Elasticity is driven by the principles of supply and demand, meaning the higher the demand for an item, the more elastic its price is. The elasticity dynamic is also affected by the number of alternative options in the market. In other words, when people have plenty of similar options, price elasticity will be lower.
What is elasticity in economics?
Elasticity is an economic measure of how sensitive an economic factor is to another, for example, changes in price to supply or demand, or changes in demand to changes in income.
What determines the elasticity of demand for stocks?
neous beliefs are determining factors of demand elasticities. More liquid stocks (as measured by VOL) experience a smaller price decline, while stocks with more heterogeneous information (as proxied by VAR) experience larger price declines. In the second regression (column (2)), we investigate the
How does offering size affect stock price elasticity?
Consequently, the elasticity of the stock price with respect to offering size should be inversely related to return variance (VAR) and firm size (SIZE), and positively related to the size of the investor base (BASE). Notice that the elasticity of the stock price with respect to
Is the price elasticity of demand for common stock 629 offering less than zero?
The Price Elasticity of Demand for Common Stock 629 offering is less than zero. We also use a sign-rank test to gauge whether the median cumulative prediction error is similarly smaller than zero. A3. Announcement Effects and Finite Price Elasticities of Demand The preceding measures of new information can be used to isolate the

Are stocks elastic or inelastic?
Like any other good, stocks with closer substitutes will have more elastic demand curves. If a stock has close substi- tutes, small deviations from the stock's true price will lead investors to make large shifts in quantities demanded to sub- stitute assets, generating an elastic demand curve.
Is elasticity of 1 elastic or inelastic?
If elasticity is greater than 1, the curve is elastic. If it is less than 1, it is inelastic. If it equals one, it is unit elastic.
What does it mean when elasticity is 1?
unitaryIf the number is equal to 1, elasticity of demand is unitary. In other words, quantity changes at the same rate as price.
Are stock prices elastic?
Stock price elasticity, defined as the percentage change in quantity associated with a percentage change in price, has conventionally been argued to be close to infinite. For example, Brealey and Myers (1996) p.
Is 0 elastic or inelastic?
If elasticity = 0, then it is said to be 'perfectly' inelastic, meaning its demand will remain unchanged at any price. There are probably no real-world examples of perfectly inelastic goods.
What if elasticity is greater than 1?
Elasticity of Demand by Price Price elasticity of demand is an indicator of the impact of a price change, up or down, on a product's sales. If the price elasticity of demand is greater than 1, it is deemed elastic. That is, demand for the product is sensitive to an increase in price.
What does an elasticity of 0.5 mean?
Demand for a good is said to be elastic when the elasticity is greater than one. A good with an elasticity of −2 has elastic demand because quantity falls twice as much as the price increase; an elasticity of -0.5 has inelastic demand because the quantity response is half the price increase.
Is a negative number elastic or inelastic?
Income elasticity of demandIf the sign of Y E D YED YED is...and the elasticity isthe goods arenegativeelastic or inelasticinferior good0perfectly inelasaticabsolute necessitypositiveinelasticnormal necessitypositiveelasticnormal luxury
What is an inelastic good?
Inelastic products are usually necessities without acceptable substitutes. The most common goods with inelastic demand are utilities, prescription drugs, and tobacco products. Businesses offering such products maintain greater flexibility with prices because demand remains constant even if prices increase or decrease.
Why are elastic stocks down?
Shares of Elastic NV (NYSE: ESTC) plummeted 24.2% in January, according to data provided by S&P Global Market Intelligence. The enterprise search and data company announced a transition for its CEO and got pushed down by the broad sell-off in growth stocks last month.
Is price elasticity good or bad?
If demand for a good is elastic (the price elasticity of demand is greater than 1), an increase in price reduces total revenue. In this case, the quantity effect is stronger than the price effect. demand is less than 1), a higher price increases total revenue.
What goods are elastic?
Common elastic items include:Soft Drinks. Soft drinks aren't a necessity, so a big increase in price would cause people to stop buying them or look for other brands. ... Cereal. Like soft drinks, cereal isn't a necessity and there are plenty of different choices. ... Clothing. ... Electronics. ... Cars.
Is elasticity the same as supply and demand?
No, elasticity depends on supply and demand principles, but it describes how changing market factors affect specific market elements, such as price...
What is price elasticity?
Price elasticity refers to how much supply or demand moves when the price changes.
What is demand elasticity?
Demand elasticity measures how demand affects the price of a good or service.
What is elastic product?
As a rule of thumb, if the quantity of a product demanded or purchased changes more than the price changes, the product is termed elastic. (For example, the price changes by +5%, but the demand falls by -10%).
Why are other goods more elastic?
Other goods are much more elastic, so price changes for these goods cause substantial changes in their demand or their supply. Not surprisingly, this concept is of great interest to marketing professionals. It could even be said that their purpose is to create inelastic demand for the products they market.
Does price elasticity affect demand?
That is, a reduction in price does not increase demand much, and an increase in price does not hurt demand either. For example, gasoline has little price elasticity of demand.
What is the elasticity of demand?
Elasticity is a general measure of the responsiveness of an economic variable in response to a change in another economic variable. The three major forms of elasticity are price elasticity of demand, cross-price elasticity of demand, and income elasticity of demand. The four factors that affect price elasticity of demand are (1) ...
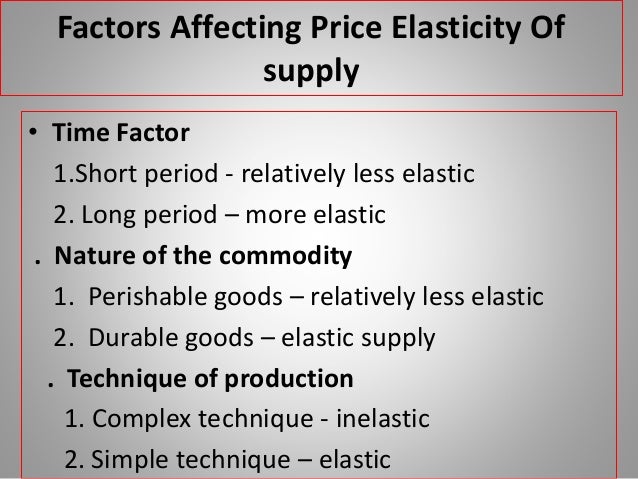
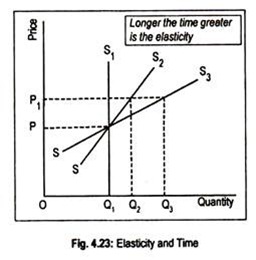
What are the factors that affect price elasticity?
The four factors that affect price elasticity of demand are (1) availability of substitutes, (2) if the good is a luxury or a necessity, (3) the proportion of income spent on the good, and (4) how much time has elapsed since the time the price changed. If income elasticity is positive, the good is normal.
What is the difference between inelastic demand and inelastic demand?
The lower the price elasticity of demand, the less responsive the quantity demanded is given a change in price. When the price elasticity of demand is less than one , the good is considered to show inelastic demand. Inelastic Demand Inelastic demand is when the buyer’s demand does not change as much as the price changes.
How is cross price elasticity calculated?
It is calculated as the percentage change of Quantity A divided by the percentage change in the price of the other.
Why is price elasticity of demand lower?
The price elasticity of demand is lower if the good is something the consumer needs, such as Insulin. The price elasticity of demand tends to be higher if it is a luxury good.
Why is demand curve downwards sloping?
The law of demand states that an increase in price reduces the quantity demanded, and it is why demand curves are downwards sloping unless the good is a Giffen good. Giffen Good A Giffen good, a concept commonly used in economics, refers to a good that people consume more of as the price rises. Therefore, a Giffen.
What are the three forms of elasticity?
The three major forms of elasticity are price elasticity of demand, cross-price elasticity of demand, and income elasticity of demand.