
- A restricted stock unit (RSU) is stock-based compensation issued by an employer.
- A vesting period exists before the RSU converts to actual common stock. Until then, it has no monetary worth.
- Once the RSU converts to stock, the stockholder may pay taxes on its value.
- RSUs are better than stock options. ...
Full Answer
What is restricted stock and how is it taxed?
Apr 04, 2021 · Restricted stock refers to unregistered shares of ownership in a corporation that are issued to corporate affiliates, such as executives and directors. Restricted stock is non-transferable and must...
What are the tax implications of restricted stock?
Dec 28, 2021 · Restricted stock is a type of equity compensation plan offered by employers in which employees are granted stock but only gain full ownership after specific requirements are met, such as a vesting schedule or achieving performance metrics. There are two types of restricted stock: restricted stock units (RSUs) and restricted stock awards (RSAs).
How to sell restricted stock?
What is Restricted Stock? summary Awarded to you by your company, restricted stock is a share of ownership in your company, subject to limitations. The limitation, or restriction, applies to the length of time before you fully own the stock and have the right to sell or transfer it. This length of time is known as the vesting period.
What should I do with my restricted stock units?
Dec 28, 2021 · Restricted stock (not to be confused with a restricted stock unit, or RSU) is typically awarded to company directors and executives who then own the stock at the end of the vesting period. Also called letter stock or Section 1244 stock, a restricted stock award comes with strings attached. For example, it cannot be transferred and it may be forfeited if the …
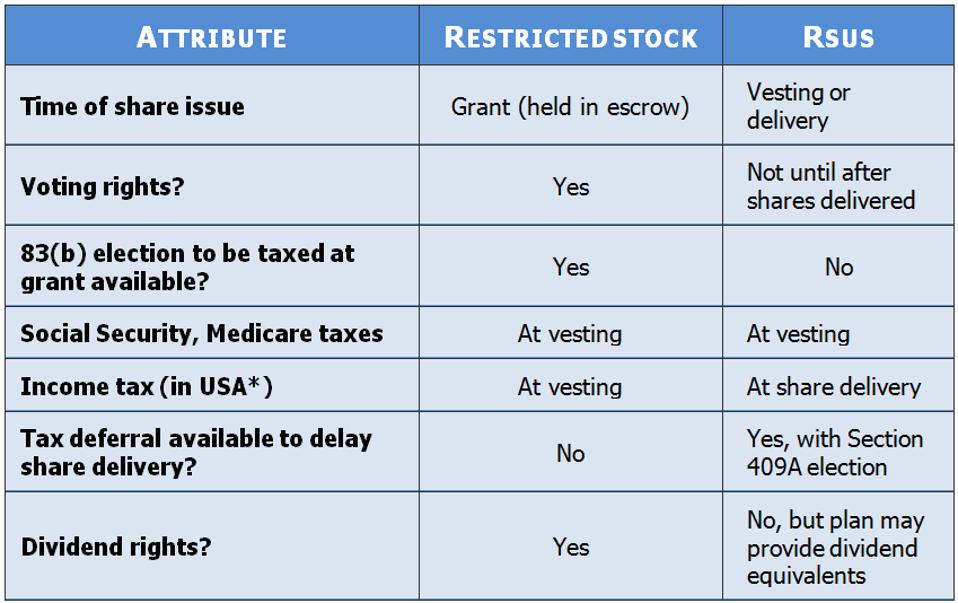
What does it mean when a stock is restricted?
What Is Restricted Stock? Restricted stock refers to unregistered shares of ownership in a corporation that are issued to corporate affiliates, such as executives and directors. Restricted stock is non-transferable and must be traded in compliance with special Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) regulations.
How do restricted stocks work?
Restricted stock units are a way an employer can grant company shares to employees. The grant is "restricted" because it is subject to a vesting schedule, which can be based on length of employment or on performance goals, and because it is governed by other limits on transfers or sales that your company can impose.
Why do companies give restricted stock?
RSUs provide an incentive for employees to stay with a company for the long term and help it perform well so that their shares increase in value.
Can I sell my restricted stock?
When they are vested, these restricted stocks are presented with a fair market value. Additionally, it is termed as income; thus, a part of it is reserved for paying taxes on income. The remainder of the RSUs is with the employee, and he can sell them when he wants.Jul 29, 2021
How do I cash out RSU?
An RSU is like a cash bonus that you use right away to buy company stock. It has the same tax treatment as a cash bonus....How do RSUs work?# of Restricted Stock Units (RSUs) that Vest100 shares# of RSU shares sold for taxes (22% x 100 shares)22 shares6 more rows•Jul 25, 2021
Can a company take back restricted stock?
Once you have shares in an RSU that vest (becomes yours), the company can no longer take them back, and you must pay ordinary income taxes on the fair market value of the shares at the time they vest. This is the case even if you do not sell the shares of the stock that you now own.
Should I choose stock options or RSUs?
Stock options are only valuable if the market value of the stock is higher than the grant price at some point in the vesting period. Otherwise, you're paying more for the shares than you could in theory sell them for. RSUs, meanwhile, are pure gain, as you don't have to pay for them.Oct 22, 2021
What is the difference between ESOP and RSU?
ESOPs are paid with only through stocks, whereas RSUs may be paid for by stocks or cash. Under ESOPs, the employee may suffer losses if the market price at the time of vesting is less than exercise price.Aug 26, 2020
Why are RSU taxed so high?
Restricted stock units are equivalent to owning a share in your company's stock. When you receive RSUs as part of your compensation, they are taxed as ordinary income. Think of it like a cash bonus that your company immediately invests into company stock and gives you the stock instead.Feb 26, 2021
How long can you hold RSU?
Traditionally RSUs, like most equity compensation, have a 4 year vesting period. Certain high-value employees could receive a refresh, a promotion, or retention incentives. However, these additional grants of RSUs are not guaranteed.Jun 17, 2020
Do you get RSU every year?
Like stock options, RSUs usually vest over several years. It's common to receive 1/4 of the RSUs you were granted after your first year of employment, and every month after that, receive another 1/36 of the remaining grant. When doing your taxes, the value of the shares at the date of vest is taxed as ordinary income.Aug 5, 2021
Does 1 RSU equal 1 stock?
Each RSU will correspond to a certain number and value of employer stock. For example, suppose your RSU agreement states that one RSU corresponds to one share of company stock, which currently trades for $20 per share. If you're offered 100 RSUs, then your units are worth 100 shares of stock with a value of $2,000.Jan 4, 2022
Restricted Stock Explained
Cameron Williams has nearly a decade of experience working in the financial industry. A former investment advisor, Cameron now writes about investing, banking, insurance, and general personal finance. He studied economics at Utah State University and holds FINRA securities licenses including Series 6, Series 63, and Series 65.
Definition and Examples of Restricted Stock
Restricted stock, also referred to as restricted stock units (RSUs), is a type of equity compensation through which a company pays its employees in shares of stock. The stock is “restricted” because it is often accompanied by a vesting schedule before the employee has full ownership of the stock.
How Restricted Stock Works
Restricted stock plans give employees of a company a personal interest in how well the company does. The vesting schedule of restricted stock units is usually dependent on length of employment or based on performance goals being met. Once you are fully vested, you have voting rights and possibly dividend payments with the shares you are granted.
Types of Restricted Stock
There are two types of restricted stock. They are restricted stock units (RSUs) and restricted stock awards (RSAs). Both are stock compensation plans given to company employees that have certain restrictions to be met before the stock can be delivered to the employee.
Restricted Stock vs. Stock Options
Restricted stock and stock options are some of the more popular equity compensation plans offered by employers. What’s the difference between the two?
What It Means for Individual Investors
How a company compensates its employees is a vital piece of information that can be an indicator of future company success. Restricted stock can be an excellent way for companies to include their employees in the overall ownership of the company and its performance.
What Is a Restricted Stock Unit (RSU)?
The term restricted stock unit (RSU) refers to a form of compensation issued by an employer to an employee in the form of company shares.
Understanding Restricted Stock Units (RSUs)
Restricted stock gained popularity as a form of employee compensation as a better alternative to stock options after accounting scandals in the mid-2000s involving companies like Enron and WorldCom came to light.
Special Considerations
RSUs are treated differently than other forms of stock options when it comes to how they are taxed. Unlike these other plans, the entire value of an employee's vested stock is counted as ordinary income in the same year of vesting.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Restricted Stock Units (RSUs)
RSUs provide an incentive for employees to stay with a company for the long term and help it perform well so that their shares increase in value.
Examples of Restricted Stock Units (RSUs)
Suppose Madeline receives a job offer. Because the company thinks Madeline's skill set is valuable and hopes she remains a long-term employee, it offers her 1,000 RSUs in addition to a salary and other benefits.
How Do Restricted Stock Units Work?
Restricted stock units are a type of compensation in which a company gradually transfers shares to an employee. Depending on the performance of the company, restricted stock units can fluctuate in value. From a company’s perspective, restricted stock units can help employee retention by incentivizing employees to stay with the company long-term.
What Is the Difference Between Restricted Stock Units and Stock Options?
Stock options provide employees with the right but not the obligation to acquire shares at a specified price, which is typically higher than the market price prevalent at the time the options are given. This typically means that the employee benefits only if the company’s share price rises within a specified period of time.

What Is A Restricted Stock Unit (Rsu)?
Understanding Restricted Stock Units
- Restricted stock gained popularity as a form of employee compensation as a better alternative to stock options after accounting scandals in the mid-2000s involving companies like Enron and WorldCom came to light. At the end of 2004, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) issued a statement requiring companies to book an accounting expense for stock options issue…
Special Considerations
- RSUs are treated differently than other forms of stock options when it comes to how they are taxed. Unlike these other plans, the entire value of an employee's vested stock is counted as ordinary income in the same year of vesting.3 In order to declare the amount, an employee must subtract the original purchase of the stock or its exercise price from the FMV on the date it beco…
Advantages and Disadvantages of RSUs
- Advantages
RSUs provide an incentive for employees to stay with a company for the long term and help it perform well so that their shares increase in value. If an employee decides to hold their shares until they receive the full vested allocation and the company's stock rises, the employee receive… - Disadvantages
RSUs don't provide dividends because actual shares aren't allocated.6 But an employer may pay dividend equivalents that can be moved into an escrow account to help offset withholding taxes, or be reinvested through the purchase of additional shares. The taxation of restricted stocks is g…
Examples of RSUs
- Suppose Madeline receives a job offer. Because the company thinks Madeline's skill set is valuable and hopes she remains a long-term employee, it offers her 1,000 RSUs in addition to a salary and other benefits. The company's stock is worth $10 per share, making the RSUs potentially worth an additional $10,000. To give Madeline an incentive to stay with the …