
Summary
- Shareholders’ equity is the shareholders’ claim on assets after all debts owed are paid up.
- It is calculated by taking the total assets minus total liabilities.
- Shareholders’ equity determines the returns generated by a business compared to the total amount invested in the company.
What items affect stockholders equity?
- Accounts payable
- Accounts receivable
- Equipment
- Sales revenue
- Service revenue
- Inventory
- Mortgage payable
- Supplies expense
- Rent expense
- Salaries and wages expense
What is shareholders equity and how to calculate it?
Shareholders’ Equity = Total Assets – Total Liabilities. The above formula is known as the basic accounting equation, and it is relatively easy to use. Take the sum of all assets in the balance sheet and deduct the value of all liabilities. Total assets are the total of current assets, such as marketable securities.
What are the basic sources of stockholders equity?
What Are the Two Main Sources of Stockholders' Equity?
- Paid-in Capital. One of the two main sources of stockholders' equity is paid-in capital. ...
- Retained Earnings. Retained earnings are the other main source of stockholders' equity. ...
- Other Sources. In addition to paid-in capital and retained earnings, there are other sources of stockholders' equity.
- Warning: Stockholders' Equity Can Drop. ...
How do you calculate shareholders' equity?
This will replace the existing program that is due to be completed in November at a 3% discount to net asset value, less costs. Strategic Equity then plans to use up to 9% of its net asset value to buyback shares over the rest of this year at a 5% discount to net asset value.
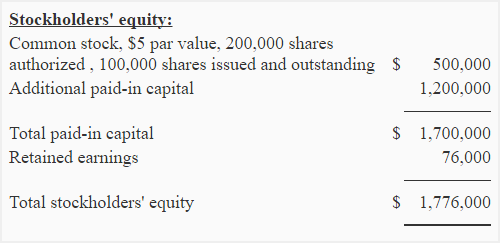
What is an example of stockholders equity?
Equity is anything that is invested in the company by its owner or the sum of the total assets minus the sum of the total liabilities of the company. E.g., Common stock, additional paid-in capital, preferred stock, retained earnings and the accumulated other comprehensive income.
What is stockholders equity for dummies?
Stockholders' equity has three common components: paid-in capital, treasury stock, and retained earnings.\nThree types of business entities exist: corporations, sole proprietorships, and flow-through entities such as partnerships. Stockholders' equity applies only to the corporate business entity.
What is stockholders equity formula?
Shareholders' Equity = Total Assets − Total Liabilities \text{Shareholders' Equity}=\text{Total Assets }-\text{ Total Liabilities} Shareholders' Equity=Total Assets − Total Liabilities
Is stockholders equity good or bad?
For most companies, higher stockholders' equity indicates more stable finances and more flexibility in case of an economic or financial downturn. Understanding stockholders' equity is one way that investors can learn about the financial health of a firm.
What is another name for stockholders equity?
share capitalShareholders' equity refers to the owners' claim on the assets of a company after debts have been settled. It is also known as share capital, and it has two components.
What is considered stockholders equity on a balance sheet?
Key Takeaways. Shareholder equity is the owner's claim after subtracting total liabilities from total assets. You can calculate shareholder equity by adding together all assets and all liabilities from a company's balance sheet.
Why is shareholder equity important?
The statement of shareholders' equity enables shareholders to see how their investments are faring. It's also a useful tool for companies in helping them make decisions about future issuances of stock shares.
What is the difference between equity and shareholders equity?
While equity typically refers to the ownership of a public company, shareholders' equity is the net amount of a company's total assets and total liabilities, which are listed on the company's balance sheet. For example, investors might own shares of stock in a publicly-traded company.
Is shareholders equity the same as dividends?
Are Dividends Part of Stockholder Equity? Dividends are not specifically part of stockholder equity, but the payout of cash dividends reduces the amount of stockholder equity on a company's balance sheet. This is so because cash dividends are paid out of retained earnings, which directly reduces stockholder equity.
What affects stockholders equity?
Items that impact stockholder's equity include net income, dividend payments, retained earnings and Treasury stock. A high stockholder's equity balance in comparison to such items as debt is a positive sign for investors.
What is stockholders equity made up of?
Four components that are included in the shareholders' equity calculation are outstanding shares, additional paid-in capital, retained earnings, and treasury stock. If shareholders' equity is positive, a company has enough assets to pay its liabilities; if it's negative, a company's liabilities surpass its assets.
What does it mean if stockholder equity increases?
When stockholders' equity rises, it may indicate growth in a company's profits. This is because the basic formula for determining stockholders' equity involves subtracting liabilities, or debts, from the company's assets. As a business makes money by selling goods and services, it takes in cash.
What is shareholder equity?
Shareholder equity (SE) is the owner's claim after subtracting total liabilities from total assets. If shareholder equity is positive that means the company has enough assets to cover its liabilities, but if it is negative, then the company's liabilities exceed its assets. Retained earnings is part of shareholder equity and is the percentage ...
How to calculate shareholder equity?
The steps to calculate shareholder equity are as follows: 1 Locate the company's total assets on the balance sheet for the period. 2 Total all liabilities, which should be a separate listing on the balance sheet. 3 Locate total shareholder's equity and add the number to total liabilities. 4 Total assets will equal the sum of liabilities and total shareholder equity.
What happens to assets in liquidation?
In liquidation, physical asset values have been reduced and other extraordinary conditions exist. Shareholder equity can be either negative or positive. If positive, the company has enough assets to cover its liabilities. If negative, the company's liabilities exceed its assets.
What is long term liability?
Long-term liabilities are obligations that are due for repayment in periods longer than one year (e.g., bonds payable, leases, and pension obligations). Upon calculating the total assets and liabilities, shareholder equity can be determined.
What is total assets?
All the information needed to compute a company's shareholder equity is available on its balance sheet. Total assets include current and non-current assets. Current assets are assets that can be converted to cash within a year (e.g., cash, accounts receivable, inventory, et al.).
Is retained earnings the same as cash?
Retained earnings should not be confused with cash or other liquid assets. This is because years of retained earnings could be used for either expenses or any asset type to grow the business. Shareholders’ equity for a company that is a going concern is not the same as liquidation value.
Is negative shareholder equity a good indicator of financial health?
For this reason, many investors view companies with negative shareholder equity as risky or unsafe investments. Shareholder equity alone is not a definitive indicator of a company's financial health.
What are the components of stockholders equity?
Stockholders Equity is influenced by several components: 1 Share Capital – amounts received by the reporting entity from transactions with its owners are referred to as share capital#N#Share Capital Share capital (shareholders' capital, equity capital, contributed capital, or paid-in capital) is the amount invested by a company’s#N#. 2 Retained Earnings – amounts earned through income, referred to as Retained Earnings and Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (for IFRS only). 3 Net Income & Dividends – Net income increases retained earnings while dividend payments reduce retained earnings.
How to calculate retained earnings?
To calculate retained earnings, the beginning retained earnings balance is added to the net income or loss and then dividend payouts are subtracted. A summary report called a statement of retained earnings is also maintained, outlining the changes in retained earnings for a specific period.
What is the purpose of calculating stockholders equity?
Calculating stockholders equity is an important step in financial modeling. This is usually one of the last steps in forecasting the balance sheet items. Below is an example screenshot of a financial model where you can see the shareholders equity line completed on the balance sheet.
Why are debt holders not interested in equity?
Therefore, debt holders are not very interested in the value of equity beyond the general amount of equity to determine overall solvency. Shareholders, however, are concerned with both liabilities and equity accounts because stockholders equity can only be paid after bondholders have been paid.
What is a share capital?
Share Capital (contributed capital) refers to amounts received by the reporting company from transactions with shareholders. Companies can generally issue either common shares or preferred shares. Common shares represent residual ownership in a company and in the event of liquidation or dividend payments, common shares can only receive payments after preferred shareholders have been paid first.
How many dates are there for dividends?
There are four key dates in terms of dividend payments, two of which require specific accounting treatments in terms of journal entries. There are various kinds of dividends that companies may compensate its shareholders, of which cash and stock are the most prevalent. Date. Explanation.
What is authorized number of shares?
The number of shares authorized is the number of shares that the corporation is allowed to issue according to the company’s articles of incorporation. The number of shares issued refers to the number of shares issued by the corporation and can be owned by either external investors or by the corporation itself.
What is the difference between a positive and negative shareholder equity?
A negative shareholders’ equity means that shareholders will have nothing left when assets are liquidated and used to pay all debts owed. On the other hand, positive shareholder equity shows that the company’s assets have been grown to exceed the total liabilities, meaning that the company has enough assets to meet any liabilities that may arise.
What is dividend policy?
Dividend Policy A company’s dividend policy dictates the amount of dividends paid out by the company to its shareholders and the frequency with which the dividends are paid. by showing its decision to pay profits earned as dividends to shareholders or reinvest the profits back into the company. On the balance sheet, shareholders’ equity is broken ...
How to find total liabilities?
Total liabilities are obtained by adding current liabilities and long-term liabilities. All the values are available in a company’s balance sheet. What remains after deducting total liabilities from the total assets is the value that shareholders would get if the assets were liquidated and all debts were paid up.
What is the difference between current liabilities and long term liabilities?
On the other hand, liabilities are the total of current liabilities (short-term liabilities) and long-term liabilities. Current liability comprises debts that require repayment within one year, while long-term liabilities are liabilities whose repayment is due beyond one year.
What is shareholder equity?
Shareholders’ equity refers to the owners’ claim on the assets of a company after debts have been settled. It is also known as share capital. Share Capital Share capital (shareholders' capital, equity capital, contributed capital, or paid-in capital) is the amount invested by a company’s. , and it has two components.
How to calculate shareholder equity?
Shareholders’ equity is the shareholders’ claim on assets after all debts owed are paid up. It is calculated by taking the total assets minus total liabilities. Shareholders’ equity determines the returns generated by a business compared to the total amount invested in the company.
What is total assets?
Total assets are the total of current assets, such as marketable securities. Marketable Securities Marketable securities are unrestricted short-term financial instruments that are issued either for equity securities or for debt securities of a publicly listed company.
What are the risks of investing in equity?
Investors in equity must consider a number of risks that are unique to these types of securities. Here are some of the widely observed risks that impact broad sections of the market: 1 Market price – The market price of a stock can give you the market's appraisal of the worth of that company at a particular point in time. Price changes are typically driven not only by objectively measurable changes in business conditions and the economic environment, but also by changes in investor emotion. 2 Price-to-earnings ratio – This number, which is derived by dividing the stock price by the company's earnings per share, is used to determine what an investor is paying for the earning power of the company. The ratio can be calculated using either the most recent reported earnings, or an analyst's projection of expected future earnings. It's one figure that can be used in comparing the value of several companies even though their prices may be vastly different. 3 Dividend yield – The dividend yield, determined by dividing the amount of the dividend by the share price, simply indicates what percent return the company is paying its investors. This number can also be used in a comparison of companies. 4 Payout ratio – This figure represents the percentage of earnings a company is paying out to its investors. It's an indication of whether most of a company's earnings are being paid to its investors or whether they are being reinvested in the growth of the company.
What is common stock?
Common stock is the term used to describe shares representing an equity stake in the firm. A common shareholder can only receive a share of annual profits (i.e., dividends) after all bondholders receive their interest payments and other investors and creditors receive any payment preferences they might have been due.
What is dividend yield?
Dividend yield – The dividend yield, determined by dividing the amount of the dividend by the share price, simply indicates what percent return the company is paying its investors. This number can also be used in a comparison of companies.
What is preferred stock?
Preferred stock is the term used for shares that give their holders a higher claim on any profits or proceeds from asset sales, putting their shareholders ahead of common stockholders, but behind bondholders. Preferred stock does not represent a company debt that must be repaid.
What does stock represent?
Stock represents ownership of a company. In a historical and legal sense, this ownership could be expressed as a portion of the company's net realizable asset value, in other words, a share of the cash that would remain after all assets are liquidated (presumably at fair market value) and all liabilities are satisfied.
Is preferred stock a debt?
Preferred stock does not represent a company debt that must be repaid. It is, rather, a fixed claim on future profits. It does not generally give shareholders any voting rights. Additionally, some companies may report the existence of restricted stock.
Do common shareholders have the right to vote?
Common shareholders also generally have the right to vote in elections determining the company's board of directors. Some companies issue multiple classes of common stock, generally to give a limited number of shareholders influence over corporate governance well beyond their numbers.
What is shareholder equity?
Shareholders' equity represents the net worth of a company, which is the dollar amount that would be returned to shareholders if a company's total assets were liquidated, and all of its debts were repaid. Typically listed on a company's balance sheet, this financial metric is commonly used by analysts to determine a company's overall fiscal health.
How to calculate shareholder equity?
How to Calculate Shareholders' Equity. Shareholders' equity may be calculated by subtracting its total liabilities from its total assets —both of which are itemized on a company's balance sheet. Total assets can be categorized as either current or non-current assets. Current assets are those that can be converted to cash within a year, ...
What is considered long term assets?
Long-term assets are those that cannot be converted to cash or consumed within a year, such as real estate properties, manufacturing plants, equipment, and intangible items like patents. Total liabilities consist of current liabilities and long-term liabilities.
Is shareholders equity a financial indicator?
But shareholders' equity isn't the sole indicator of a company's financial health. Hence, it should be paired with other metrics to obtain a more holistic picture of an organization's standing.
Is shareholder equity positive or negative?
Shareholders' equity can be either negative or positive. If it's in positive territory, the company has sufficient assets to cover its liabilities. If it's negative, its liabilities exceed assets, which may deter investors, who view such companies as risky investments. But shareholders' equity isn't the sole indicator of a company's financial ...

Components of Stockholders Equity
Applications in Personal Investing
- With various debt and equity instruments in mind, we can apply this knowledge to our own personal investment decisions. Although many investment decisions depend on the level of risk we want to undertake, we cannot neglect all the key components covered above. Bonds are contractual liabilities where annual payments are guaranteed unless the issuer defaults, while di…
Applications in Financial Modeling
- Calculating stockholders equity is an important step in financial modeling. This is usually one of the last steps in forecasting the balance sheet items. Below is an example screenshot of a financial model where you can see the shareholders equity line completed on the balance sheet. To learn more, launch our financial modeling coursesnow!
Learn More
- Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Stockholders equity. To keep learning and advancing your career, the following resources will be helpful: 1. Free Reading Financial Statements Course 1. How to Link the 3 Financial Statements 2. Financial Statement Analysis Guide 3. Financial Modeling Guide 4. How to be a Great Financial Analyst