why are put options so popular?
Put options remain popular because they offer more choices in how to invest and make money. One lure for put buyers is to hedge or offset the risk of an underlying stock's price falling. Other reasons to use put options include:
Can you exercise a put option at the strike price?
For a put buyer, if the market price of the underlying stock moves in your favor, you can elect to "exercise" the put option or sell the underlying stock at the strike price. American-style options allow the put holder to exercise the option at any point up to the expiration date. European-style options can be exercised only on the date ...
Options trading differs from stock trading
Options trading gives the investor the right to buy or sell an underlying asset for a specific price. Options involve contracts that the buyer pays a premium for. There are also puts and calls in this type of trading. Options trading isn't to be confused with trading stocks.
What are put options and how do investors sell them?
Put options are either in the money or out of the money. A put is in the money if the market price is under the strike price. The owner of the put can sell the asset for more than the current market price. Puts are out of the money if the stock stays at or rises above the strike price, which causes the put to likely expire worthless.
What is a put in options trading?
As of Oct. 11, Moderna Inc. (NASDAQ:MRNA) had a relatively high put-call ratio of 0.7, which means the number of put options is equal to about 70 percent of the call options on MRNA stock for the contract ending Oct. 15.
How puts work in the options market
Puts have an inverse relationship with stocks. Put contracts increase in value when the associated stock falls in value. Someone with a put contract must buy the stock at a specified strike price, which is lower than the stock's current price. However, they don't need to buy the stock until they exercise the put contract.
Knowing when to buy (and sell) puts
Traders buy puts when they expect a stock's value to fall to a lower strike price by a certain date. Both the price and date must be specified in order to conduct the trade.
How to buy puts
If you have access to an options brokerage account, you're technically ready to buy puts. You will need to identify:
What does it mean to buy uncovered puts?
You don't have to own the shares you buy put contracts with until you exercise the position. Puts can be based on an individual stock or index. Buying an uncovered put (or "naked put") means holding off on purchasing the underlying asset until you're ready to exercise. There is more risk involved in this strategy than with a covered put.
What happens when you sell a short put?
When you sell a short put, you pick the strike price that offers the balance of profit potential and risk that best suits you. The deeper OTM the put is, the lower the profit potential and the more the the underlying can drop before you are at risk.
Do you pay more than the FMV when selling put options?
Note that when you sell put options, you will always pay more than the FMV at the moment the option is exercised. If the strike is below the FMV, the option will not be exercised. You make your profit selling options from the premium. The same is true in reverse when selling call options.
What is the most important position to sell ITM puts on a dog?
Most important is your delta position. At the end of the day, it doesn’t matter what volatility data you are looking at if you sell ITM puts on a dog. If we are not moderately bullish on the underlying there is no need to place an order or continue to hold a position.
Can I unsubscribe from money puts?
You can unsubscribe at any time. Chances are if you are an average investor you have not considered selling in the money puts. Though ironically, you may have already placed similar trades in the past. This article will explain the basics of the trade.

Speculative Long Puts vs. Protective Puts
Practical Considerations
- Besides buying puts, another common strategy used to profit from falling share prices is to sell stock short. Short sellers borrow the shares from their brokerand then sell the shares. If the price falls, the stock is bought back at the lower price and returned to the broker. The profit equals the sale price minus the purchase price. In some cases, an investor can buy puts on stocks that can…
An Example: Puts at Work
- Let's consider stock ABC, which trades for $100 per share. Its one-month puts, which have a $95 strike price, trade for $3. An investor who thinks that the price of ABC shares are too high and due to fall within the next month can buy the puts for $3. In such a case, the investor pays $300 ($3 option quote x 100, which is known as the multiplierand represents how many shares one optio…
Close vs. Exercise
- Closing out a long put position on stock involves either selling the put (sell to close) or exercising it. Let us assume that you are long the ABC puts from the previous example, and the current price on the stock is $90, so the puts now trade at $5. In this case, you can sell the puts for a profit of $200 ($500-$300). If you wished to exercisethe ...
Call Options vs. Put Options
Best Practices For Selling Put Options
- Investors should only sell put options if they’re comfortable owning the underlying security at the predetermined price, because you’re assuming an obligation to buy if the counterparty chooses to exercise the option. In addition, you should only enter trades where the net price paid for the underlying security is attractive. This is the most important consideration in selling put options p…
Put Selling in Practice
- Let’s look at an example of prudent put selling. Suppose that Company A is dazzling investors with increasing profits as a result of a new, revolutionary product. Company A’s stock is currently trading at $270, and the price-to-earnings ratio is at an extremely reasonable valuationfor this company’s fast growth track. If you’re bullish about their ...
The Bottom Line
- The sale of put options can generate additional portfolio income while potentially gaining exposure to securities that you would like to own but at a price below the current market price.