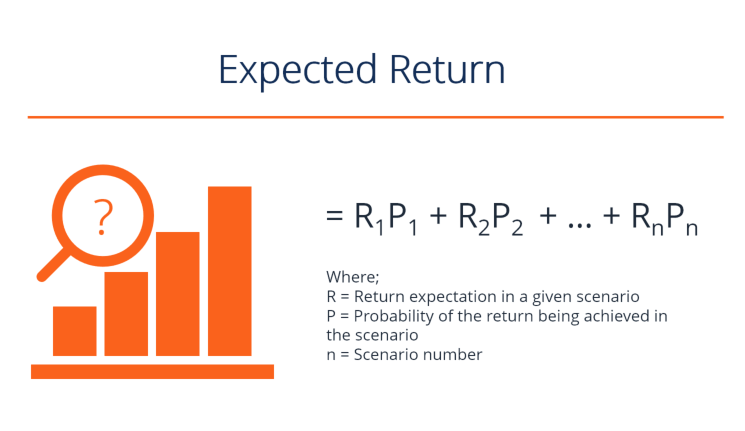
What does Roa stand for?
What Is Return on Assets (ROA)? The term return on assets (ROA) refers to a financial ratio that indicates how profitable a company is in relation to its total assets. Corporate management, analysts, and investors can use ROA to determine how efficiently a company uses its assets to generate a profit.
What does Roa tell you?
The Calculations for ROE, ROA, and ROIC
- Return on Equity (ROE) = Net Income / Average Shareholders’ Equity
- Return on Assets (ROA) = Net Income / Average Assets
- Return on Invested Capital (ROIC) = NOPAT / (Total Debt + Equity + Other Long-Term Funding Sources)
What does a high Roa mean?
Return on assets indicates the amount of money earned per dollar of assets. Therefore, a higher return on assets value indicates that a business is more profitable and efficient. 2. Using ROA to compare performance between companies. It is important to note that return on assets should not be compared across industries.
Is a high Roa good?
Usually, an ROA ratio, or return on assets ratio, is considered “good” if it is above five percent. However, ROA ratios should be looked at historically for the company being evaluated as well as against companies that are similar in business type and product line when doing peer company comparisons.

What is a good ROA for stocks?
5%An ROA of 5% or better is typically considered good, while 20% or better is considered great. In general, the higher the ROA, the more efficient the company is at generating profits. However, any one company's ROA must be considered in the context of its competitors in the same industry and sector.
What does a 5% ROA mean?
A ROA of 5% or lower might be considered low, while a ROA over 20% high. However, it's best to compare the ROAs of similar companies. A ROA for an asset-intensive company might be 2%, but a company with an equivalent net income and fewer assets might have a ROA of 15%.
Is a 10% ROA good?
As mentioned above, higher ROAs are generally better because they show the company is efficiently managing its assets to produce more net profits. In general, an ROA over 5% is considered good.
Do you want high or low ROA?
The higher the ROA number, the better, because the company is able to earn more money with a smaller investment. Put simply, a higher ROA means more asset efficiency.
Can ROA be too high?
With a lot of measures of profitability ratios, like gross margin and net margin, it's hard for them to be too high. “You generally want them as high as possible” says Knight. ROA, on the other hand, can be too high.
Is a high ROE good?
The higher a company's ROE percentage, the better. A higher percentage indicates a company is more effective at generating profit from its existing assets. Likewise, a company that sees increases in its ROE over time is likely getting more efficient.
What if ROA is low?
A low ROA indicates that the company is not able to make maximum use of its assets for getting more profits. If you want to increase the ROA then you must try to increase the profit margin or you must try to make maximum use of the company assets to increase sales. A higher ratio is always better.
What is ROA example?
Return on assets is represented as a percentage. For example, if a company's ROA is 7.5%, this means the company earns seven and a half cents per dollar in assets.
What if ROA is decreasing?
An ROA that rises over time indicates the company is doing a good job of increasing its profits with each investment dollar it spends. A falling ROA indicates the company might have over-invested in assets that have failed to produce revenue growth, a sign the company may be trouble.
What is a good return on equity ratio?
15-20%Return on equity interpretation In most cases, the higher your return on equity, the better. Investors want to see a high ROE because it indicates that the business is using funds effectively. Generally, a return on equity of 15-20% is considered good.
What does a return on assets of 12.5% represent?
What does a return on assets of 12.5% represent? The company generates a profit of $12.5 for every $1 in sales. The company generates $1 in profit for every $12.5 in total assets.
Why is ROA important?
What is the importance of ROA? ROA is a very important indicator for a corporation, as it shows investors how the company is actually behaving in terms of converting assets into net capital. As a result, it can be inferred that the higher the metric (given in percentage), the better it is for the business's management.
What is ROA in finance?
Return on assets (ROA) is a measure of how efficiently a company uses the assets it owns to generate profits. Managers, analysts and investors use ROA to evaluate a company’s financial health.
Why use ROA?
For these reasons, it’s best to use ROA as a way to analyze a single business over time. Plotting out the ROA of a company quarter over quarter or year over year can help you understand how well it’s performing. Rising or falling ROA can help you understand longer-term changes in the business.
How is ROE calculated?
ROE is calculated by dividing a company’s net profits over a given period by shareholders’ equity— it measures how effectively the company is leveraging the capital it has generated by selling shares of stock. If ROA examines how well a company is managing the assets it owns to generate profits, ROE examines how well the company is managing the money invested by its shareholders to generate profits.
How to find percentage of assets?
Once you’ve determined the average value of a company’s assets, divide net profit by average assets and multiply it by 100 to get the percentage.
Why is return on assets important?
Return on assets is important to keep in mind because it’s how a company’s managers and outside analysts determine how effectively a company is using its financial resources. ROA is closely related to other measures used to gauge company success, like return on investment (ROI) and return on equity (ROE).
Why do investors use ROE?
Investors use ROE to understand the efficiency of their investments in a public company. ROA’s measure of a company’s efficiency in terms of assets complements the conclusions you can draw from ROE.
What is return on assets?
Return on assets is a tool used by managers and financial analysts to determine how effectively a company is using its resources to make a profit.
What does ROA mean in business?
It is a measure of a company’s profitability and efficiency – the higher the ROA, the more profitable and efficient a company is with their capital assets.
Why is ROA important?
The ROA ratio is important for several reasons: 1 It is a measure of a company’s profitability and efficiency – the higher the ROA, the more profitable and efficient a company is with their capital assets. 2 It allows investors to compare the performance of companies across industries. 3 It can show investors if a company is asset-intensive or asset-light
What is the difference between asset turnover and return on assets?
On a balance sheet, total assets are balanced by liabilities and shareholders’ equity. This means that by understanding total assets, investors can understand how those assets relate to a company’s debt and equity structure. With that in mind, ROA is about calculating how the return in profit for each dollar invested in assets. The asset turnover ratio, on the other hand, measures the amount of sales that are generated from every dollar invested in total assets.
Why should ROA be compared to other competitors?
This is because different industries use assets differently. Banks, for example, will have far fewer capital intensive assets as opposed to a construction company.
How to calculate return on assets?
First, they need a company’s net income (also called “net profit after taxes”) over a period of time, which is typically 12 months or a fiscal year. This can be found on the bottom line of their income statement.
Why do analysts use average assets instead of period assets?
Analysts frequently choose to use average assets instead of the end of period assets because a company’s assets may fluctuate over time for many reasons such as purchases or sales of equipment, seasonal sales, or changes in inventory . Using the average is an attempt to smooth out these fluctuations to get a more accurate picture of a company’s total asset base.
Do investors get value from ROA?
However, as with other ratios, investors will only get value out of the ROA ratio if they use it to compare a single company’s performance over several periods of time, and if they’re comparing one company to another it’s critical that those companies be in the same industry.
How to calculate ROA?
Calculating ROA using net income and total assets 1 Find Johnson & Johnson's 2020 net income on its income statement. The income statement for 2020 is found in the company's latest 10K (annual) filing with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). The Johnson & Johnson 10K report for 2020 indicates that the company generated net income of $14.7 billion. 2 Find the company's total assets on its balance sheet, which is also contained in the 10K filing. J&J's total assets at the end of 2020 were valued at $174.9 billion. 3 Divide Johnson & Johnson's net income by its total assets and then multiply that amount by 100. Net income of $14.7 billion divided by total assets of $174.9 billion gives a result of 0.084, which is multiplied by 100 to produce the ROA result of 8.4% for Johnson & Johnson in 2020.
Which method of ROA calculation is simpler?
The ROA calculation method that uses only net income and total assets is simpler than the method that uses net profit margin and asset turnover. However, the latter method more accurately conveys a company's ROA throughout the reporting period, while the simpler method expresses a company's ROA only at the close of the period. Using the more complex method also enables you to learn more about the company by additionally determining its net profit margin and asset turnover rate along the way.
How to calculate return on assets?
There are two ways to calculate return on assets -- by using net income and total assets and by using net profit margin and asset turnover. We'll use healthcare giant Johnson & Johnson ( NYSE:JNJ), and specifically its results from 2020, as an example to illustrate both methods.
Why is return on assets important?
The significance of return on assets. Return on assets is a useful metric because it provides insight on how effectively a company generates profits from its assets. Companies with high ROAs derive more profits from the same amount of assets than companies with low ROAs.
What is return on assets?
Return on assets is a financial metric that tells you how much profit a company generates relative to the value of its assets. A company's assets encompass all of the resources that it owns or controls that produce business value.
How to calculate asset turnover rate?
Calculate asset turnover rate by dividing the company's total revenue into the average asset value and multiplying that amount by 100. Dividing the total revenue of $82.6 billion by the average asset value of $166.3 billion and converting that value into a percentage yields an asset turnover rate of 50%.
Which countries have significant equity return anomalies?
A pre-specified set of nine prominent U.S. equity return anomalies produce significant alphas in Canada, France, Germany, Japan, and the U.K. All of the anomalies are consistently significant across these five countries, whose developed stock markets afford the most extensive data. The anomalies remain significant even in a test that assumes their true alphas equal zero in the U.S. Consistent with the view that anomalies reflect mispricing, idiosyncratic volatility exhibits a strong negative relation to return among stocks that the anomalies collectively identify as overpriced, similar to results in the U.S.
What is market factor?
The market factor, an investment factor, and a return-on-assets factor summarize the cross-sectional variation of expected stock returns. The new three-factor model substantially outperforms traditional asset pricing models in explaining anomalies associated with short-term prior returns, financial distress, net stock issues, asset growth, earnings suprises, and valuation ratios. The model’s performance, cobined with its economic intuition based on q-theory, suggests that it can be used to obtain expected return estimation in practice.
Is the long leg of the strategy strongly correlated to the equity market?
Not known - Source and related research papers don’t offer insight into correlation structure of proposed trading strategy to equity market risk; therefore, we do not know if this strategy can be used as a hedge/diversification during the time of market crisis. The strategy is built as a long-short, but it can be split into two parts. The long leg of the strategy is surely strongly correlated to the equity market; however, the short-only leg might be used as a hedge during bad times. Rigorous backtest is, however, needed to determine return/risk characteristics and correlation.
Is ROA good for short or long stocks?
However, recent academic studies confirm what every Wall-Streeter (and also Main-Streeter) already knew. They show there is a robust and strong return premium in holding profitable stocks and so it makes sense to go long firms with strong ROA (Return on Assets) and short firms with weak ROA. Source paper for this effect also shows that the ROA effect could explain a lot of other anomalies (mainly earnings and profitability related – like popular price-to-earnings ratio, etc.). The strategy is built as a long-short portfolio and for example, is using thousands of stocks in an investment portfolio. Still, it is indeed possible to exploit this effect also in a smaller portfolio.
What is ROE N?
ROE#N#"The amount of net income returned as a percentage of shareholders equity. Return on equity measures a corporation's profitability by revealing how much profit a company generates with the money shareholders have invested."
Why is the stock market called the share market?
The stock market is also called the share market. That is because you share the company's stock (assets) as well as liabilities with all the other shareholders.
How many stocks did Till.Tgat move to?
When I completed my research till.tgat stock moved from 22 to 30.
Should I buy a stock before doing research?
Never buy a stock before completing your research. When I came to know about Company that time it is trading at 20 but I have taken 30–40 days to complete research and in between stock moved by 10 rupees. But I still bought at 30 also because of conviction. Let's say if you bought before doing research and then you found that Company is worthless in between your stock gone down that time you have to face problem better to keep safe yourself do research and then buy.
What Is Return on Assets (ROA)?
Example of How to Calculate Return on Assets
- There are two ways to calculate return on assets -- by using net income and total assets and by using net profit margin and asset turnover. All the numbers needed in these calculations can be obtained from a company's financial statements. We'll use 2020 results from healthcare giant Johnson & Johnson (NYSE:JNJ)as an example to illustrate both methods.
Return on Assets vs. Return on Equity
- Return on assets is similar to another financial metric -- return on equity (ROE). Both ROA and ROE measure how well a business is performing. The key difference between the two is that ROE divides net income by shareholder's equity instead of by total assets as ROA does.
The Significance of Return on Assets
- Return on assets is a useful metric because it provides insight on how effectively a company generates profits from its assets. Companies with high ROAs derive more profits from the same amount of assets than companies with low ROAs. The stocksof companies with high ROAs are more likely to perform well over the long term.