
What Is Vesting Stock?
- Employee Stock Options (ESOs) : For ESOs, when stock becomes fully vested, the employee has earned the right to an...
- Restricted Stock Units (RSUs) : For RSUs, when stock becomes fully vested, the employee has earned the ownership of the...
What is the best stock trading option?
Feb 02, 2021 · What Is Vesting Stock? Employee Stock Options (ESOs) : For ESOs, when stock becomes fully vested, the employee has earned the right to an... Restricted Stock Units (RSUs) : For RSUs, when stock becomes fully vested, the employee has earned the ownership of the...
How do I invest in stock options?
Jun 14, 2021 · What Is Stock Vesting? Stock vesting is another employer benefit that some companies offer. Companies can offer three main types of stock options: incentive stock options (ISOs), non-qualified stock options (NSOs), and/or restricted stock units (RSUs). Incentive Stock Options (ISOs) Incentive stock options qualify for special tax treatment.
When to exercise stock options?
A stock option vesting schedule refers to a schedule of how an employee earns their shares over time. For example, in Silicon Valley, the most popular form of vesting happens each month over a four year time period with a one-year cliff.
What does it mean to vest shares?
What Is the Meaning of Vesting Date in Stock Options? Employee Stock Options. All kinds of companies give their employees stock options as incentives. ... If the strike... Vesting Date. When you get an incentive stock option, you typically can't …
What does vesting mean for stock options?
Vesting is the process of earning an asset, like stock options or employer-matched contributions to your 401(k) over time. Companies often use vesting to encourage you to stay longer at the company and/or perform well so you can earn the award.Jul 11, 2019
Should I buy my vested options?
If you believe in your company's future prospects, you may want to hold on to your options. If your company's share price rises, your options' worth will continue to grow while putting off any tax consequences. This optionality or flexibility for a longer time frame gives your options even more value.Mar 18, 2022
Can you lose vested options?
Often, vested stock options expire if they are not exercised within the specified timeframe after service termination. Typically, stock options expire within 90 days of leaving the company, so you could lose them if you don't exercise your options.Jan 15, 2022
What happens if you don't exercise options?
If you don't exercise an out-of-the-money stock option before expiration, it has no value. If it's an in-the-money stock option, it's automatically exercised at expiration.Apr 24, 2019
When should I exercise stock options?
You have taxable income or deductible loss when you sell the stock you bought by exercising the option. You generally treat this amount as a capital gain or loss. However, if you don't meet special holding period requirements, you'll have to treat income from the sale as ordinary income.Jan 21, 2022
How do I cash out my vested stock?
Contact your company's plan administrator and indicate you'd like to cash out your stock. For a privately held company, the company must buy back your stock for a price set by an outside auditor. Complete the required paperwork and wait for your check.
Can a company take back vested stock options?
It may be couched in language such as “company repurchase rights,” “redemption” or “forfeiture.” But what it means is that the company can “claw back” your vested stock options before they become valuable.Jan 10, 2018
What happens to vested stock options when you quit?
When you leave, your stock options will often expire within 90 days of leaving the company. If you don't exercise your options, you could lose them.Mar 14, 2022
What is vesting stock?
In employee compensation, vesting stock refers to shares held by an employee that were granted either through employee stock options (ESOs) or restricted stock units (RSUs), that is not yet earned by the employee. Vesting is a legal term that means the point in time where property is earned or gained by some person.
When does stock become fully vested?
Before stock is fully vested, it is considered vesting stock . Vesting is commonly tied to time, but can also be tied to certain milestones. For example, vesting stock may become fully vested after four years, with shares becoming incrementally vested on shorter timeframes. Vesting stock can also become fully vested when an employee completes ...
What is vesting schedule?
A vesting schedule is the term in the stock-based grant that outlines when the stock will be considered vested and the employee earns the right to purchase or own the stock. For example, if you receive stock options with a vesting schedule of four years, after the four years you will have earned the right to purchase all ...
What is restricted stock option?
In practical terms, many employers grant stock options or restricted stock as part of their compensation plans that are accompanied with vesting schedules, which means the employee needs to hit certain achievements in order to gain the right to own the shares. Employee Stock Options (ESOs) : For ESOs, when stock becomes fully vested, ...
What is milestone based vesting?
Milestone-based Vesting: Milestone-based vesting is not tied to time, but rather a value-creating task completed by an employee that would trigger the shares to vest. One example of this may be a software developer completing a version one of a software product for their options to vest.
What is stock option?
Stock options are different than restricted stock, in the sense the employees earn the right to purchase the shares are a pre-set price, or exercise price. In order for the employee to exercise their options, the stock options will have need to vested.
What is hybrid vesting?
Hybrid vesting is simply a mix of the two. An employee will need to spend a certain amount of time at an employer AND complete certain value-creating tasks in order to earn the right to the shares.
What is cliff vesting?
Cliff vesting is the process that entitles an employee to their full benefits on a given date. For example, if a company has a two-year cliff vesting schedule, an employee will be 100% vested after 2 years of employment.
Do incentive stock options qualify for tax?
Incentive stock options qualify for special tax treatment. While you are not getting shares of the stock initially, you instead get the right to buy a set number of shares at a fixed price in the future.
What is vesting in stock?
What is Vesting? Vesting is the process by which an employee acquires a “vested interest” or stock option. Stock Option A stock option is a contract between two parties which gives the buyer the right to buy or sell underlying stocks at a predetermined price and within a specified time period.
When is stock option offered?
The stock option, equity, or employer-specific contribution is typically offered by the company when the employee has been at the organization for a given number of years. Employers may also make contributions to the 401 (k) retirement plan. for employees as part of the vesting process.
What is hybrid vesting?
Hybrid vesting is a combination of time-based vesting and milestone-based vesting. In this method, employees must stay at the company for a certain amount of time and reach a particular goal or milestone to be eligible for exercisable stock options.
What is time based vesting?
Time-based vesting is a method of vesting through which employees earn their share of stock options over time, usually based on a set schedule and a cliff – which is the time when the employee’s first option is granted and exercisable. After reaching the cliff, the remaining options are issued on a monthly or quarterly basis, depending on the vesting schedule.
Why is it important to vest a team?
For start-ups that highly depend on a small number of team members (say, a founder and co-founder) for success, vesting is an important way to protect the business and increase sustainability. By providing a time-based vesting schedule, team members can ensure loyalty and long-term security.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of stock options?
Advantages and Disadvantages for Employers. 1. Availability of cash. Stock options and equity are a form of compensation for employees and are also substitutes for cash bonuses and rewards. They enable the company to maintain a higher share of cash, which can be used to pay off current liabilities and in cases of emergency. 2.
What is an ESOP?
Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP) An Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP) refers to an employee benefit plan that gives the employees an ownership stake in the company . The employer allocates a percentage of the company’s shares to each eligible employee at no upfront cost.
How long are stock options vested?
The most regular schedule has an equal percentage of options vested each year for four years. In the case of qualified stock options, they're given through employee stock ownership plans and get monitored by the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974.
What is vesting schedule?
What is a Vesting Schedule? One of the main factors to think about when you set up a stock option plan is to create a vesting schedule. This defines when you can exercise any stock options or if there are forfeiture restrictions lapse on the stock that's restricted.
How long do ESOPs vest?
With cliff vesting, the options will vest 100 percent after five years of employment or all together.
What happens when you terminate restricted stock?
Termination will stop vesting with the exception of disability, retirement, or death, depending on what the grant and plan agreement is.
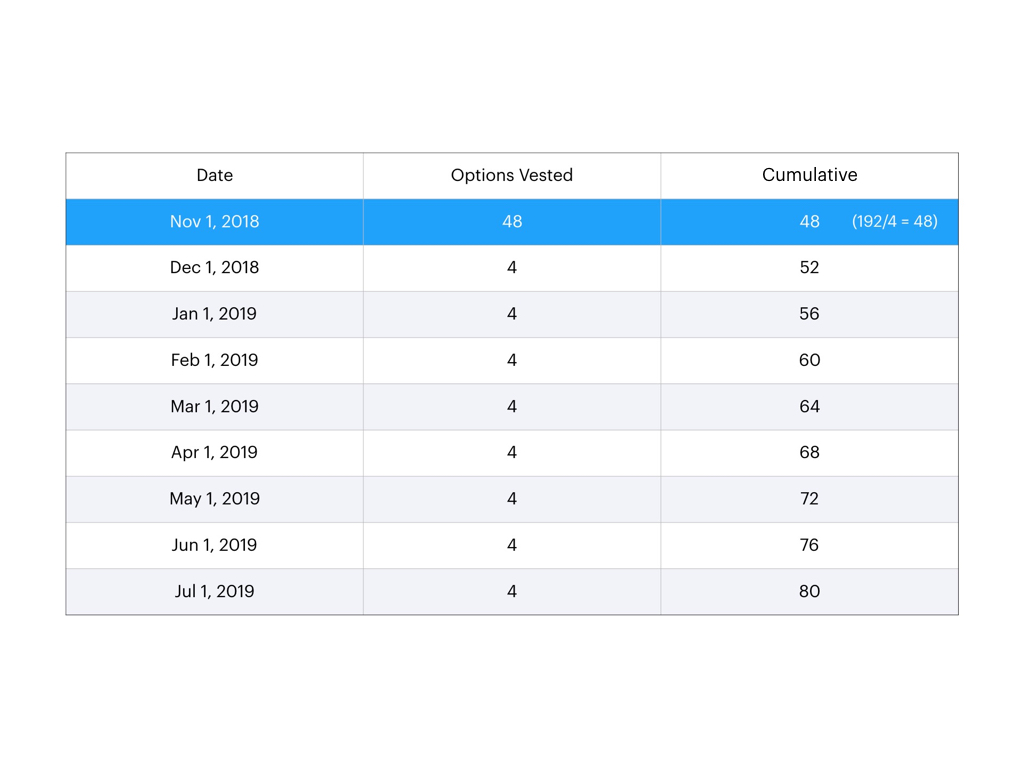
How long do you have to keep 1/48 stock?
This means you have the right to 1/48 of those shares that were granted each month over a four year period, or 48 months. However, if you leave the company before your one-year employment date, you won't get anything (known as going over the cliff).
How long do you have to exercise your shares?
Time to exercise shouldn't be confused with vesting. It's required by many companies to use your shares within 90 days of leaving your job and a maximum of 10 years from when they were granted even if you don't leave the company.
Is a stock option plan regulated?
Most stock option plans that are broad-based are non-qualified options. These aren't regulated as well as qualified stock options are and let the vesting schedule be more flexible. Companies that have stock option plans that are broad-based have a three- to five-year schedule where a specific percentage of options are vested every year.
How long do stock options vest?
Stock options "vest" according to a vesting schedule, and companies can set the schedules to reflect the kind of incentive they're trying to give. For example, a company could give you options on 6,000 shares that vest all at once in five years, which would be designed to keep you around for the long haul. Or you could get staggered options that reward you in stages, with, say, 100 options a month for five years. The company may let you exercise options immediately after each batch "vests," or only in stages, or you may not be able to exercise them until you either get fully vested or you leave the company.
Why do companies give employees stock options?
All kinds of companies give their employees stock options as incentives . An employee stock option gives you the opportunity to buy shares of your employer's stock at a predetermined "strike price.". If the strike price is lower than the market price of the stock at the time you can exercise the option, then you stand to make a nice profit.
How long do you have to work before you can vest your options?
This requires a specific period of time before any options vest at all. For example, you may have to work for a full year or two years before vesting begins, after which your options begin to vest on a regular schedule.
Can you use an incentive stock right away?
Vesting Date. When you get an incentive stock option, you typically can't use it right away. It wouldn't be much of an "incentive," after all, if your profit came baked right in and you could enjoy it immediately. You usually have to stay with the company a certain length of time to become eligible to exercise your options.
How long do non-founders vest their stock?
As I said before, non-founder employees typically vest their stock over four years. In some instances on the east coast I have seen companies require their employees to vest over five years, but I have never seen less than four years. Companies backed by buyout firms, who are not used to broadly sharing equity with employees, often require the strangest and most unfair vesting. Skype, which was acquired by Silver Lake Partners, took a lot of heat in 2011 because there was a clause buried in their option agreement that required employees to be employed by the company at the time of a liquidation event (sale or IPO) to qualify for their vesting. In other words employees who left after one and a half years into their four-year vesting got nothing when the company was acquired by Microsoft because they were no longer employees at the time the deal closed. That’s not the way vesting is supposed to work. You are supposed to get your share of the acquisition proceeds whether you are there at the time of the deal or not. Unfortunately Skype employees who left after their one year cliff thought they had vested their stock because that is the norm. The more non-standard the vesting the harder it usually is for a company to recruit outstanding people. Why should someone agree to five-year vesting if they can get four-year vesting across the street? Unfortunately some founders look at vesting through the lens of their desire to lockup employees and minimize their personal dilution and fail to see the unattractive and unfair nature inherent in the packages they offer.
How long do you have to exercise stock options?
Most companies require you to exercise your shares within 90 days of your departure (we covered the downside of this term in When Success & Stock Options Make It Expensive to Leave) and 7-10 years from the time of grant even if you stay with the company.
Do you vest stock after 4 years?
You don’t vest all your stock just because you stayed more than four years. The good news about follow on grants is that they typically don’t have a one-year cliff. The logic is you are already a known quantity, so there’s no need for another evaluation period.
Can unvested shares be put back into the pool?
Unvested shares can be put back into the pool and used to hire a replacement. Based on the argument raised above it should come as little surprise that founders typically get preferential vesting relative to regular employees.
What is gradual vesting?
The term describes the schedule in which an employee's benefits are paid (or "vested") all at once on a given date. Alternatively, vesting can happen over time on a defined schedule. This is known as gradual vesting. As an example, an employee’s stock options could vest either at a rate of 20% a year for five years (gradual vesting) ...
What is cliff vesting?
Cliff vesting is when an employee becomes fully vested on a specified date rather than becoming partially vested in increasing amounts over an extended period. Typically, plans have a four-year vesting schedule plan with a one-year cliff. Upon completing the cliff period, the employee receives full benefits.
What happens if you leave a company before you are fully vested?
Partial vesting would occur if the employee were considered 20% vested after two years of employment, 30% vested after three years of employment, and 100% vested after 10 years of employment. In a cliff vesting pension plan, if an employee leaves the company before becoming fully vested, they would not receive any retirement benefits. 1.
Why do companies give employees equity?
Companies often give their employees equity as part of their overall compensation package. Equity represents partial ownership of the company, and offering ownership is a way to incentivize employees—to encourage them to stay and to perform well. However, a company is unlikely to give an employee stock until they have earned it.
How long do you have to be at a company to exercise options?
Typically, an employee will be required to remain at the company for at least a year to exercise any options. For milestone vesting, an employee earns options or shares after completing a specific project or when the company or the employee reaches a business goal.
Is cliff vesting a risky proposition?
To a new employee, cliff vesting can seem like a risky proposition. The contract or arrangement could terminate for some reason just before the initial qualifying period is complete. For example, there may be a hostile takeover of the company or a buyout whereby new policies nullify the cliff.
What is vesting in benefits?
Vesting helps a business hold onto valuable employees by requiring them to stay with the company for a few years to get the maximum benefit. The effect of vesting on your tax circumstances depends on the type ...
How does vesting work?
How vesting works. With vesting, an employee earns benefits over time, rather than receiving them upfront. For example, a company might offer job candidates shares of stock if they accept an offer, but they will receive those shares only if they remain with the company a certain amount of time—six months, a year, 3 years, and other variations. ...
What are the two types of stock options?
There are two basic types of stock options: incentive options and nonstatutory options. Each gets taxed differently. However, vesting does not create a tax liability with either kind of option. In general: With incentive options, you are not taxed when the options vest or when you exercise the option.
What is cliff vesting?
Benefits generally vest in one of two ways: In "cliff vesting," you receive the entire benefit all at once when you reach a certain date.
What is the exercise price of a stock?
A stock option gives you the right to buy company stock at a specific price, called the exercise price or strike price. If the market price of the stock is higher than the strike price when you exercise the option (meaning, when you use the option to buy stock), then you make a profit.
Do you report vested benefits on W-2?
Those taxes will be reported on the W-2, as well. If your vested benefits are nontaxable, they won 't appear on your W-2, and you have nothing to report on your tax return that year.
Do you pay capital gains tax on an option?
When you sell the stock you bought with the option, you pay capital gains taxes. With nonstatutory options, you also are not taxed when the options vest. When you exercise the option, the difference between the strike price and the market price is taxed as income. When you sell the stock, you pay capital gains taxes.
Types of Vesting
- 1. Time-based Vesting
Time-based vesting is a method of vesting through which employees earn their share of stock options over time, usually based on a set schedule and a cliff – which is the time when the employee’s first option is granted and exercisable. After reaching the cliff, the remaining option… - 2. Milestone-based Vesting
Milestone-based vesting refers to the method of vesting whereby the employer grants stock options and/or benefits based on the completion of specific tasks or the achievement of certain objectives that are set by the employer. For example, employees working in the sales departmen…
Vesting For Start-Ups
- For start-ups that highly depend on a small number of team members (say, a founder and co-founder) for success, vesting is an important way to protect the business and increase sustainability. By providing a time-based vesting schedule, team members can ensure loyalty and long-term security. A cliff periodCliff VestingCliff vesting is a process where employees are entit…
Advantages and Disadvantages For Employers
- 1. Availability of cash
Stock options and equity are a form of compensationfor employees and are also substitutes for cash bonuses and rewards. They enable the company to maintain a higher share of cash, which can be used to pay off current liabilities and in cases of emergency. - 2. Lower employee turnover rate
By providing employees with the incentive of stock options that are triggered by time-based milestones, companies can ensure loyalty and long-term futures with certain talented employees that they wish to retain.
Related Readings
- CFI offers the Commercial Banking & Credit Analyst (CBCA)™Program Page - CBCAGet CFI's CBCA™ certification and become a Commercial Banking & Credit Analyst. Enroll and advance your career with our certification programs and courses.certification program for those looking to take their careers to the next level. To keep learning and advancing your career, the following CF…