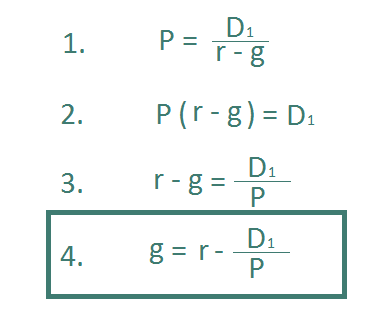
In order to determine the future expected price of a stock, you start off by dividing the annual dividend payment by the current stock price. For example, if a stock is currently priced at $80 and offers a $3 annual dividend, you would then divide $3 by $80 to get 0.0375.
Full Answer
Will the stock pay a dividend in the next 9 years?
No dividends will be paid on the stock over the next 9 years, because the firm needs to plow back its earnings to fuel growth. The company will pay a dividend of $15.75 per share in 10 years and will increase the dividend by 4.8 percent per year thereafter. If the required return on this stock is 12 percent, what is the current share price?
What is the dividend yield on the nearside Co stock?
The Nearside Co. just paid a dividend of $2.07 per share on its stock. The dividends are expected to grow at a constant rate of 4.3 percent per year, indefinitely. Investors require a return of 11 percent on the stock. a.What is the current price? b.What will the price be in 3 years? c.What will the price be in 15 years?
What is the expected return on the stock price?
The dividends are expected to grow at a constant rate of 4.3 percent per year, indefinitely. Investors require a return of 11 percent on the stock. a.What is the current price?
What is a dividend yield?
Dividend yield is a calculation of the amount (in dollars) of a company’s current annual dividend per share divided by its current stock price: Current annual dividend per share/current stock price. For example: A company that pays $2 in dividends on an annual basis with a stock price of $60 has a dividend yield of 3.33%. It’s that simple.
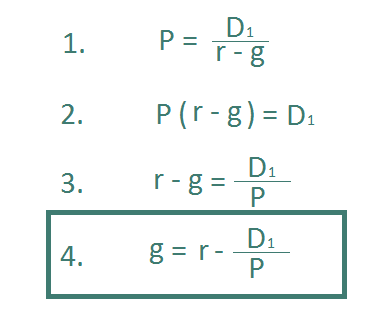
How do you calculate stock price after dividend?
To figure the new average price after a stock dividend, convert the percentage of the stock dividend to a decimal by dividing by 100. Then, add it to 1. Finally, divide the initial stock price by the result to find the new stock price.
How do you find the expected dividend price?
Divide the forward annual dividend rate by the stock's price and multiply your result by 100 to calculate its expected dividend yield as a percentage. For example, assume a stock has a current price of $32.50 and a forward annual dividend rate of $1.20. Divide $1.20 by $32.50 to get 0.037.
How do you calculate expected stock price change?
Multiply this year's dividends by the dividends' growth rate to calculate the next year's dividend rise. For example, if a stock pays a dividend of $1.70 per share and is expected to pay 10 percent more each year, multiply $1.70 by 0.10 to get $0.17.
How do you calculate expected annual dividend growth rate?
0:009:47Calculating the Dividend Growth Rate - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIn a previous video we looked at how you value to stock using the constant growth dividend formulaMoreIn a previous video we looked at how you value to stock using the constant growth dividend formula and the formula is listed right up here the price of the stock. Today is equal to the dividend one
What is dividend formula?
The formula to find the dividend in Maths is: Dividend = Divisor x Quotient + Remainder. Usually, when we divide a number by another number, it results in an answer, such that; x/y = z. Here, x is the dividend, y is the divisor and z is the quotient.
How is stock price calculated?
To figure out how valuable the shares are for traders, take the last updated value of the company share and multiply it by outstanding shares. Another method to calculate the price of the share is the price to earnings ratio.
How do you calculate the future price of a stock without dividends?
The P/E Ratio. The price-to-earnings ratio or P/E ratio is a popular metric for valuing stocks that works even when they have no dividends. Regardless of dividends, a company with high earnings and a low price will have a low P/E ratio. Value investors see such stocks as undervalued.
How do you calculate expected iv move?
1:545:46Expected Move Explained | Options Trading Concept Guide - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd implied volatilities between expiration cycles and just make sure you use the implied volatilityMoreAnd implied volatilities between expiration cycles and just make sure you use the implied volatility of the expiration cycle that's nearest to the expected. Move period that you're calculating.
How do you arrive at an expected market value and an expected rate of return for the stock market?
An expected return is calculated by multiplying potential outcomes by the odds of them occurring and then totaling these results. Expected returns cannot be guaranteed. The expected return for a portfolio containing multiple investments is the weighted average of the expected return of each of the investments.
What is dividend in stocks?
A dividend is a portion of a company’s profit that is paid back to shareholders. In most cases, companies that issue a dividend are financially stable. Many of these companies are in mature industries and have stable, predictable revenue and earnings. Utility stocks and consumer discretionary stocks are good examples of companies ...
What does it mean when a company projects a dividend increase?
If the company is expecting growth in earnings and revenue, they may project a dividend increase. If the company is expecting slowing and/or declining earnings and revenue, they may project keeping the dividend the same.
What is the dividend yield of Company B?
However, Company B was able to increase its annual dividend from $1.50 to $1.75. Now its dividend yield is 3.5%. This means investors will have to look at other factors to decide which company’s stock is better to own. For example, maybe analysts are projecting that Company A will raise its dividend later in the year.
Why is dividend yield a trap?
A dividend yield trap occurs when the stock of a company falls faster than its earnings. This will make its yield look more attractive than it really is. Here’s why it’s a trap. Let’s say you buy the stock at its low price and then the company cuts its dividend. Now, investors may start to sell off even more, lowering the share price which means you’ve lost capital growth and are looking at a lower yield.
What is dividend payout ratio?
The payout ratio is the amount of a company’s net income that goes towards dividends.
How often do companies pay dividends?
Companies typically pay dividends quarterly (i.e. four times per year) or annually (once a year). When a company delivers its earnings report to shareholders, it usually provides guidance about the direction of the dividend. If the company is expecting growth in earnings and revenue, they may project a dividend increase.
Can dividend stocks grow in a bull market?
However, although dividend stocks are traditionally lumped into the “value” category, many of these companies can generate significant capital growth, particularly in a bull market. One of the distinctions, however, is the ability of these companies to pay a dividend in a bear market.
Is it hard to value long established stocks?
On the other hand, long-established stocks, especially those that have a consistent record of dividend payments and increases, aren't too difficult to value -- at least in theory.
Can we predict the price of a stock in the future?
None of us has a crystal ball that allows us to accurately project the price of a stock in the future. However, if we make a few basic assumptions, it is possible to determine the price a stock should be trading for in the future, also known as its intrinsic value.
How do dividends affect stock prices?
Dividends can affect the price of their underlying stock in a variety of ways. While the dividend history of a given stock plays a general role in its popularity, the declaration and payment of dividends also have a specific and predictable effect on market prices .
How much does a dividend drop at $200?
As with cash dividends, smaller stock dividends can easily go unnoticed. A 2% stock dividend paid on shares trading at $200 only drops the price to $196.10, a reduction that could easily be the result of normal trading. However, a 35% stock dividend drops the price down to $148.15 per share, which is pretty hard to miss.
What is dividend yield?
The dividend yield and dividend payout ratio (DPR) are two valuation ratios investors and analysts use to evaluate companies as investments for dividend income. The dividend yield shows the annual return per share owned that an investor realizes from cash dividend payments, or the dividend investment return per dollar invested. It is expressed as a percentage and calculated as:
Why do dividends go unnoticed?
However, because a stock dividend increases the number of shares outstanding while the value of the company remains stable, it dilutes the book value per common share, and the stock price is reduced accordingly. As with cash dividends, smaller stock dividends can easily go unnoticed.
What happens to stock after ex dividend?
After a stock goes ex-dividend, the share price typically drops by the amount of the dividend paid to reflect the fact that new shareholders are not entitled to that payment. Dividends paid out as stock instead of cash can dilute earnings, which can also have a negative impact on share prices in the short term.
How to calculate dividends per share?
DPS can be calculated by subtracting the special dividends from the sum of all dividends over one year and dividing this figure by the outstanding shares.
Why do companies pay dividends?
Companies pay dividends to distribute profits to shareholders, which also signals corporate health and earnings growth to investors. Because share prices represent future cash flows, future dividend streams are incorporated into the share price, and discounted dividend models can help analyze a stock's value. ...
