Diversificationis the process of creating a portfolio that includes a mix of different types or classes of investments in order to balance risk and reward. Doing so can help you to manage stock market volatility over time as the market moves through different cycles.
How much stock diversification is enough?
There's no absolute cutoff point that distinguishes an adequately diversified portfolio from an over-diversified one. As a general rule of thumb, most investors would peg a sufficiently diversified portfolio as one that holds 20 to 30 investments across various stock market sectors.
What are some disadvantages of diversification?
Disadvantages of Diversification in Investing
- Reduces Quality. There are only so many quality companies and even less that are priced at levels that provide a margin of safety.
- Too Complicated. Many investors include so many assets in their portfolio they don’t really understand what’s in them.
- Indexing. ...
- Market Risk. ...
- Below Average Returns. ...
- Bad Investment Vehicles. ...
Is stock diversification overrated?
Diversification is overrated. My opinion of course, and I don't think this applies to long positions you're holding for 1 year +. Mainly this is directed at traders, short swings/ day trades etc. When I first started trading about 2 years ago, I had it in my head to focus on spreading my money out and not going too heavy on any one stock.
How many stocks is diversified?
How Many Stocks Make a Diversified Portfolio? MeirStatman* Abstract We show that a well-diversified portfolio of randomly chosen stocks must include at least 30 stocks for a borrowing investor and 40 stocks for a lending investor. This contradicts the widely accepted notion that the benefits of diversification are virtually exhausted when

What does diversification mean in stocks?
Diversification is the practice of spreading your investments around so that your exposure to any one type of asset is limited. This practice is designed to help reduce the volatility of your portfolio over time.
Is diversification in stocks good?
Diversification reduces risk by investing in vehicles that span different financial instruments, industries, and other categories. Unsystematic risk can be mitigated through diversification while systemic or market risk is generally unavoidable.
How do you diversify stocks?
To achieve a diversified portfolio, look for asset classes that have low or negative correlations so that if one moves down, the other tends to counteract it. ETFs and mutual funds are easy ways to select asset classes that will diversify your portfolio, but one must be aware of hidden costs and trading commissions.
What is diversification in investing example?
In other words, investors use diversification to avoid the huge losses that can happen by putting all of their eggs in one basket. For example, when you diversify, you allocate a portion of your investments to riskier stock market trading, which you spread out across different types of stocks and companies.
Does Warren Buffett believe in diversification?
Indeed, much of the traditional advice that investors receive comes straight from Buffett's playbook, with a notable exception: diversification. “Diversification is protection against ignorance,” Buffett famously says. “It makes little sense if you know what you're doing.”
What are the pros and cons of diversification?
Advantages and Disadvantages of Portfolio DiversificationAdvantagesDisadvantages1. Risk management 2. Align with your goals 3. Growth opportunity1. Increases chances of mistakes 2. Rules differ for each asset 3. Tax implications & cost of investment 4. Caps growthDec 13, 2021
How many stocks do you need to be diversified?
Investors should have no less than 60 stocks in their investments in order to have a well-diversified portfolio. If you don't have time to research but want to start investing, consider a low-cost, broad-market index fund instead.
What are 4 types of investments?
There are four main investment types, or asset classes, that you can choose from, each with distinct characteristics, risks and benefits.Growth investments. ... Shares. ... Property. ... Defensive investments. ... Cash. ... Fixed interest.
What is a good diversified portfolio?
A diversified portfolio should have a broad mix of investments. For years, many financial advisors recommended building a 60/40 portfolio, allocating 60% of capital to stocks and 40% to fixed-income investments such as bonds. Meanwhile, others have argued for more stock exposure, especially for younger investors.
What is a good mix of stocks?
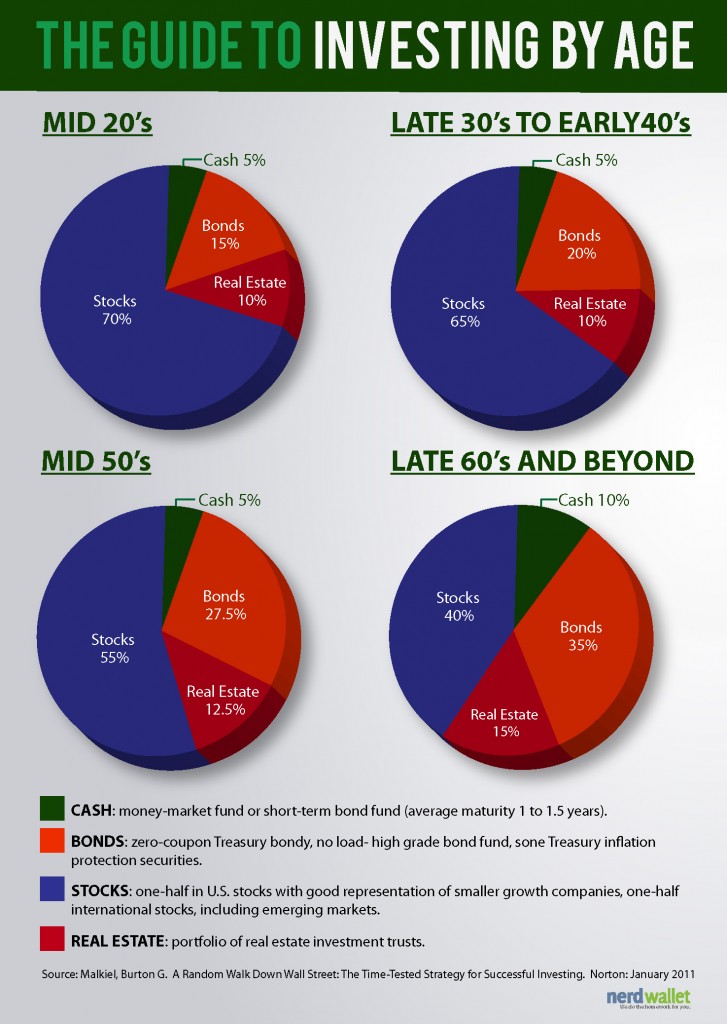
The rule of thumb advisors have traditionally urged investors to use, in terms of the percentage of stocks an investor should have in their portfolio; this equation suggests, for example, that a 30-year-old would hold 70% in stocks, 30% in bonds, while a 60-year-old would have 40% in stocks, 60% in bonds.
Which stock is riskier for a diversified investor?
Which stock is riskier for a diversified investor? For diversified investors the relevant risk is measured by beta. Therefore, the stock with the higher beta is more risky.
What are the three types of diversification?
There are three types of diversification techniques:Concentric diversification. Concentric diversification involves adding similar products or services to the existing business. ... Horizontal diversification. ... Conglomerate diversification.
What Is Diversification in Investing?
Diversification is a technique that reduces risk by allocating investments across various financial instruments, industries, and other categories. It aims to maximize returns by investing in different areas that would each react differently to the same event.
Understanding Diversification in Investing
Let's say you have a portfolio that only has airline stocks. Share prices will drop following any bad news, such as an indefinite pilot strike that will ultimately cancel flights. This means your portfolio will experience a noticeable drop in value .
How Many Stocks You Should Have
Obviously, owning five stocks is better than owning one, but there comes a point when adding more stocks to your portfolio ceases to make a difference. There is a debate over how many stocks are needed to reduce risk while maintaining a high return.
Different Types of Risk
Investors confront two main types of risk when they invest. The first is known as systematic or market risk. This type of risk is associated with every company. Common causes include inflation rates, exchange rates, political instability, war, and interest rates.
Problems with Diversification
Professionals are always touting the importance of diversification but there are some downsides to this strategy. First, it may be somewhat cumbersome managing a diverse portfolio, especially if you have multiple holdings and investments.
What Does Diversification Mean in Investing?
Diversification is a strategy that aims to mitigate risk and maximize returns by allocating investment funds across different vehicles, industries, companies, and other categories.
What Is an Example of a Diversified Investment?
A diversified investment portfolio includes different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and other securities. But that's not all. These vehicles are diversified by purchasing shares in different companies, asset classes, and industries.
What Is Diversification?
Diversification is a risk management strategy that mixes a wide variety of investments within a portfolio. A diversified portfolio contains a mix of distinct asset types and investment vehicles in an attempt at limiting exposure to any single asset or risk.
The Basics of Diversification
Studies and mathematical models have shown that maintaining a well-diversified portfolio of 25 to 30 stocks yields the most cost-effective level of risk reduction. The investing in more securities generates further diversification benefits, albeit at a drastically smaller rate.
Diversification by Asset Class
Fund managers and investors often diversify their investments across asset classes and determine what percentages of the portfolio to allocate to each. Classes can include:
Foreign Diversification
Investors can reap further diversification benefits by investing in foreign securities because they tend to be less closely correlated with domestic ones. For example, forces depressing the U.S. economy may not affect Japan's economy in the same way.
Diversification and the Retail Investor
Time and budget constraints can make it difficult for noninstitutional investors—i.e., individuals—to create an adequately diversified portfolio. This challenge is a key reason why mutual funds are so popular with retail investors. Buying shares in a mutual fund offers an inexpensive way to diversify investments.
Disadvantages of Diversification
Reduced risk, a volatility buffer: The pluses of diversification are many. However, there are drawbacks, too. The more holdings a portfolio has, the more time-consuming it can be to manage—and the more expensive, since buying and selling many different holdings incurs more transaction fees and brokerage commissions.
Diversification and Smart Beta
Smart beta strategies offer diversification by tracking underlying indices but do not necessarily weigh stocks according to their market cap. ETF managers further screen equity issues on fundamentals and rebalance portfolios according to objective analysis and not just company size.
How diversification works
Diversification works by building a portfolio that contains a variety of asset types, investment vehicles and includes investment in both domestic and foreign markets to lower the risk of any individual holding or security.
Types of diversification
Fund managers and investors will typically diversify their portfolios by investing in a variety of different asset classes and assigning a percentage of the portfolio to each. Different asset classes can include stocks, bonds, real estate, EFTs, commodities, and cash and short-term cash equivalents.
Advantages of diversification
Building a diversified portfolio can help investors significantly reduce their exposure to risk and avoid losing a large percentage of their investment.
Disadvantages of diversification
If a particular stock or security in your portfolio achieves short-term gains, your share of these gains will be reduced compared. For example, that security may only make up 10% of your portfolio but if you had invested 50% your returns would be higher.
Good Deal
You may get a good deal on company stock and load up in your retirement fund and buy more for your investment fund because you believe in your company.
An Example
For example, if all of the stocks you owned were extra sensitive to interest rates, then you would not be diversified. The stocks would move in correlation with the interest rates and each other.
Another type of Diversification
Another type of diversification involves the other parts of your portfolio.
The 4 primary components of a diversified portfolio
Stocks represent the most aggressive portion of your portfolio and provide the opportunity for higher growth over the long term. However, this greater potential for growth carries a greater risk, particularly in the short term.
Additional components of a diversified portfolio
Although these invest in stocks, sector funds, as their name suggests, focus on a particular segment of the economy. They can be valuable tools for investors seeking opportunities in different phases of the economic cycle.
How diversification can help reduce the impact of market volatility
The primary goal of diversification isn't to maximize returns. Its primary goal is to limit the impact of volatility on a portfolio. To better understand this concept, look at the charts below, which depict hypothetical portfolios with different asset allocations.
Factoring time into your diversification strategy
People are accustomed to thinking about their savings in terms of goals: retirement, college, a down payment, or a vacation. But as you build and manage your asset allocation—regardless of which goal you're pursuing—there are 2 important things to consider.
A look at how to build a diversified portfolio
Matthew is a senior energy and materials specialist with The Motley Fool. He graduated from Liberty University with a degree in Biblical Studies and a Masters of Business Administration. You can follow him on Twitter for the latest news and analysis of the energy and materials industries: Follow @matthewdilallo
What is portfolio diversification and why does it matter?
A diversified portfolio is a collection of different investments that combine to reduce an investor's overall risk profile. Diversification includes owning stocks from several different industries, countries, and risk profiles, as well as other investments such as bonds, commodities, and real estate.
What goes into a diversified portfolio?
A diversified portfolio should have a broad mix of investments. For years, many financial advisors recommended building a 60/40 portfolio, allocating 60% of capital to stocks and 40% to fixed-income investments such as bonds. Meanwhile, others have argued for more stock exposure, especially for younger investors.
Three tips for building a diversified portfolio
Building a diversified portfolio can seem like a daunting task since there are so many investment options. Here are three tips to make it easy for beginners to diversify.
Diversification reduces the risk of cracking your nest egg
Diversification is about trade-offs. It reduces an investor's exposure to a single stock, industry, or investment option. While that can potentially cut into an investor's return potential, it also reduces volatility, and, more importantly, the risk of a bad outcome. Investors should take diversification seriously.
Why Do You Need Diversification?
You need diversification to minimize investment risk. If we had perfect knowledge of the future, everyone could simply pick one investment that would perform perfectly for as long as needed.
Diversification Strategy
There are plenty of different diversification strategies to choose from, but their common denominator is buying investments in a range of different asset classes. An asset class is nothing more than a group of investments with similar risk and return characteristics.
Wealthfront
Creating a diversified portfolio with mutual funds is a simple process. Indeed, an investor can create a well diversified portfolio with a single target date retirement fund. One can also create remarkable diversity with just three index funds in what is known as the 3-fund portfolio.
Why diversify?
The goal of diversification is not necessarily to boost performance—it won't ensure gains or guarantee against losses. Diversification does, however, have the potential to improve returns for whatever level of risk you choose to target.
Diversification has proven its long-term value
During the 2008–2009 bear market, many different types of investments lost value at the same time, but diversification still helped contain overall portfolio losses.
Building a diversified portfolio
To start, you need to make sure your asset mix (e.g., stocks, bonds, and short-term investments) is aligned to your investment time frame, financial needs, and comfort with volatility. The sample asset mixes below combine various amounts of stock, bond, and short-term investments to illustrate different levels of risk and return potential.
Diversification is not a one-time task
Once you have a target mix, you need to keep it on track with periodic checkups and rebalancing. If you don't rebalance, a good run in stocks could leave your portfolio with a risk level that is inconsistent with your goal and strategy.
A 3-step approach
Investing is an ongoing process that requires regular attention and adjustment. Here are 3 steps you can take to keep your investments working for you:
The bottom line
Achieving your long-term goals requires balancing risk and reward. Choosing the right mix of investments and then periodically rebalancing and monitoring your choices can make a big difference in your outcome.
What Is Diversification?
- Diversification is a risk managementstrategy that mixes a wide variety of investments within a portfolio. A diversified portfolio contains a mix of distinct asset types and investment vehicles in an attempt at limiting exposure to any single asset or risk. The rationale behind this technique is that a portfolio constructed of different kinds of ass...
The Basics of Diversification
- Studies and mathematical models have shown that maintaining a well-diversified portfolio of 25 to 30 stocks yields the most cost-effective level of risk reduction. The investing in more securities generates further diversification benefits, albeit at a drastically smaller rate. Diversification strives to smooth out unsystematic risk events in a portfolio, so the positive performance of some inve…
Diversification by Asset Class
- Fund managers and investors often diversify their investments across asset classes and determine what percentages of the portfolio to allocate to each. Classes can include: 1. Stocks—shares or equity in a publicly traded company 2. Bonds—government and corporate fixed-income debt instruments 3. Real estate—land, buildings, natural resources, agriculture, livestock…
Foreign Diversification
- Investors can reap further diversification benefits by investing in foreign securities because they tend to be less closely correlated with domestic ones. For example, forces depressing the U.S. economy may not affect Japan's economy in the same way. Therefore, holding Japanese stocks gives an investor a small cushion of protection against losses during an American economic do…
Diversification and The Retail Investor
- Time and budget constraints can make it difficult for noninstitutional investors—i.e., individuals—to create an adequately diversified portfolio. This challenge is a key reason why mutual fundsare so popular with retail investors. Buying shares in a mutual fund offers an inexpensive way to diversify investments. While mutual funds provide diversification across vari…
Disadvantages of Diversification
- Reduced risk, a volatility buffer: The pluses of diversification are many. However, there are drawbacks, too. The more holdings a portfolio has, the more time-consuming it can be to manage—and the more expensive, since buying and selling many different holdings incurs more transaction fees and brokerage commissions. More fundamentally, diversification's spreading-o…
Diversification and Smart Beta
- Smart beta strategiesoffer diversification by tracking underlying indices but do not necessarily weigh stocks according to their market cap. ETF managers further screen equity issues on fundamentals and rebalance portfolios according to objective analysis and not just company size. While smart beta portfolios are unmanaged, the primary goal becomes outperformance of the in…
Real World Example
- Say an aggressive investorwho can assume a higher level of risk, wishes to construct a portfolio composed of Japanese equities, Australian bonds, and cotton futures. He can purchase stakes in the iShares MSCI Japan ETF, the Vanguard Australian Government Bond Index ETF, and the iPath Bloomberg Cotton Subindex Total Return ETN, for example. With this mix of ETF shares, due to t…