- Restricted stock units are a form of stock-based employee compensation.
- RSUs are restricted during a vesting period that may last several years, during which time they cannot be sold.
- Units are just like any other shares of company stock once they are vested.
What is restricted stock unit or RSU?
- Stock Value = $20 per share
- RSU Value (when vested) = $20 per share
- Taxable income (when vested): $20 x 1000 = $20,000
What is restricted stock and how is it taxed?
Restricted stock units, or RSUs, are a form of equity compensation offered ... will depend on the value of the underlying stock when the RSUs vest and are then taxed on the delivery date, usually the same as the vest date." RSUs can be confused with ...
Is it better to take RSU or stock options?
The restricted stock units can also be structured in such a way you can have all the benefits of stock options. In this sense, between RSU vs stock options, RSUs are more versatile than stock options. The final major difference between RSU and stock options is the way they are taxed. The RSUs are taxed based on the ordinary income rates.
Do you know the difference between a RSA and a RSU?
RSAs vs RSUs
- As RSAs are purchased on the grant date they are therefore subject to tax from the date of grant. ...
- RSAs usually have time-based vesting conditions. ...
- Termination: Unvested RSA shares are subject to repurchase upon termination. ...
- RSAs are eligible for 83 (b) elections. ...

Is restricted stock the same as RSUs?
Restricted stock (also called letter stock or section 1244 stock) is usually awarded to company directors and other high-level executives, whereas restricted stock units (RSUs) are typically awarded to lower-level employees. Restricted stock tends to have more conditions and restrictions than an RSU.
Is it better to take RSU or stock options?
Stock options are only valuable if the market value of the stock is higher than the grant price at some point in the vesting period. Otherwise, you're paying more for the shares than you could in theory sell them for. RSUs, meanwhile, is pure gain, as you don't have to pay for them.
Why are RSUs called restricted?
A restricted stock unit is a promise made to an employee by an employer to grant a given number of shares of the company's stock to the employee at a predetermined time in the future. Since RSUs are not actually stocks, but only a right to the promised stock, they carry no voting rights.
What is the benefit of restricted stock?
Restricted stock entitles you to receive dividends when they are paid to shareholders. Unlike stock options, which rarely carry dividend equivalent rights, restricted stock typically entitles you to receive dividends when they are paid to shareholders.
Do I get taxed twice on RSU?
Are RSUs taxed twice? No. The value of your shares at vesting is taxed as income, and anything above this amount, if you continue to hold the shares, is taxed at capital gains.
What happens to RSU if you leave?
Whenever you decide to quit, the vested portion of your RSUs will stay yours. Since shares of company stock are released to you upon a vesting date, those RSUs become shares that you own outright. And since you now own company shares outright, your departure from the company has no effect on your ownership.
Can restricted stock be sold?
Restricted stock refers to unregistered shares issued by public companies in private placement transactions and also to registered and unregistered securities held by affiliates and issuers. Restricted stock cannot be sold through public transactions due to securities laws and regulations.
Can you cash out restricted stock?
If you're granted RSUs, you get to essentially own company shares without putting any money down (unlike when you are exercising stock options). So, when is the best time to sell your RSUs? If your company is public, the best thing to do is to cash them out as soon as they vest.
Do you get dividends on restricted stock?
RSUs do not offer voting rights until actual shares are issued at vesting. No Dividends. RSUs cannot pay dividends, because no actual shares are used (employers can pay cash dividend equivalents if they choose).
Do you get more RSU after 4 years?
Restricted Stock Units (RSUs): Stock vests will begin on your first anniversary. You will receive additional stock vests at the end of year 2 and then every 6 months until you've been with the company for 4 years. Many Amazon employees receive additional refresher RSUs as an Amazon employee over time.
What are the disadvantages of using restricted stock to compensate employees?
Restricted Stock Bonus/Purchase Plans The disadvantage of a restricted stock bonus/purchase plan is that the employee has income but no cash with which to pay tax (of course, the Company can bonus cash to employee to cover the tax).
Do you pay capital gains tax on RSU?
You will also pay capital gains tax when you sell your RSU shares. After vesting, your RSU shares become yours. If you decide to sell your RSU shares, and the selling price is higher than the fair market value of your stocks, you will be liable for capital gains tax.
Why is restricted stock considered restricted stock?
With restricted stock, you own the shares from the day they are issued. But the stock is “restricted” stock because you still need to earn them. The most common restrictions are time-based and involve a vesting schedule, which means you earn them over time. This incentivizes employees to stay with the company.
What happens to restricted stock when an employee leaves?
If the employee leaves, the company can repurchase the stock. There are two main types of restricted stock: Restricted Stock Awards (RSAs) and Restricted Stock Units (RSUs).
What is an RSU grant?
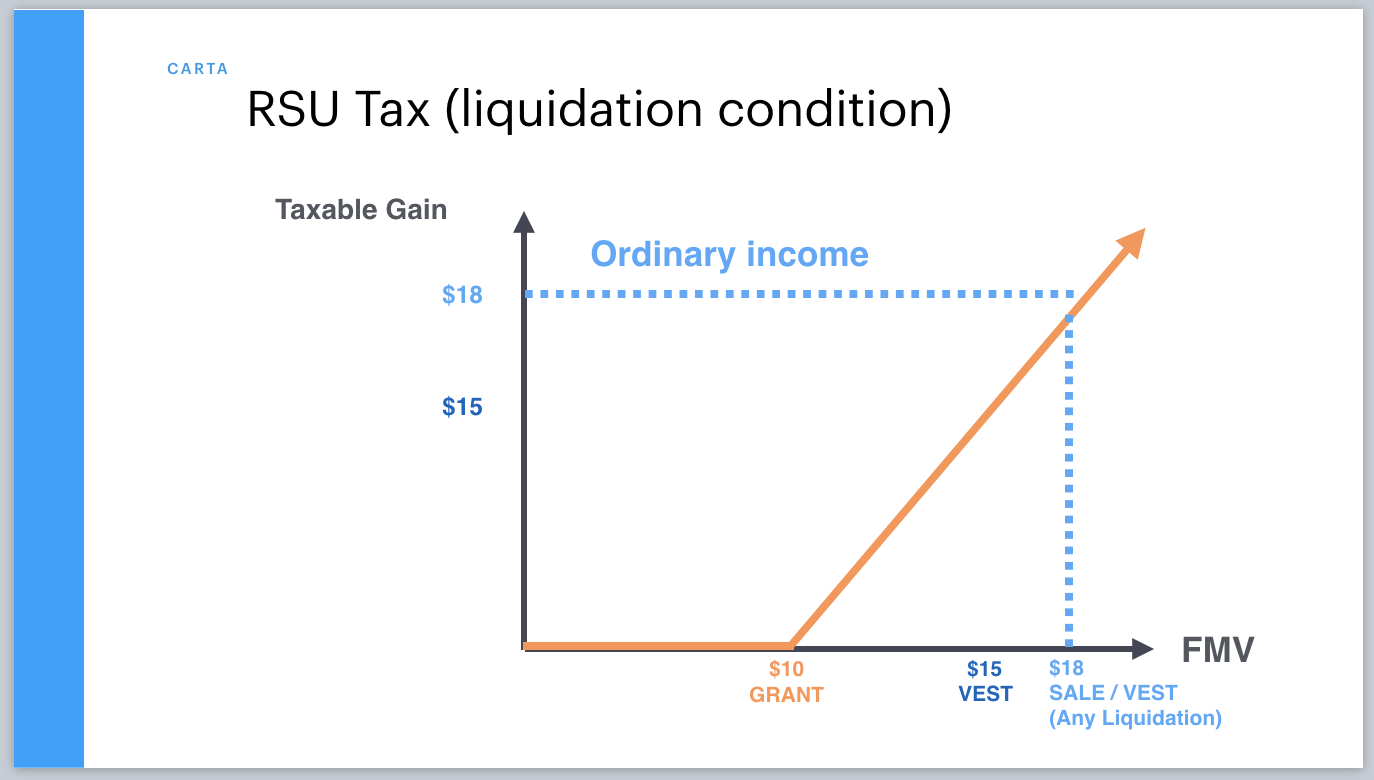
Unlike RSAs, when shares are “owned” by the employee on the grant date, an RSU is a promise from the company to give an employee shares at a later date. The date you actually receive your RSU shares can be a vesting date, a liquidation event, a specified date in the future, or some combination of these.
Why is Sean's taxable gain zero?
After this window passes Sean will not be able to file the election. Sean’s taxable gain is zero at grant because the FMV is the same as what he paid ($1). By filing an 83 (b) election, Sean is choosing to recognize ordinary income tax up front. Since the taxable gain is $0, Sean pays no ordinary income tax.
When are RSA shares given?
RSA shares are given to employees on the day they are granted. RSAs are typically issued to early employees before the first round of equity financing, when the FMV of common stock is very low. RSAs provide the individual the right to purchase shares at FMV, at a discount, or at no cost on the grant date.
Is a RSA eligible for 83 B?
Taxes: RSAs are eligible for 83 (b) elections. RSUs are not eligible for 83 (b) elections and are taxed when they vest. Timing is key with RSAs and RSUs – when they vest, when you sell, and when you can expect to receive them are important factors in determining the full value of these equity compensation awards.
Does Sean pay income tax on RSA shares?
Since the taxable gain is $0, Sean pays no ordinary income tax. Even when the RSA shares vest, Sean pays no tax. Instead, he pays a capital gains tax on the full $9 gain when he sells the shares. This is favorable for two reasons: 1) the capital gains tax is a lower rate than the ordinary income tax.
What is restricted stock?
Restricted stock, on the other hand, is a grant of stock that has certain vesting conditions, usually related to the passage of time and continued employment. The holder has legal title to the stock, which is subject to the company's contractual right to repurchase if the vesting conditions are not met ...
When a startup has implemented an employee incentive plan that allows for grants of restricted stock or restricted stock units, the plan
When a startup has implemented an employee incentive plan that allows for grants of restricted stock or restricted stock units, the plan administrator may consider a couple of different factors in deciding which instrument to use.
Do RSUs have stock?
Since RSUs are not actual stock in the company, but rather a contractual right to such stock, the grant recipient only acquires shareholder status when, and to the extent, that the company settles the right with stock.
How do stock options work?
Stock options are normally restricted by a market standoff provision, which restricts the sale of shares for a certain period of time after an initial public offering (IPO) to stabilize the market price of the stock.
What is restricted stock?
Restricted shares and stock options are both forms of equity compensation that are awarded to employees. Restricted shares represent actual ownership of stock but come with conditions on the timing of their sale. Stock options are the right to buy a certain number of shares at a certain price in the future, with the employee benefiting only if ...
What is stock option?
Stock options are the right to buy a certain number of shares at a certain price in the future , with the employee benefiting only if the stock price then exceeds the stock option price.
What happens to an employee's shares after a merger?
That means that an employee's shares become unrestricted if the company is acquired by another and the employee is fired in the restructuring that follows. Insiders are often awarded restricted shares after a merger or other major corporate event.
What happens if an executive leaves a company?
An executive who leaves the company fails to meet performance goals or runs afoul of SEC trading restrictions may have to forfeit their restricted stock. Both are awarded to motivate employees, but restricted shares are most often granted by established companies, while stock options are popular with startups.
Do restricted shares have to be vested?
However, they are usually vested. That is, when restricted shares are given to an employee, it is on condition that the employee will continue working at the company for a number of years or until a particular company milestone is met. This might be an earnings goal or another financial target.
What is restricted stock?
Restricted stock units are a promise from an employer to grant shares to you. Before the shares are received, they are said to be unvested. Upon meeting the pre-determined condition (s), the shares vest and you receive them.
What is ordinary income per share?
The ordinary income per share realized when the shares vest equals the market price at the time of vesting less the price paid for the shares, if any (generally you pay nothing for the shares). For example, you are granted shares worth $10,000 but they are worth $15,000 when you satisfy the vesting condition.
Do you pay dividends on shares?
Dividends are paid on your shares. You are confident you will satisfy the vesting condition. You have cash to pay the ordinary income tax prior to selling the shares. Despite the potential benefits, there are many scenarios where you could end up paying more (or a lot more) in tax by filing the 83b election:
Do you get RSA shares if you are still employed?
Most often, you will receive the shares only if you are still employed at the end of the pre-determined period. Less often, you must meet a pre-determined performance goal to receive the shares. Generally, employees receive RSA or RSU shares as additional compensation without needing to pay anything for the shares.
Do you have to title shares in your name?
Prior to receiving the shares, they are not actually titled in your name. The implications of this are that any dividends paid on the shares while they are unvested are generally not paid to you and you will not have voting rights that come with owning the shares.
Is RSU a part of annual compensation?
RSU or RSA plans can be a substantial part of your annual compensation if you remain at your company and are able to meet the vesting condition . With an RSU plan, it’s important to understand and be prepared to have taxes withheld on your shares upon vesting.
Why are stock options given at a discount rate?
And also, stock options are given at a discount rate (less than the price of the stock at that time) so that the stock option can be considered as a reward .
How long do you have to keep stock after non qualifying disposition?
In the case of RSUs, taxes are based on vesting. If at the time of settlement, the company grants stocks, and the employee keeps the stock for more than 12 months, then capital gains treatment can be possible.
What is stock option?
The Stock Option Stock options are derivative instruments that give the holder the right to buy or sell any stock at a predetermined price regardless of the prevailing market prices.
When can stock options be issued?
Stock options can be issued any time after the issuance. Restricted stock units can also be issued any time after the issuance. There’s a full right of the shareholders offered. There’s a restricted right of the shareholders offered.
Is the payment during settlement always stock?
The payment during settlement is always stock in the case of stock options. On the other hand, the payment during settlement can be cash or stock. After the vesting period, the stock option becomes the common stock. But for the RSUs, the settlement is done once the vesting period is over.
Do employees get voting rights in restricted stock?
In the case of stock options, the employee receives the full right of the shareholders. On the other hand, in the case of restricted stock units, the employee doesn’t receive the full right. The stock option offers both voting rights and dividend rights. In the case of restricted stock units, voting rights are not given, ...
What is a Restricted Stock Award?
If you have an RSA or restricted stock award, you own the right to purchase shares of your company’s stock at a set price, often a cheaper price than a regular investor would pay. Alternately, you own the right to claim a set number of shares for free.
What is a Restricted Stock Unit?
A RSU is simpler than an RSA. It’s basically just a promise from your employer to give you a set number of shares of the company stock at a future date. An RSU is not stock and it’s not stock options. Again, it’s just a promise from your company to give you a certain number of shares at a future date.
RSA vs RSU: What Happens to Unvested Stock if You Leave Before Vesting?
If you leave a job before the shares of your RSA or RSU are fully vested, things can get a little complicated.
What Do I Need to Do With My RSU or RSA?
RSAs and RSUs are far from simple. Even when they understand the rules around them, a lot of people are at a loss for what they actually need to do to make sure they are managing their investment correctly.
What If I Want to Sell the Stock?
Some people will choose to sell the stock they gain through an RSA or RSU because they don’t believe it will go up in value. Others choose to sell for allocation reasons. Sometimes it isn’t a good idea for company stock to make up too large of a percentage of your portfolio.
What is an RSU?
An RSU is a promise from your employer to grant you shares of the company stock in the future if certain restrictions are met, often at no cost to you. Each grant of RSUs also typically has its own vesting schedule. Tax Implications. A major difference between NQSOs and RSUs is the way in which they are taxed.
What is a non qualified stock option?
What Are Non-Qualified Stock Options? NQSOs give you the right to buy a certain number of company shares, at a specified price (known as the exercise price) during a window of time (usu ally 10 years). Typically, your right cannot be exercised until you have satisfied the vesting requirements set forth by the company.
Do RSUs have flexibility?
RSUs offer limited flexibility in comparison to NQSOs. With NQSOs, you have some control over the timing of the exercise and thus when the taxes from the options are triggered. In the case of RSUs, however, the entire value of RSUs must be reported as ordinary income in the year of vesting.