
Any one-day market decline of 10% or more in a single day is generally described as a market crash. A steep market decline on a key index, like the Dow
Dow Jones Industrial Average
The Dow Jones Industrial Average, or simply the Dow, is a stock market index that indicates the value of 30 large, publicly owned companies based in the United States, and how they have traded in the stock market during various periods of time. These 30 companies are also included in the S&…
What is a stock market crash?
Jan 02, 2022 · A stock market crash is a steep and sudden collapse in the price of a stock or the broader stock market. ... they are generally considered as abrupt double-digit percentage drop in a …
What is the threshold for a stock market crash?
Mar 03, 2022 · A stock market crash depicts a situation when a broad index experienced a drastic decline (usually a double-digit one) along with other financial-related indices. This happens due to the stock market being influenced by volatility in a great way. As a result, we can observe the market tribulation either in the short or in the long-term period.
How many stock market crashes have there been since 1950?
Oct 24, 2021 · A stock market crash occurs when a market index drops severely in a day, or a few days, of trading. The main indexes in the United States are the Dow Jones Industrial Average, the S&P 500, and the Nasdaq. A crash is more sudden than a stock market correction, which occurs when the market falls 10% from its 52-week high over days, weeks, or even months. 1 Each of …
Should you sell during a stock market crash?
Oct 25, 2015 · A crash is defined as an index dropping at least 50% from some previous high. Smaller drops in the market between 20% and 50% are called "Bear Markets."
How much does the stock market have to drop to be a crash?
What is a 5% market drop called?
Can a stock fall more than 20%?
What percentage did the stock market fall in 2008?
What is a 20% correction called?
How long does it take the stock market to recover after a crash?
Do I owe money if my stock goes down?
Do you owe money if your stock goes negative?
Where should I put my money before the market crashes?
What percent did the stock market drop in the Great Depression?
How long did it take the stock market to recover from the 1929 crash?
What is the highest the stock market has ever been?
How long did it take the stock market to recover from the 1987 crash?
Unlike the 1929 stock market crash, which took almost 25 years to recover, the 1987 market started recovering almost immediately. There were no long-lasting effects on the US economy. The Dow recovered all their stock market losses by September 1989.
What was the stock market crash of 1929?
The stock market crash of 1929 began when the market opened 11% lower than the previous day’s close. 25% was the unemployment rate during the Great Depression. With more than $200 million in deposits, New York’s Bank of the United States collapsed in 1931.
What happened between 1929 and 1932?
Between September 1929 and June 1932, the Composite Price Index fell by 86%, hitting an all-time low, as the 1929 stock market crash chart shows. The stock market crash was one of the leading causes of the Great Depression. As a result, financial markets took a few years to recover from this period (from 1932 to 1937).
What happened in 2008?
The 2008 market crash increased the unemployment rate to 10%. From 2007 to 2009, the Great Recession destroyed a $16.4 trillion net household wealth in America. The stock market crashes are common but unpredictable.
How much wealth did the Great Recession destroy?
From 2007 to 2009, the Great Recession destroyed a $16.4 trillion net household wealth in America. The stock market crashes are common but unpredictable. Keep scrolling to learn more about the biggest financial crises in US history, the consequences, what caused them, and how the economy eventually recovered.
What was the day of Black Thursday?
October 24, 1929 , is marked in history as “Black Thursday.” Various financiers and institutions tried to stop the panic by bidding above the market price. The day’s losses were minimal, and stocks appeared to have bounced back over the following two days.
What happened in the roaring 20s?
During the “Roaring Twenties,” the American stock market was booming. The economy expanded rapidly, and stocks hit an all-time high. Likewise, the market peaked when the Dow hit 381 points.
What is a stock market crash?
A stock market crash is a sudden dramatic decline of stock prices across a major cross-section of a stock market, resulting in a significant loss of paper wealth. Crashes are driven by panic selling and underlying economic factors. They often follow speculation and economic bubbles. A stock market crash is a social phenomenon where external ...
What caused the stock market to crash in 1907?
In 1907 and in 1908, stock prices fell by nearly 50% due to a variety of factors, led by the manipulation of copper stocks by the Knickerbocker Trust Company. Shares of United Copper rose gradually up to October, and thereafter crashed, leading to panic. Several investment trusts and banks that had invested their money in the stock market fell and started to close down. Further bank runs were prevented due to the intervention of J. P. Morgan. The panic continued to 1908 and led to the formation of the Federal Reserve in 1913.
How much did the stock market rise in 1929?
By September 3, 1929, it had risen more than sixfold to 381.2. It did not regain this level for another 25 years. By the summer of 1929, it was clear that the economy was contracting, and the stock market went through a series of unsettling price declines.
What happened in 1929?
By the summer of 1929, it was clear that the economy was contracting, and the stock market went through a series of unsettling price declines. These declines fed investor anxiety, and events came to a head on October 24, 28, and 29 (known respectively as Black Thursday, Black Monday, and Black Tuesday).
What were the consequences of the 1987 crash?
One of the consequences of the 1987 Crash was the introduction of the circuit breaker or trading curb on the NYSE. Based upon the idea that a cooling off period would help dissipate panic selling, these mandatory market shutdowns are triggered whenever a large pre-defined market decline occurs during the trading day .
What was the first economic bubble?
Tulip Mania (1634-1637), in which some single tulip bulbs allegedly sold for more than 10 times the annual income of a skilled artisan, is often considered to be the first recorded economic bubble.
What happened on October 11, 2008?
On October 11, 2008, the head of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) warned that the world financial system was teetering on the "brink of systemic meltdown". The economic crisis caused countries to close their markets temporarily. On October 8, the Indonesian stock market halted trading, after a 10% drop in one day.
What is a stock market crash?
A stock market crash occurs when there is a significant decline in stock prices. While there's no specific numeric definition of a stock market crash, the term usually applies to occasions in which the major stock market indexes lose more than 10% of their value in a relatively short time period. Market crashes typically happen without warning, ...
What was the worst stock market crash in history?
The worst stock market crash in history started in 1929 and was one of the catalysts of the Great Depression. The crash abruptly ended a period known as the Roaring Twenties, during which the economy expanded significantly and the stock market boomed.
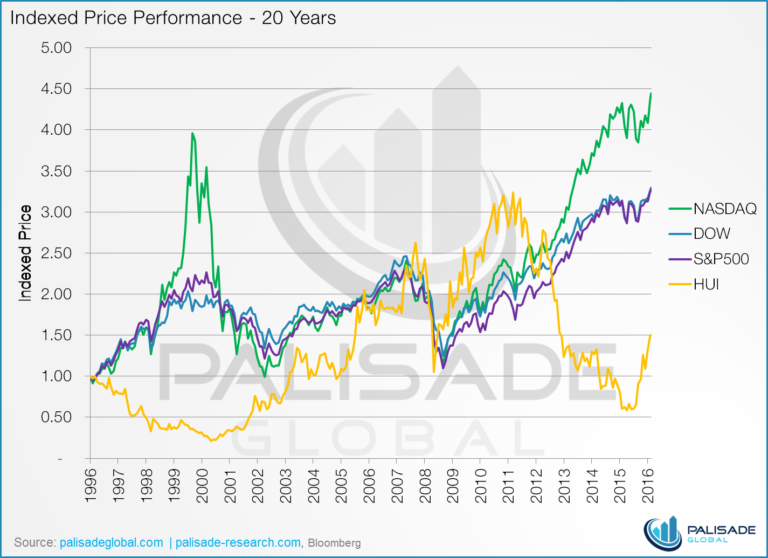
When did the dot-com bubble burst?
As a result, the technology-dominated NASDAQ Composite Index (NASDAQINDEX: ^IXIC) surged from 1,000 points in 1995 to more than 5,000 in 2000. But in early 2001, the dot-com stock bubble started to burst.
Why did the Dow drop in 1929?
The Dow didn't regain its pre-crash value until 1954. The primary cause of the 1929 stock market crash was excessive leverage. Many individual investors and investment trusts had begun buying stocks on margin, meaning that they paid only 10% of the value of a stock to acquire it under the terms of a margin loan.
What happened on Oct 19 1987?
On Monday, Oct. 19, 1987, the Dow Jones Industrial Average plunged by nearly 22%. Black Monday, as the day is now known, marks the biggest single-day decline in stock market history. The remainder of the month wasn't much better; by the start of November, 1987, most of the major stock market indexes had lost more than 20% of their value.
When did the Dow Jones Industrial Average rise?
The Dow Jones Industrial Average ( DJINDICES:^DJI) rose from 63 points in August, 1921, to 381 points by September of 1929 -- a six-fold increase. It started to descend from its peak on Sept. 3, before accelerating during a two-day crash on Monday, Oct. 28, and Tuesday, Oct. 29.
What was the cause of the 1929 stock market crash?
The primary cause of the 1929 stock market crash was excessive leverage. Many individual investors and investment trusts had begun buying stocks on margin, meaning that they paid only 10% of the value of a stock to acquire it under the terms of a margin loan.
What is a stock market crash?
A stock market crash occurs when a market index drops severely in a day, or a few days, of trading. The main indexes in the United States are the Dow Jones Industrial Average, the S&P 500, and the Nasdaq. A crash is more sudden than a stock market correction, which is when the market falls 10% from its 52-week high over days, weeks, or even months.
Can a stock market crash cause a recession?
A stock market crash can also cause a recession. 5. Stocks are an important source of capital that corporations use to manage and grow their businesses. If stock prices fall dramatically, corporations have less ability to grow. Firms that don't produce will eventually lay off workers in order to stay solvent.
Is gold a hedge against a stock market crash?
Gold Can Be a Hedge. Gold may be the best hedge against a potential stock market crash. A study done by researchers at Trinity College found that, for 15 days after a crash, gold prices increased dramatically. 6 Frightened investors panicked, sold their stocks, and bought gold.
Who is Thomas Brock?
Thomas Brock is a well-rounded financial professional, with over 20 years of experience in investments, corporate finance, and accounting. A stock market crash occurs when a market index drops severely in a day, or a few days, of trading.
How to protect yourself from a recession?
Protect Yourself by Rebalancing. Rebalance your portfolio as market conditions change. If you've done this well, then you've sold off stocks when they gained in value. If the economy does enter a recession, continued rebalancing means that you will buy stocks when the prices are down.
What happens when the economy goes into recession?
If the economy does enter a recession, continued rebalancing means that you will buy stocks when the prices are down. When they go up again, as they always do, you will profit from the upswing in stock prices. Rebalancing a diversified portfolio is the best way to protect yourself from a crash.
Who is Kimberly Amadeo?
Kimberly Amadeo is an expert on U.S. and world economies and investing, with over 20 years of experience in economic analysis and business strategy. She is the President of the economic website World Money Watch.
The Financial Crisis of 2007-2008
On 11/20/2008, the S&P 500 was at 752.44, down -51.93% from its previous high on 10/9/2007 at 1,565.15. The following day, the markets rose and the S&P 500 was down less than 50% from its prior peak until 2/19/2009 when the S&P 500 was at 778.94, down -50.23%. By then the markets had been dropping for 499 days or 1.4 years.
The Technology Bubble of 2000-2002
Toward the end of the Dot Com Technology Bubble, the S&P 500 Price Index bottomed on 10/9/2002, down -49.15% from its previous high on 3/24/2000.
The Flash Crash of 2010
After investors and their advisors experienced the precipitous market drop during the fall of 2008, many people searched for ways to protect their assets.
Conclusion
While they do happen, market crashes are unlikely. Crashes in smaller indexes or sectors are more common than large ones like the S&P 500 because smaller indexes are more volatile.
What is a stock crash?
Stock Market Crash is a strong price decline across majority of stocks on the market which results in the strong decline over short period on the major market indexes (NYSE Composite, Nasdaq Composite DJIA and S&P 500).
How much wealth was lost in the 1929 stock market crash?
The Crash of 1929. In total, 14 billion dollars of wealth were lost during the market crash. On September 4, 1929, the stock market hit an all-time high. Banks were heavily invested in stocks, and individual investors borrowed on margin to invest in stocks.
What happened to the stock market in 1929?
Banks were heavily invested in stocks, and individual investors borrowed on margin to invest in stocks. On October 29, 1929, the stock market dropped 11.5%, bringing the Dow 39.6% off its high. After the crash, the stock market mounted a slow comeback. By the summer of 1930, the market was up 30% from the crash low.
When did the Dow hit a new high?
The markets hit a new high on August 25, 1987 when the Dow hit a record 2722.44 points. Then, the Dow started to head down. On October 19, 1987, the stock market crashed. The Dow dropped 508 points or 22.6% in a single trading day. This was a drop of 36.7% from its high on August 25, 1987.
When did the Dow drop?
The Dow dropped 508 points or 22.6% in a single trading day. This was a drop of 36.7% from its high on August 25, 1987.
How much did the Dow drop in 1987?
On October 19, 1987, the stock market crashed. The Dow dropped 508 points or 22.6% in a single trading day. This was a drop of 36.7% from its high on August 25, 1987.
How much did the NASDAQ drop in 2000?
On September 1, 2000, the NASDAQ traded at 4234.33. From September 2000 to January 2, 2001, the NASDAQ dropped 45.9%.
Overview
Examples
- What were the biggest stock market crashes by percentage?
The top three are: 1. The Wall Street Crash (1929) was the biggest crash by percentage, with -33.6%. 2. Black Monday (1987) took second place with -31.3%. 3. End of Gold Standard (1931) is the “lucky” third contestant with -26.7%. Honourable mentions: 1. Lehman Crisis (2008): -25.2% 2… - How many times has the stock market crashed?
The stock market has witnessed eight big crashes so far. The first one happened in 1907 when investors borrowed the bank’s money to finance the shares of UCC (United Copper Company). The stock value loss amounted to 15%–20% of their value. The following one was the biggest on the …
Historical background
Mathematical theory
Trading curbs and trading halts
Tulip Mania (1634-1637), in which some single tulip bulbs allegedly sold for more than 10 times the annual income of a skilled artisan, is often considered to be the first recorded economic bubble.
In 1907 and in 1908, stock prices fell by nearly 50% due to a variety of factors, led by the manipulation of copper stocks by the Knickerbocker Trust Company. …
See also
Business ventures with multiple shareholders became popular with commenda contracts in medieval Italy and shareholder companies date back to ancient Rome.
The world's first stock market was that of 17th-century Amsterdam, where an active secondary market in company sharesemerged. The two major companie…
Further reading
The conventional assumption is that stock markets behave according to a random log-normal distribution. Among others, mathematician Benoit Mandelbrotsuggested as early as 1963 that the statistics prove this assumption incorrect. Mandelbrot observed that large movements in prices (i.e. crashes) are much more common than would be predicted from a log-normal distribution. Mandelbrot and others suggested that the nature of market moves is generally much better expl…
External links
One mitigation strategy has been the introduction of trading curbs, also known as "circuit breakers", which are a trading halt in the cash market and the corresponding trading halt in the derivative markets triggered by the halt in the cash market, all of which are affected based on substantial movements in a broad market indicator. Since their inception after Black Monday (1987), trading curbs have been modified to prevent both speculative gains and dramatic losse…