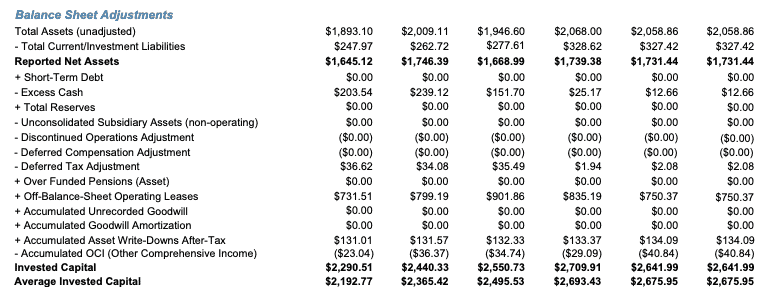
If a company pays stock dividends, the dividends reduce the company's retained earnings and increase the common stock account. Stock dividends do not result in asset changes to the balance sheet but rather affect only the equity side by reallocating part of the retained earnings to the common stock account. Contents
Do stock dividends affect the balance sheet?
Stock dividends do not result in asset changes to the balance sheet but rather affect only the equity side by reallocating part of the retained earnings to the common stock account. For example, say a company has 100,000 shares outstanding and wants to issue a 10% dividend in the form of stock.
What is the balance sheet account for dividends after they are paid?
There is no separate balance sheet account for dividends after they are paid. However, after the dividend declaration and before the actual payment, the company records a liability to its shareholders in the dividend payable account.
Do stock dividends reduce the price of a stock?
Stock dividends don’t reduce the stock price by the same percentage as cash dividends. How a stock dividend affects the balance sheet is a bit more involved than cash dividends, although it only involves shareholder equity.
What is a stock split and how does it affect dividends?
When a cash dividend is paid, the stock price drops by the amount of the dividend. For example, a company pays a 2% cash dividend, the stock price should fall by 2%. Large stock dividends, of more than 20% or 25%, might be considered a stock split. Consider a company with two million common shares that declares a cash dividend of $0.25 per share.

Does a stock dividend result in a liability?
There is no change in total assets, total liabilities, or total stockholders' equity when a small stock dividend, a large stock dividend, or a stock split occurs. Both types of stock dividends impact the accounts in stockholders' equity. A stock split causes no change in any of the accounts within stockholders' equity.
Are dividends an asset on a balance sheet?
Understanding Dividends When cash dividends are paid, this reduces the cash balance stated within the assets section of the balance sheet, as well as the offsetting amount of retained earnings in the equity section of the report.
What is the effect of a stock dividend on total assets?
Stock dividends have no effect on the total amount of stockholders' equity or on net assets. They merely decrease retained earnings and increase paid-in capital by an equal amount. Immediately after the distribution of a stock dividend, each share of similar stock has a lower book value per share.
How do you record stock dividends?
Stock dividends are recorded by moving amounts from retained earnings to paid-in capital. The amount to move depends on the size of the distribution. A small stock dividend (generally less than 20-25% of the existing shares outstanding) is accounted for at market price on the date of declaration.
How do dividends affect the accounting equation?
The payment of both cash and stock dividends impacts the accounting equation by immediately reducing the amount of retained earnings for the company. This requires offsetting accounting entries in other financial accounts with slight changes based on the type of dividend provided.
Is a stock dividend an asset or liability?
Key Takeaways. For shareholders, dividends are an asset because they increase the shareholders' net worth by the amount of the dividend. For companies, dividends are a liability because they reduce the company's assets by the total amount of dividend payments.
What is the effect of a stock dividend on the balance sheet quizlet?
What is the effect of a stock dividend on the balance sheet? The reduction in the par or stated value of common stock, accompanied by the issuance of a proportionate number of additional shares, is called a stock split.
Are dividends on the balance sheet or income statement?
Cash or stock dividends distributed to shareholders are not recorded as an expense on a company's income statement. Stock and cash dividends do not affect a company's net income or profit. Instead, dividends impact the shareholders' equity section of the balance sheet.
How does a stock dividend affect the balance sheet?
When a stock dividend is declared, the amount to be debited is calculated by multiplying the current stock price by shares outstanding by the dividend percentage. When paid, the stock dividend amount reduces ...
What happens to the balance sheet after dividends are paid?
After declared dividends are paid, the dividend payable is reversed and no longer appears on the liability side of the balance sheet. When dividends are paid, the impact on the balance sheet is a decrease in the company's dividends payable and cash balance. As a result, the balance sheet size is reduced.
What happens if a company pays dividends by year end?
If the company has paid the dividend by year-end then there will be no dividend payable liability listed on the balance sheet.
How does a stock dividend work?
Cash dividends can be made via electronic transfer or check.
What is cash dividend 2021?
Updated May 27, 2021. Cash dividends offer a way for companies to return capital to shareholders. A cash dividend primarily impacts the cash and shareholder equity accounts. There is no separate balance sheet account for dividends after they are paid.
How do you make a cash dividend?
Cash dividends can be made via electronic transfer or check. When a cash dividend is paid, the stock price drops by the amount of the dividend. For example, a company pays a 2% cash dividend, the stock price should fall by 2%. Large stock dividends, of more than 20% or 25%, might be considered a stock split.
Is there a separate dividend account on the balance sheet?
After cash dividend payments are made there are no separate dividend or dividend-related accounts left on the balance sheet.
How does cash dividend affect the balance sheet?
Cash dividends affect the cash and shareholder equity on the balance sheet; retained earnings and cash are reduced by the total value of the dividend.
What happens to the balance sheet after dividends are paid?
After the dividends are paid, the dividend payable is reversed and is no longer present on the liability side of the balance sheet. When the dividends are paid, the effect on the balance sheet is a decrease in the company’s retained earnings and its cash balance. In other words, retained earnings and cash are reduced by the total value of the dividend.
How to calculate dividends from retained earnings?
When a stock dividend is declared, the total amount to be debited from retained earnings is calculated by multiplying the current market price per share by the dividend percentage and by the number of shares outstanding. If a company pays stock dividends, the dividends reduce the company’s retained earnings and increase the common stock account. Stock dividends do not result in asset changes to the balance sheet but rather affect only the equity side by reallocating part of the retained earnings to the common stock account.
How does a dividend affect a company?
Stock dividends have no impact on the cash position of a company and only impact the shareholders’ equity section of the balance sheet. If the number of shares outstanding is increased by less than 20% to 25%, the stock dividend is considered to be small. A large dividend is when the stock dividend impacts the share price significantly and is typically an increase in shares outstanding by more than 20% to 25%. A large dividend can often be considered a stock split .
What does it mean when a company issues a dividend?
When a company issues a stock dividend, it distributes additional quantities of stock to existing shareholders according to the number of shares they already own. Dividends impact the shareholders’ equity section of the corporate balance sheet—the retained earnings, in particular.
What is dividend in stock?
A dividend is a method of redistributing a company’s profits to shareholders as a reward for their investment. Companies are not required to issue dividends on common shares of stock, though many pride themselves on paying consistent or constantly increasing dividends each year. When a company issues a dividend to its shareholders, the dividend can be paid either in cash or by issuing additional shares of stock. The two types of dividends affect a company’s balance sheet in different ways.
What is retained earnings?
Retained earnings are the amount of money a company has left over after all of its obligations have been paid. Retained earnings are typically used for reinvesting in the company, paying dividends, or paying down debt. While net profit is the amount of income that remains after accounting for the cost of doing business in a given period, retained earnings are the amount of income accrued over the years that has not been reinvested in the business or distributed to shareholders.