
If the company sells the common stock at the price of its par value or stated value, it can make the journal entry by debiting the cash account and crediting the common stock account. However, the common stock is usually sold at a price that is higher than its par value or stated value.
How is a journal entry of capital introduced?
To record capital introduced.
- Go to Journals and click New Journal.
- Enter the reference, date and a description if you want to.
- Enter the information required to record the capital introduced and click Save.
How to make journal entries for retained earnings?
if the corporation suffered a net loss, Retained Earnings will be debited. When dividends are declared by a corporation’s board of directors, a journal entry is made on the declaration date to debit Retained Earnings and credit the current liability Dividends Payable . It is the declaration of cash dividends that reduces Retained Earnings.
How to journalize common stock?
Stock dividend journal entry
- Small stock dividend journal entry. The company can make the small stock dividend journal entry on the declaration date by debiting the stock dividends account and crediting the common stock ...
- Small stock dividend example. ...
- Large stock dividend journal entry. ...
- Large stock dividend example. ...
What is the journal entry to increase retained earnings?
The key takeaways should be:
- Net profit is the corresponding account to retained earnings.
- Any transaction on the income statement has only one modification to the balance sheet. ...
- The sales cycle always includes the special Cost of Sales cycle within it.
- The expense cycle starts with the liabilities side of the balance sheet.
How do you record investments in common stock?
1:4619:59Accounting for Investments in Common Stock - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe first journal entry shows the purchase of common stock by the investor. And is recorded at costMoreThe first journal entry shows the purchase of common stock by the investor. And is recorded at cost when the invested éclairs a dividend.
What is the journal entry for common stock?
A company issues common stock to raise money, so the debit will always be to cash. There will always be a credit to common stock for the # of shares issued x the par value. Additional paid-in capital (APIC) is the plug.
How do you Journalize investments?
To record this in a journal entry, debit your investment account by the purchase price and credit your cash account by the same amount. For example, if your small business buys a 40-percent stake in one of your suppliers for $400,000, you would debit the investment account and credit cash each by $400,000.
How do you record common stock on a balance sheet?
On a company's balance sheet, common stock is recorded in the "stockholders' equity" section. This is where investors can determine the book value, or net worth, of their shares, which is equal to the company's assets minus its liabilities.
Is common stock credit or debit?
CreditNormal Balance of an AccountType of accountIncreases withNormal balanceCommon StockCreditCreditDividendsDebitDebitRevenueCreditCreditExpenseDebitDebit2 more rows
How do you Journalize stock transactions?
1:557:15Journalizing Treasury Stock Transactions (Cost Method)YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo a contra capital will increase with a debit. And decrease with a credit. So when we say that we'MoreSo a contra capital will increase with a debit. And decrease with a credit. So when we say that we're going to be debiting treasury stock we are actually making it go up.
Is common stock an asset or liability?
No, common stock is neither an asset nor a liability. Common stock is an equity.
What are the types of transactions you need to know when preparing a journal entry for common stock?
These are issuing stock exchange for cash, for other non-cash assets or companies buying back their own stock. Each of these we’ll discuss briefly below.
What is Common Stock?
At its most basic, common stock is a financial instrument representing a share of ownership in a company. And hence we also use the word shares as well. You will hear the words “stock market” and “share market” used interchangeably.
What does the debit to the Treasure Stock account mean?
The debit to the Treasure Stock account reflects the new asset ABC Ltd holds in its own stock. This is equivalent to it owning shares in another company. And the credit reflects the company pays Kevin to buy his position out. Kevin is now off to play golf and travel.
What is par value in stock?
In the example below, we will look at when this transaction takes place and how to issue stock above par value. As a quick refresh, par value is the face-value or legally issued price of the share. Typically, shares have a par value of $0.01 or $1.00 etc., normally a round figure. From an accounting point of view, the actual par value matters little until we get to an issue price that is different to the par value. And we’ll look at this very thing in the examples coming up below.
What is class A in stock market?
all shares are class A, carrying equal rights;
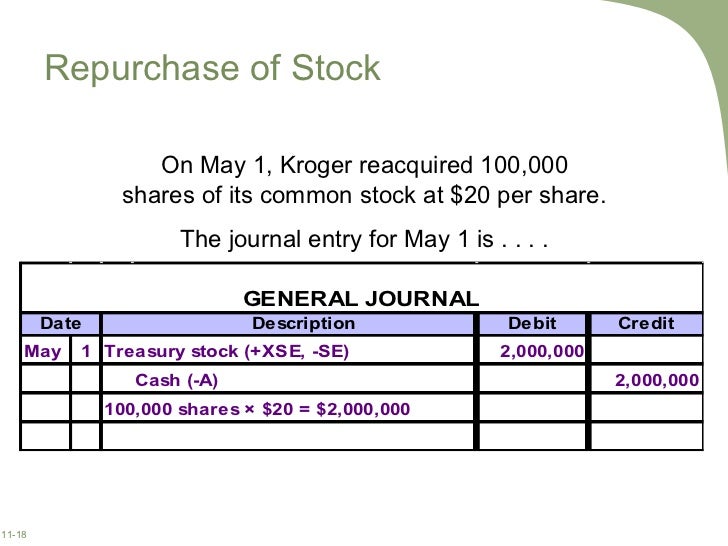
What is a company buying back its own stock?
And in the last example, we will look at is a company buying back its own stock. This process is often referred to as a share buy-back or a Treasury stock purchase. Once the shares are purchased back from shareholders, the company can either hold them as Treasury stock or cancel them, which is the permanent retirement of the shares.
Where is common stock disclosed?
Therefore you will find common stock disclosed in the balance sheet (often referred to as the statement of financial position).
What is common stock?
When a company issues just one type of stock it is called common stock, and it includes the equity shares that the owners of a company receive. Common stockholders in a company usually receive returns on their investment in the form of dividends, they usually receive a portion of the assets at the time of sale, ...
What is the purpose of selling common stock?
Companies regularly sell their common stock in exchange for investment capital. The investor receives common shares of the company and becomes an owner of the company as well. There are three major types of stock transactions including repurchasing common stock, selling common stock, and exchanging stock for non-cash assets and services.
What happens if ABC sells preferred stock?
If ABC Advertising sold preferred stock instead of common stock, the only difference would be to change the label for the Common Stock row to Preferred Stock. Stock Repurchase Journal Example.
What is the par value of a stock?
The par value of a stock is shown on the front of the certificate, and in many cases the par value of a stock is set at $0.01 per share , or not may have no par value at all.
What is the first account debited to cover the cost of a stock?
If the stock is later sold at a lower amount than the repurchase cost, the first account that is debited to cover the cost is the additional paid-in capital account, followed by the company’s retained earnings account.
When the sale of a stock is recorded, should the total columns match?
When the sale has been recorded, both total columns should match. The common stock row shows the total par value of the stock that is sold. The par value plus the additional-paid in capital amount should always equal the debit to the cash account. In the rare case that the company sold the stock for its par value, there would be no additional paid-in capital entry to the common stock account.
When treasury stock is purchased by the board of directors, is it listed as a debit or credit?
When treasury stock is purchased by the board of directors, it is listed as a debit to the treasury stock account and a credit to the cash account.
What is journal entry for stock investment?
The company can make the journal entry for purchase of stock investment by debiting the stock investments account and crediting the cash account. Stock investments account is an asset account on the balance sheet, in which its normal balance is on the debit side.
What is stock investment account?
Stock investments account is an asset account on the balance sheet, in which its normal balance is on the debit side. Likewise, in this journal entry, there is no impact on the total assets of the balance sheet as it results in the increase of one asset (stock investment) and the decrease of another asset (cash).
What are the benefits of buying stock?
Purchase of stock investment provides two main benefits to the company, in which the first one is that it can earn the dividend revenue from the investment . And another one is that it can enjoy the benefits from the value gain when the investee company performs well in the market.
Why do companies invest in the stock market?
The company may sometimes make an equity investment in the stock market in order to earn extra revenue to support the business operation. And one common equity investment is purchasing the stock in the capital market. Likewise, the company needs to make the journal entry for the purchase of stock investment when it decides to purchase it as an investment asset.
Is journal entry for stock purchase similar to debt investment?
It is useful to note that even though the journal entry for the purchase of stock investment is similar to the purchase of debt investments, it may be different from one investment to another when it comes to the recognition of revenue and dividend from the stock investments. This will depend on how much ownership the company has in other companies.
How to make journal entry for common stock?
If the company sells the common stock at the price of its par value or stated value, it can make the journal entry by debiting the cash account and crediting the common stock account.
What is the purpose of selling common stock?
Selling the common stock is one of the funding sources that the company may use to operate or expend the business. Likewise, the company needs to make the sale of common stock journal entry when such transactions occur.
Is common stock higher than par value?
However, the common stock is usually sold at a price that is higher than its par value or stated value. Hence, the journal entry for the sale of common stock usually also includes the additional paid-in capital account for the difference between the par value and the selling price.
Overview
In business, we may need to make the investment in another company for some reasons, such as to earn extra income, to gain some influence in the industry, or to have complete control over another company. In any case, we need to make the journal entry for investment in another company when we decide to invest in one.
Journal entry for investment in another company
As mentioned, we may make investments in another company in form of debt investment or in form of stock investment. Likewise, the journal entry for investment in another company in form of debt investment will be different from those in form of stock investment.
Investment in another company example
For example, on January 1, we make an investment in another company by buying a 6%, 5-year, $100,000 bond for $100,000 in cash, as it is not a discount nor a premium bond.
What does the owner of a company need to invest in?
Overview. The owner of the company usually needs to invest the money or other assets in the business to start- up the company or to expand the business. Likewise, the company needs to make the owner investment journal entry when that happens.
Does equity increase with cash?
Either owner’s investment in the company is in the form of cash or other assets, both assets and equity on the balance sheet will increase in the same amount of the investment.

What Is Common Stock?
Types of Common Stock Transactions
- There are three types of transactions you will need to know when preparing a journal entry for common stock. These are issuing stock exchange for cash, for other non-cash assets or companies buying back their own stock. Each of these we’ll discuss briefly below.
Examples with Journal Entries
- Now we are into the exciting part of the article, the journal entries. I always say if you don’t like the debits and credits, you shouldn’t be an accountant. In my current career as an airline pilot, it’s the same with aircraft; if you don’t like aircraft, you shouldn’t be a pilot. And yes, I do fly with people who don’t care much for aircraft! Perhaps all of that for another article one day. Back to the jour…
Conclusion
- Well, this guide turned out longer than it was meant to be. But once we started to look into the different scenarios a reader could face, we had to keep going. We trust that all the examples and explanations will be helpful and cover what you need. If you have any questions or comments, please use our Ask a Question section or our contact us page.