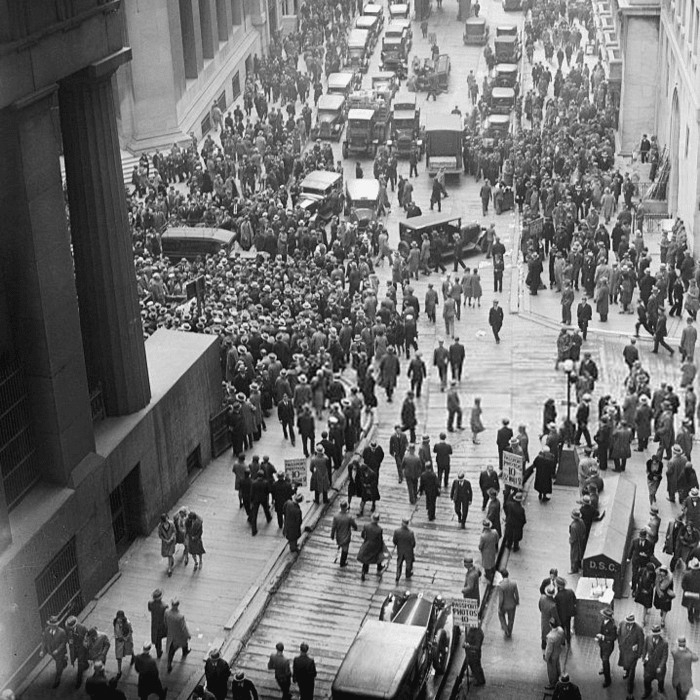What Caused the Stock Market Crash of 1929?
- A Stock Market Peak Occurred Before the Crash. During the “ Roaring Twenties ”, the U.S. ...
- The Market—And People—Were Overconfident. ...
- People Bought Stocks With Easy Credit. ...
- The Government Raised Interest Rates. ...
- Panic Made the Situation Worse. ...
- There Was No Single Cause for the Turmoil. ...
Why did the US Stock Exchange collapse in 1929?
What caused the Wall Street crash of 1929? The main cause of the Wall Street crash of 1929 was the long period of speculation that preceded it, during which millions of people invested their savings or borrowed money to buy stocks, pushing prices to unsustainable levels.
What caused the stock market crash of 1929?
What Caused the Stock Market Crash of 1929? The stock market crash of 1929 was largely caused by bad stock market investments, low wages, a crumbling agricultural sector and high amounts of debt that could not be liquidated.
How much did stocks drop in 1929?
On September 4, 1929, the stock market hit an all-time high. Banks were heavily invested in stocks, and individual investors borrowed on margin to invest in stocks. On October 29, 1929, the stock market dropped 11.5%, bringing the Dow 39.6% off its high. After the crash, the stock market mounted a slow comeback.
What caused the run on banks in 1929?
The run on America’s banks began immediately following the stock market crash of 1929. Overnight, hundreds of thousands of customers began to withdraw their deposits. With no money to lend and loans going sour as businesses and farmers went belly up, the American banking crisis deepened. After taking office in March 1933, Franklin D ...

What caused 1929 stock market crash?
The main cause of the Wall Street crash of 1929 was the long period of speculation that preceded it, during which millions of people invested their savings or borrowed money to buy stocks, pushing prices to unsustainable levels.
What were three major causes of the crash of 1929?
What were the major causes of the Great Depression? Among the suggested causes of the Great Depression are: the stock market crash of 1929; the collapse of world trade due to the Smoot-Hawley Tariff; government policies; bank failures and panics; and the collapse of the money supply.
What were the 4 main causes of the Great Depression?
However, many scholars agree that at least the following four factors played a role.The stock market crash of 1929. During the 1920s the U.S. stock market underwent a historic expansion. ... Banking panics and monetary contraction. ... The gold standard. ... Decreased international lending and tariffs.
What were the 5 causes of the Great Depression?
of 05. Stock Market Crash of 1929. Workers flood the streets in a panic following the Black Tuesday stock market crash on Wall Street, New York City, 1929. ... of 05. Bank Failures. ... of 05. Reduction in Purchasing Across the Board. ... of 05. American Economic Policy With Europe. ... of 05. Drought Conditions.
What were the causes of the 1929 stock market crash?
Among the other causes of the stock market crash of 1929 were low wages, the proliferation of debt, a struggling agricultural sector and an excess of large bank loans that could not be liquidated.
What was the stock market crash of 1929?
The stock market crash of 1929 was not the sole cause of the Great Depression, but it did act to accelerate the global economic collapse ...
What happened to stock market in 1929?
Stock prices began to decline in September and early October 1929, and on October 18 the fall began. Panic set in, and on October 24, Black Thursday, a record 12,894,650 shares were traded. Investment companies and leading bankers attempted to stabilize the market by buying up great blocks of stock, producing a moderate rally on Friday. On Monday, however, the storm broke anew, and the market went into free fall. Black Monday was followed by Black Tuesday (October 29, 1929), in which stock prices collapsed completely and 16,410,030 shares were traded on the New York Stock Exchange in a single day. Billions of dollars were lost, wiping out thousands of investors, and stock tickers ran hours behind because the machinery could not handle the tremendous volume of trading.
What happened on October 29, 1929?
On October 29, 1929, Black Tuesday hit Wall Street as investors traded some 16 million shares on the New York Stock Exchange in a single day. Billions of dollars were lost, wiping out thousands of investors. In the aftermath of Black Tuesday, America and the rest of the industrialized world spiraled downward into the Great Depression (1929-39), ...
What happened after Black Tuesday?
In the aftermath of Black Tuesday, America and the rest of the industrialized world spiraled downward into the Great Depression (1929-39), the deepest and longest-lasting economic downturn in the history of the Western industrialized world up to that time .
When did stock prices drop in 1929?
Stock prices began to decline in September and early October 1929 , and on October 18 the fall began. Panic set in, and on October 24, Black Thursday, a record 12,894,650 shares were traded.
When did the stock market peak?
During the 1920s, the U.S. stock market underwent rapid expansion, reaching its peak in August 1929 after a period of wild speculation during the roaring twenties. By then, production had already declined and unemployment had risen, leaving stocks in great excess of their real value.
What was the 1929 stock market crash?
The Wall Street crash of 1929, also called the Great Crash, was a sudden and steep decline in stock prices in the United States in late October of that year.
What caused the stock market to go down in 1929?
Other causes included an increase in interest rates by the Federal Reserve in August 1929 and a mild recession earlier that summer, both of which contributed to gradual declines in stock prices in September and October, eventually leading investors to panic. During the mid- to late 1920s, the stock market in the United States underwent rapid ...
What was the Great Depression?
Stock market crash of 1929, also called the Great Crash, a sharp decline in U.S. stock market values in 1929 that contributed to the Great Depression of the 1930s. The Great Depression lasted approximately 10 years and affected both industrialized and nonindustrialized countries in many parts of the world. Crowds gathering outside the New York ...
Why did people sell their Liberty bonds?
People sold their Liberty Bonds and mortgaged their homes to pour their cash into the stock market. In the midsummer of 1929 some 300 million shares of stock were being carried on margin, pushing the Dow Jones Industrial Average to a peak of 381 points in September.
What was the cause of the 1929 Wall Street crash?
The main cause of the Wall Street crash of 1929 was the long period of speculation that preceded it , during which millions of people invested their savings or borrowed money to buy stocks, pushing prices to unsustainable levels. Other causes included an increase in interest rates by the Federal Reserve in August 1929 and a mild recession earlier ...
How many points did the Dow close down?
Still, the Dow closed down only six points after a number of major banks and investment companies bought up great blocks of stock in a successful effort to stem the panic that day. Their attempts, however, ultimately failed to shore up the market. The panic began again on Black Monday (October 28), with the market closing down 12.8 percent.
What lessons did the Federal Reserve learn from the 1929 stock market crash?
9. First, central banks – like the Federal Reserve – should be careful when acting in response to equity markets. Detecting and deflating financial bubbles is difficult.
What happened in 1929?
Commercial banks continued to loan money to speculators, and other lenders invested increasing sums in loans to brokers. In September 1929, stock prices gyrated, with sudden declines and rapid recoveries.
How much did the Dow drop in 1932?
The slide continued through the summer of 1932, when the Dow closed at 41.22, its lowest value of the twentieth century, 89 percent below its peak.
What happened on Black Monday 1929?
On Black Monday, October 28, 1929, the Dow Jones Industrial Average declined nearly 13 percent. Federal Reserve leaders differed on how to respond to the event and support the financial system.
When did the Dow Jones Industrial Average increase?
The Dow Jones Industrial Average increased six-fold from sixty-three in August 1921 to 381 in September 1929 . After prices peaked, economist Irving Fisher proclaimed, “stock prices have reached ‘what looks like a permanently high plateau.’” 2. The epic boom ended in a cataclysmic bust.
Who created the Dow Jones Industrial Average?
Dow Jones Industrial Average (Created by: Sam Marshall, Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond) Enlarge. The financial boom occurred during an era of optimism. Families prospered. Automobiles, telephones, and other new technologies proliferated. Ordinary men and women invested growing sums in stocks and bonds.
Who published a monetary history of the United States in 1963?
Consensus coalesced around the time of the publication of Milton Friedman and Anna Schwartz’ s A Monetary History of the United States in 1963.
What was the cause of the 1929 stock market crash?
Cause. Fears of excessive speculation by the Federal Reserve. The Wall Street Crash of 1929, also known as the Great Crash, was a major American stock market crash that occurred in the autumn of 1929. It started in September and ended late in October, when share prices on the New York Stock Exchange collapsed.
How did the stock market crash of 1929 affect the world?
The stock market crash of October 1929 led directly to the Great Depression in Europe. When stocks plummeted on the New York Stock Exchange, the world noticed immediately. Although financial leaders in the United Kingdom, as in the United States, vastly underestimated the extent of the crisis that ensued, it soon became clear that the world's economies were more interconnected than ever. The effects of the disruption to the global system of financing, trade, and production and the subsequent meltdown of the American economy were soon felt throughout Europe.
How many points did the Dow Jones Industrial Average recover from the 1929 crash?
The Dow Jones Industrial Average recovered, closing with it down only 6.38 points for the day. The trading floor of the New York Stock Exchange Building in 1930, six months after the crash of 1929.
What was the prediction of the Great Bull Market?
The optimism and the financial gains of the great bull market were shaken after a well-publicized early September prediction from financial expert Roger Babson that "a crash is coming, and it may be terrific". The initial September decline was thus called the "Babson Break" in the press.
What was the biggest stock crash in 1929?
The Great Crash is mostly associated with October 24, 1929, called Black Thursday, the day of the largest sell-off of shares in U.S. history, and October 29, 1929, called Black Tuesday, when investors traded some 16 million shares on the New York Stock Exchange in a single day.
Why did wheat prices fall in August?
In August, the wheat price fell when France and Italy were bragging about a magnificent harvest, and the situation in Australia improved. That sent a shiver through Wall Street and stock prices quickly dropped, but word of cheap stocks brought a fresh rush of "stags", amateur speculators, and investors.
What happened to the stock market in 1929?
On September 20, 1929, the London Stock Exchange crashed when top British investor Clarence Hatry and many of his associates were jailed for fraud and forgery. The London crash greatly weakened the optimism of American investment in markets overseas: in the days leading up to the crash, the market was severely unstable.
How many times did stock prices go up in 1929?
Until the peak in 1929, stock prices went up by nearly 10 times. In the 1920s, investing in the stock market became somewhat of a national pastime for those who could afford it and even those who could not—the latter borrowed from stockbrokers to finance their investments. The economic growth created an environment in which speculating in stocks ...
What happened in 1929?
In October of 1929, the stock market crashed, wiping out billions of dollars of wealth and heralding the Great Depression. Known as Black Thursday, the crash was preceded by a period of phenomenal growth and speculative expansion. A glut of supply and dissipating demand helped lead to the economic downturn as producers could no longer readily sell ...
Why did companies acquire money cheaply?
Essentially, companies could acquire money cheaply due to high share prices and invest in their own production with the requisite optimism. This overproduction eventually led to oversupply in many areas of the market, such as farm crops, steel, and iron.
What was the result of the Great War?
The result was a series of legislative measures by the U.S. Congress to increase tariffs on imports from Europe.
What happens when the stock market falls?
However, when markets are falling, the losses in the stock positions are also magnified. If a portfolio loses value too rapidly, the broker will issue a margin call, which is a notice to deposit more money to cover the decline in the portfolio's value.
Why did the economy stumbled in 1929?
In mid-1929, the economy stumbled due to excess production in many industries, creating an oversupply.
What happens if a broker doesn't deposit funds?
If the funds are not deposited, the broker is forced to liquidate the portfolio. When the market crashed in 1929, banks issued margin calls. Due to the massive number of shares bought on margin by the general public and the lack of cash on the sidelines, entire portfolios were liquidated.
What happened in 1929?
Updated September 02, 2020. The stock market crash of 1929 was a collapse of stock prices that began on Oct. 24, 1929. By Oct. 29, 1929, the Dow Jones Industrial Average had dropped 24.8%, marking one of the worst declines in U.S. history. 1 It destroyed confidence in Wall Street markets and led to the Great Depression .
What happened on September 26th 1929?
September 26: The Bank of England also raised its rate to protect the gold standard. September 29, 1929: The Hatry Case threw British markets into panic. 6. October 3: Great Britain's Chancellor of the Exchequer Phillip Snowden called the U.S. stock market a "speculative orgy.".
How much did the Dow rise in 1933?
On March 15, 1933, the Dow rose 15.34%, a gain of 8.26 points, to close at 62.1. 8. The timeline of the Great Depression tracks critical events leading up to the greatest economic crisis the United States ever had. The Depression devastated the U.S. economy.
What was the Dow down in 1932?
By July 8, 1932, the Dow was down to 41.22. That was an 89.2% loss from its record-high close of 381.17 on September 3, 1929. It was the worst bear market in terms of percentage loss in modern U.S. history. The largest one-day percentage gain also occurred during that time.
Why did banks honor 10 cents for every dollar?
That's because they had used their depositors' savings, without their knowledge, to buy stocks. November 23, 1954: The Dow finally regained its September 3, 1929, high, closing at 382.74. 8.
What was the stock market crash of 1929?
The stock market crash of 1929 followed an epic period of economic growth during what's now known as the Roaring Twenties. The Dow Jones Industrial Average ( DJINDICES:^DJI) was at 63 points in August 1921 and increased six-fold over the next eight years, closing at a high of 381.17 points on Sept. 3, 1929. That September day marked the peak of the ...
What happened to the stock market in 1929?
When the stock market crashed in September 1929, all of the entwined investment trusts similarly collapsed. In the wake of the crash, the banks and other lenders that financed the stock-buying spree had little means to collect what they were owed. Their only collateral was stocks for which the amount of debt outstanding exceeded the stocks' worth.
What was the total non-corporate debt in 1929?
By September 1929, total noncorporate debt in the U.S. amounted to 40% of the nation's Gross Domestic Product (GDP). At the same time that readily available credit was fueling consumer spending, the buoyant stock market gave rise to many new brokerage houses and investment trusts, which enabled the average person to buy stocks.
What happened after 1929?
The bursting of the stock market's bubble unleashed a cascade of market forces that plagued the U.S. economy for years after 1929 . The economy likely could have recovered more quickly in those ensuing years had the combined effects of excessive borrowing, business closures, and mass layoffs not exacerbated and prolonged the crisis.
What percentage of all consumer purchases were made on installment plans in 1927?
By 1927, 15% of all major consumer purchases were being made on installment plans. People in the 1920s acquired six of every 10 automobiles and eight of every 10 radios on credit.
When did the Dow drop?
By mid-November 1929, the Dow had declined by almost half. It didn't reach its lowest point until midway through 1932, when it closed at 41.22 points -- 89% below its peak. The Dow didn't return to its September 1929 high until November 1954.
What happens when investment trusts are heavily leveraged?
Some investment trusts, themselves heavily leveraged, also invested in other similarly leveraged investment trusts , which, in turn, invested in other investment trusts employing the same strategy. As a result, each of these trusts became inordinately affected by the movements of others' stock holdings. When the stock market crashed in September ...
How it started?
It all started after the end of World War I, when, as per the Versailles Treaty (which helped end World War I, and involved the Germans and other Central Powers to forcefully take the blame for World War I, thus implying loss of territories, reduction in military forces, and reparation payments to Allied powers), Germany had to pay a huge compensation as remunerations for the war.
The Stock Market Crash
Then in 1929, things changed, but for the worse. After the stock market crash of the US, the American banks called back their loans, and Germany’s already struggling economy, collapsed. Unemployment and poverty skyrocketed, and with no option left, people became desperate.
The rise of Nazis
The Nazis took advantage of this situation and even people at this desperate point readily accepted the rule of Nazis and even their extremist policies.