How to calculate portfolio turnover ratio?
What is the Portfolio Turnover Ratio?
- Formula for the Portfolio Turnover Ratio. Minimum of securities bought or sold refers to the total dollar amount of new securities purchased or the total amount of securities sold (whichever ...
- Interpreting the Portfolio Turnover Ratio. ...
- Portfolio Turnover Ratio and Investment Strategies. ...
- Practical Examples. ...
- Additional Resources. ...
How to calculate turnover in stock market?
What is the Stock Turnover Ratio Formula?
- Examples of Stock Turnover Ratio Formula (With Excel Template) Let’s take an example to better understand the Stock Turnover Ratio Formula calculation in a better manner.
- Explanation. ...
- Relevance and Uses of Stock Turnover Ratio Formula. ...
- Stock Turnover Ratio Formula Calculator. ...
What is your share turnover ratio?
What is your “ Share Turnover “ ratio ? Share turnover is a measure of stock liquidity calculated by dividing the total number of shares traded over a period by the average number of shares outstanding for the period. The higher the share turnover, the more liquid the share of the company.
What is the formula for turnover ratio?
- Locate the value of the company's assets on the balance sheet as of the start of the year.
- Locate the ending balance or value of the company's assets at the end of the year.
- Add the beginning asset value to the ending value and divide the sum by two, which will provide an average value of the assets for the year.

What is the formula for stock turnover ratio?
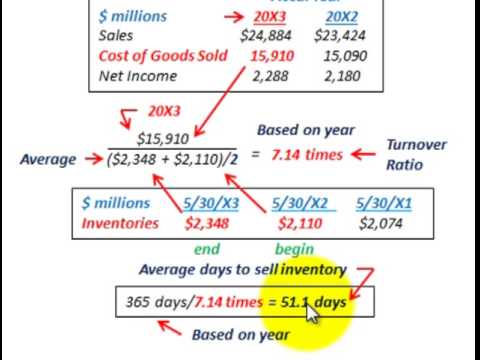
You can calculate the inventory turnover ratio by dividing the inventory days ratio by 365 and flipping the ratio. In this example, inventory turnover ratio = 1 / (73/365) = 5. This means the company can sell and replace its stock of goods five times a year.
Why do we calculate stock turnover ratio?
The stock turnover ratio determines how soon an enterprise sells its goods and products and replaces its inventories in a set duration. This ratio helps improve inventory management as it tells about the speedy or sluggish flow of inventory being utilized to create sales.
Is a high stock turnover good?
The higher the inventory turnover, the better, since high inventory turnover typically means a company is selling goods quickly, and there is considerable demand for their products. Low inventory turnover, on the other hand, would likely indicate weaker sales and declining demand for a company's products.
What is a good stock turnover rate?
between 5 and 10What Is a Good Inventory Turnover Ratio? A good inventory turnover ratio is between 5 and 10 for most industries, which indicates that you sell and restock your inventory every 1-2 months. This ratio strikes a good balance between having enough inventory on hand and not having to reorder too frequently.
What Is Turnover Ratio?
The turnover ratio or turnover rate is the percentage of a mutual fund or other portfolio's holdings that have been replaced in a given year (calendar year or whichever 12-month period represents the fund's fiscal year).
Understanding Turnover Ratio
The turnover ratio varies by the type of mutual fund, its investment objective, and/or the portfolio manager's investing style. For example, a stock market index fund usually will have a low turnover rate since it duplicates a particular index, and the component companies in indexes don't change that often.
The Significance of Turnover Ratio
As a technical indicator, the turnover ratio itself has no intrinsic value—high turnover ratios are not necessarily "bad," nor are low turnover ratios necessarily "good." But investors should be aware of the consequences of turnover frequency.
Real-World Examples of Turnover Ratio
The BNY Mellon Appreciation Fund from Fidelity (DGAGX) has a strong buy-and-hold strategy in mostly blue-chip companies with total market capitalizations of over $5 billion at the time of purchase.
Examples of Stock Turnover Ratio Formula (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to better understand the Stock Turnover Ratio Formula calculation in a better manner.
Explanation
The formula for a stock turnover ratio can be derived by using the following steps:
Relevance and Uses of Stock Turnover Ratio Formula
It is important to understand the concept of stock turnover ratio as it assesses the efficiency of a company in managing its merchandise.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Stock Turnover Ratio Formula. Here we discussed how to calculate Stock Turnover Ratio Formula along with practical examples. We also provide a Stock Turnover Ratio calculator with a downloadable excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –
Examples of Stock Turnover Ratio (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of the Stock Turnover Ratio in a better manner.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Stock Turnover Ratio
It can be used to gauge the inventory management of a company among its peers.
Conclusion
So, the stock turnover ratio is a tool that can be used to measure the inventory management capability of a company. It can be seen as the efficiency metric to see how well a company is able to use its stock inventory.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Stock Turnover Ratio. Here we discuss how the Stock Turnover Ratio can be calculated by using the formula with examples and a downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –
Practical Example of Inventory Turnover Ratio
For example, Walmart Inc. (WMT) and Target Corporation reported the following figures in financial statements:
Interpretation of Inventory Turnover Ratio
Inventory turnover ratio is an efficiency ratio that measures how well a company can manage its inventory. It is important to achieve a high ratio, as higher turnover rates reduce storage and other holding costs.
Key Takeaways
Inventory turnover ratio is an efficiency ratio that measures how efficiently inventory is managed.
More Resources
CFI offers the Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)™ Become a Certified Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® CFI's Financial Modeling and Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® certification will help you gain the confidence you need in your finance career.
What are Turnover Ratios?
A turnover ratio represents the amount of assets or liabilities that a company replaces in relation to its sales. The concept is useful for determining the efficiency with which a business utilizes its assets.
Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio
Measures the time it takes to collect an average amount of accounts receivable. It can be impacted by the corporate credit policy, payment terms, the accuracy of billings, the activity level of the collections staff, the promptness of deduction processing, and a multitude of other factors.
Inventory Turnover Ratio
Measures the amount of inventory that must be maintained to support a given amount of sales. It can be impacted by the type of production process flow system used, the presence of obsolete inventory, management's policy for filling orders, inventory record accuracy, the use of manufacturing outsourcing, and so on.
Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio
Measures the fixed asset investment needed to maintain a given amount of sales. It can be impacted by the use of throughput analysis, manufacturing outsourcing, capacity management, and other factors.
Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio
Measures the time period over which a company is allowed to hold trade payables before being obligated to pay suppliers. It is primarily impacted by the terms negotiated with suppliers and the presence of early payment discounts.
Investment Fund Turnover
The turnover ratio concept is also used in relation to investment funds. In this context, it refers to the proportion of investment holdings that have been replaced in a given year. A low turnover ratio implies that the fund manager is not incurring many brokerage transaction fees to sell off and/or purchase securities.
What Is Share Turnover?
Share turnover is a measure of stock liquidity, calculated by dividing the total number of shares traded during some period by the average number of shares outstanding for the same period. The higher the share turnover, the more liquid company shares are.
Understanding Share Turnover
Share turnover ratio indicates how easy, or difficult, it is to sell shares of a particular stock on the market. It compares the number of shares that change hands during a particular period with the total number of shares that could have been traded during that same period.
Calculating the Share Turnover Ratio
To compute a company's share turnover ratio, you need two numbers. The first is the trading volume, which is the total number of shares of the company's stock that were bought and sold during a given time period.
Example of Share Turnover and the Limitations of the Ratio
The share turnover ratio only tells you how easily an investor can get rid of shares. It doesn't necessarily tell you anything about the performance of a company behind the stock. Let's look at a large, well-known stock like Apple. At the end of 2018, Apple had approximately 4.8 billion shares outstanding.

What Is Turnover Ratio?
Understanding Turnover Ratio
- The turnover ratio varies by the type of mutual fund, its investment objective, and/or the portfolio manager's investing style. For example, a stock market index fund usually will have a low turnover rate since it duplicates a particular index, and the component companies in indexes don't change that often. On the other hand, a bond fund will often have high turnover because active tradingis …
The Significance of Turnover Ratio
- As a technical indicator, the turnover ratio itself has no intrinsic value—high turnover ratios are not necessarily "bad," nor are low turnover ratios necessarily "good." But investors should be aware of the consequences of turnover frequency. High turnover often results in increased costs for the fund due to the payment of spreads and commissions when buying and selling stocks; increase…
Real-World Examples of Turnover Ratio
- The BNY Mellon Appreciation Fund from Fidelity (DGAGX) has a strong buy-and-hold strategy in mostly blue-chip companies with total market capitalizations of over $5 billion at the time of purchase. Those companies show sustained profitability, strong balance sheets, global expansion, and above-average earnings growth, in keeping with the fund's objective of capital pr…