Key Takeaways
- A qualified dividend is taxed at the capital gains tax rate, while ordinary dividends are taxed at standard federal income tax rates.
- Qualified dividends must meet special requirements put in place by the IRS.
- The maximum tax rate for qualified dividends is 20%; for ordinary dividends for the 2019 calendar year, it is 37%.
What percentage are dividends taxed at?
To summarize, if the underlying stocks are held in a taxable account, dividends are taxed as follows: Depending on your income level and tax filing status, qualified dividends are taxed at 0 percent, 15%, or 20%. Ordinary (non-qualified) dividends and taxable distributions are taxed at your marginal rate, which is based on your taxable earnings.
Are dividends taxed at a lower rate?
In good times, they earn the spread (called the net interest margin) on the difference between the rates on the mortgages they hold and cost of the debt they use to finance the mortgages. But when rates go up, they can start to lose money fast and that can compromise their ability to pay out the mandatory 90% of their taxable earnings as dividends.
Do I get taxed on US dividends?
You may get a dividend payment if you own shares in a company. You can earn some dividend income each year without paying tax. You do not pay tax on any dividend income that falls within your Personal Allowance (the amount of income you can earn each year without paying tax).
How are dividends taxed and reported on tax returns?
- Box 1a: Ordinary dividends reflecting the total amount of dividends paid to you
- Box 1b: Qualified dividends—the portion of total dividends that qualify for the preferred capital gains tax rate
- Box 3: Non-dividend distributions, which are a nontaxable return of capital
How much tax do I pay on stock dividends?
The tax rate on qualified dividends is 0%, 15% or 20%, depending on your taxable income and filing status. The tax rate on nonqualified dividends is the same as your regular income tax bracket. In both cases, people in higher tax brackets pay a higher dividend tax rate.
How do I avoid paying tax on dividends?
One way to avoid paying capital gains taxes is to divert your dividends. Instead of taking your dividends out as income to yourself, you could direct them to pay into the money market portion of your investment account. Then, you could use the cash in your money market account to purchase under-performing positions.
What is the tax rate on dividends in 2021?
2021 Qualified Dividend Tax RateFor Single TaxpayersFor Married Couples Filing Jointly0%Up to $40,400Up to $80,80015%$40,401 to $445,850$80,801 to $501,60020%$445,851 or more$501,601 or moreMay 26, 2022
What is the qualified dividend tax rate for 2020?
The dividend tax rate for 2020. Currently, the maximum tax rate for qualified dividends is 20%, 15%, or 0%, depending on your taxable income and tax filing status. For anyone holding nonqualified dividends in 2020, the tax rate is 37%. Dividends are taxed at different rates depending on how long you've owned the stock.
How do I sell stock without paying taxes?
5 ways to avoid paying Capital Gains Tax when you sell your stockStay in a lower tax bracket. If you're a retiree or in a lower tax bracket (less than $75,900 for married couples, in 2017,) you may not have to worry about CGT. ... Harvest your losses. ... Gift your stock. ... Move to a tax-friendly state. ... Invest in an Opportunity Zone.
Are stock dividends taxable if reinvested?
Dividends are taxable regardless of whether you take them in cash or reinvest them in the mutual fund that pays them out. You incur the tax liability in the year in which the dividends are reinvested.
How much taxes do I pay on stocks?
Generally, any profit you make on the sale of a stock is taxable at either 0%, 15% or 20% if you held the shares for more than a year or at your ordinary tax rate if you held the shares for a year or less. Also, any dividends you receive from a stock are usually taxable.
Are dividends taxed twice?
If the company decides to pay out dividends, the earnings are taxed twice by the government because of the transfer of the money from the company to the shareholders. The first taxation occurs at the company's year-end when it must pay taxes on its earnings.
Do dividends count as income?
All dividends paid to shareholders must be included on their gross income, but qualified dividends will get more favorable tax treatment. A qualified dividend is taxed at the capital gains tax rate, while ordinary dividends are taxed at standard federal income tax rates.
Do dividends count against Social Security?
Pension payments, annuities, and the interest or dividends from your savings and investments are not earnings for Social Security purposes. You may need to pay income tax, but you do not pay Social Security taxes.
How do I know if my dividends are qualified?
So, to qualify, you must hold the shares for more than 60 days during the 121-day period that starts 60 days before the ex-dividend date. If that makes your head spin, just think of it like this: If you've held the stock for a few months, you're likely getting the qualified rate.
What is the dividend tax rate?
The tax rate on qualified dividends is 0%, 15% or 20%, depending on your taxable income and filing status. The tax rate on nonqualified dividends the same as your regular income tax bracket. In both cases, people in higher tax brackets pay a higher dividend tax rate.
What is the dividend tax rate for the 2020 tax year?
These are the rates that apply to the tax return you'll file in May 2021. To see the dividend tax rate for qualified dividends, expand the filing status that applies to you. (We can help you determine your tax filing status.)
What is the dividend tax rate for the 2021 tax year?
These are the rates that apply to the tax return you'll file in April 2022. To see the dividend tax rate for qualified dividends, expand the filing status that applies to you. (We can help you determine your tax filing status.)
What are qualified dividends and nonqualified dividends?
A dividend is a share of a company’s profits that is distributed to shareholders. For tax purposes, there are two kinds of dividends: qualified and nonqualified (sometimes called "ordinary").
How to report dividend income on your taxes
After the end of the year, you’ll receive a Form 1099-DIV — or sometimes a Schedule K-1 — from your broker or any entity that sent you at least $10 in dividends and other distributions. The 1099-DIV indicates what you were paid and whether the dividends were qualified or nonqualified.
How long do you have to hold stock before dividends?
The stock must have been held in excess of 60 days during the 121-day period beginning 60 days before the ex-dividend date. In the case of preferred stock, the stock must have been held in excess of 90 days during the 181-day period beginning 90 days before the ex-dividend date if the dividends are due in a period of time longer than 366 days.
What is a qualified dividend?
A qualified dividend is taxed at the lower long-term capital gains tax rate instead of at the higher tax rate used on an individual’s regular income. To be eligible for this special tax rate, a dividend must be paid by either: A U.S. company. A company in U.S. possession.
Is dividend income taxable?
Generally speaking, dividend income is taxable. This is assuming that it is not distributed in a retirement account, such as an IRA, 401 (k) plan, etc., in which case it would not be taxable. Here are two common examples of dividend income subject to taxes:
Is 20% dividend taxable?
These dividends do not meet the qualified dividend requirements and are treated as short-term capital gains. These nonqualified dividends are taxed at the same rates as an individual's regular income.
How are dividends taxed?
To summarize, here's how dividends are taxed, provided that the underlying stocks are held in a taxable account: 1 Qualified dividends are taxed at 0%, 15%, or 20%, depending on your income level and tax filing status. 2 Ordinary (non-qualified) dividends and taxable distributions are taxed at your marginal income tax rate, which is determined by your taxable earnings.
How much are qualified dividends taxed?
To summarize, here's how dividends are taxed, provided that the underlying stocks are held in a taxable account: Qualified dividends are taxed at 0%, 15%, or 20%, depending on your income level and tax filing status.
How long do you have to hold a stock to pay dividends?
You must have owned the stock paying the dividend for more than 60 days within a specific 121-day holding period. The 121-day period begins 60 days before the ex-dividend date of the stock, which is exactly 60 days before the next dividend is distributed.
Is dividend paid on a Roth IRA taxed?
A common exception is dividends paid on stocks held in a retirement account such as a Roth IRA, traditional IRA, or 401 (k). These dividends are not taxed since any income or realized capital gains earned by these types of accounts is always tax-free.
How long do you have to hold a stock to receive qualified dividends?
Investors must also hold shares for more than 60 days during the 120-day holding period.
What is a stock split?
Stock splits are quite different from dividends , as they are not distributions of business profits. When trying to understand stock splits or reverse splits, realize they are merely a restructuring of shares outstanding and price per share; no tax is incurred. For example, an investor owns 100 shares of ABC at $80 per share for a total cost ...
Is a stock split taxable?
Stock splits are generally not taxable, as the cost basis per share is updated to reflect the new stock structure and price so that the total market value is the same. Since you did not make any gains on the stock split, no taxes are owed.
Is stock dividend taxed in 2021?
Updated Mar 28, 2021. If shares are held in a retirement account, stock dividends and stock splits are not taxed as they are earned. 1 Generally, in a nonretirement brokerage account, any income is taxable in the year it is received.
What is the surtax on dividends?
In addition to these taxes, a net investment income surtax of 3.8% gets charged on dividend income of high-income taxpayers. The thresholds for this surtax are $200,000 for single and head of household filers, $250,000 for married people filing jointly, and $125,000 for married people filing separately.
How long do you have to own stock to receive dividends?
You must have owned the stock for at least 61 days in the 121-day period that starts 60 days before the stock trades ex-dividend.
What happens if you fail dividend test?
If you fail any one of these tests, then the dividend is not qualified, and ordinary income tax rates apply.
Why are dividend stocks good?
Dividend stocks are great ways to build wealth and provide much-needed income. By knowing these rules, you'll be able to do tax planning that ensures you pay as little to the IRS as possible. The Motley Fool has a disclosure policy.
How do stock investors make money?
Stock investors make money in two ways. Ideally, the share price of the stocks they own goes up, giving them a profit when they sell. Some stocks also pay dividends to shareholders at regular intervals, giving them income that they can either reinvest in the stock or use for other purposes.
What is the tax rate for 0%?
The 0% tax rate applies to all of the income in the 10% and 12% brackets. The 15% tax rate applies to just about all of the income covered in the 22%, 24%, 32%, and 35% tax brackets. The 20% tax rate applies to a small portion of income at the top end of the 35% tax bracket and to the 37% bracket.
Do dividends get taxed?
Many dividends get taxed at lower rates than other types of income. The rules governing which dividends qualify for favorable tax treatment are given below. Dividends that don't meet these qualifications get taxed at the same rates as ordinary income.
How are dividends taxed?
How dividends are taxed is very important when considering investments for cash flow. To lower your tax rate on income, consider owning investments that pay qualified dividends. These dividends are federally taxable at the capital gains rate, which depends on the investor's modified adjusted gross income (AGI) and taxable income ...
How long are dividends paid?
Also, dividends paid on shares that are not held at least 61 days in the 121-day period surrounding the ex-dividend date are not "qualified" dividends. How dividends are taxed is very important when considering investments for cash flow. Interest from money markets, bank CDs, and bonds is taxed at ordinary tax rates.
Do dividends qualify for favored tax?
Most dividends paid by domestic companies and many dividends paid by foreign companies are qualified and taxed at the preferred tax rate. However, distributions paid by real estate investment trusts, master limited partnerships, and other similar "pass-through" entities might not qualify for favored tax status.
Is dividend income taxable?
Dividends. Income tax. Taxes. Trading and investing. Dividend-paying stocks. Stocks. To lower your tax rate on income, consider owning investments that pay qualified dividends. These dividends are federally taxable at the capital gains rate, which depends on the investor's modified adjusted gross income (AGI) and taxable income ...
How much is a stock sale taxable?
Generally, any profit you make on the sale of a stock is taxable at either 0%, 15% or 20% if you held the shares for more than a year or at your ordinary tax rate if you held the shares for less than a year. Also, any dividends you receive from a stock are usually taxable. Here’s a quick guide to taxes on stocks and how to lower those taxes.
How much can you deduct from your capital gains?
If your losses exceed your gains, you can deduct the difference on your tax return, up to $3,000 per year ($1,500 for those married filing separately).
What is long term capital gains tax?
Long-term capital gains tax is a tax on profits from the sale of an asset held for longer than a year. Long-term capital gains tax rates are 0%, 15% or 20% depending on your taxable income and filing status. Long-term capital gains tax rates are usually lower than those on short-term capital gains. That can mean paying lower taxes on stocks.
Do dividends count as qualified?
You might pay less tax on your dividends by holding the shares long enough for the dividends to count as qualified. Just be sure that doing so aligns with your other investment objectives. Whenever possible, hold an asset for a year or longer so you can qualify for the long-term capital gains tax rate when you sell.
Is dividend income taxable?
Taxes on dividends. Dividends are usually taxable income. For tax purposes, there are two kinds of dividends: qualified and nonqualified. Nonqualified dividends are sometimes called ordinary dividends. The tax rate on nonqualified dividends is the same as your regular income tax bracket.
What is the tax rate for capital gains?
If the income is considered capital gains, or dividends, you would pay a lower tax rate (ranging from 0 percent to 20 percent).
How many shareholders can an S corp have?
However, you must adhere to certain guidelines: S corps may not have over 100 shareholders. Non-U.S. citizens and residents cannot own shares in an S corp. Other entities cannot an S corp. Overall, all shareholders within a corporation must get a share of corporate profits.
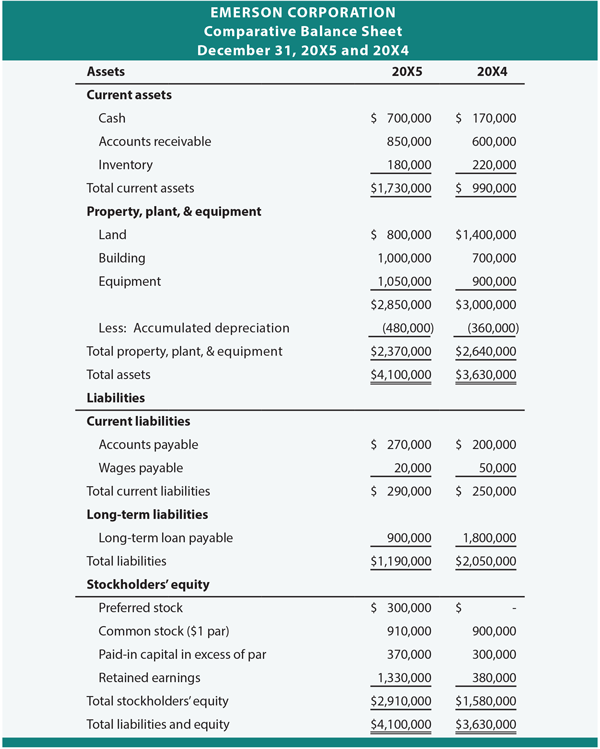
What happens to retained earnings in a C corp?
Once the C corp determines net business income and pays taxes, the remaining amount is then placed in a retained earnings account. From there, the business distributes the remaining profits to shareholders from retained earnings, and the shareholders are taxed once they file their individual tax returns.
Is a S corp distribution taxed?
S corps that issue distributions to shareholders are not taxed. For instance, a shareholder that receives a $100,000 distribution check from an S corp means the $100,000 received is not taxed. Note: One of the most important things to remember is the order in which adjustments are made.
Does S corp affect standard income?
Such a tax does not affect standard income that comes out of an S corp if a shareholder is involved in the business. Under Section 1368, a cash distribution or property via an S corp may give way to three tax ramifications to shareholders:
Does S corp have retained earnings?
An S corp does not have retained earnings in a standard sense and does not issue dividends because the dividends are paid post-tax profits, and S corps are not subject to taxation.
Do S corps have to distribute profits?
An S corp’s tax status mandates profit corporations -are-taxed-as-a-pass-through-entity" target="_blank">allocation to shareholders annually, but corporations are not required to distribute profits. The distribution of profits, or the retention of them, depends on state law.
