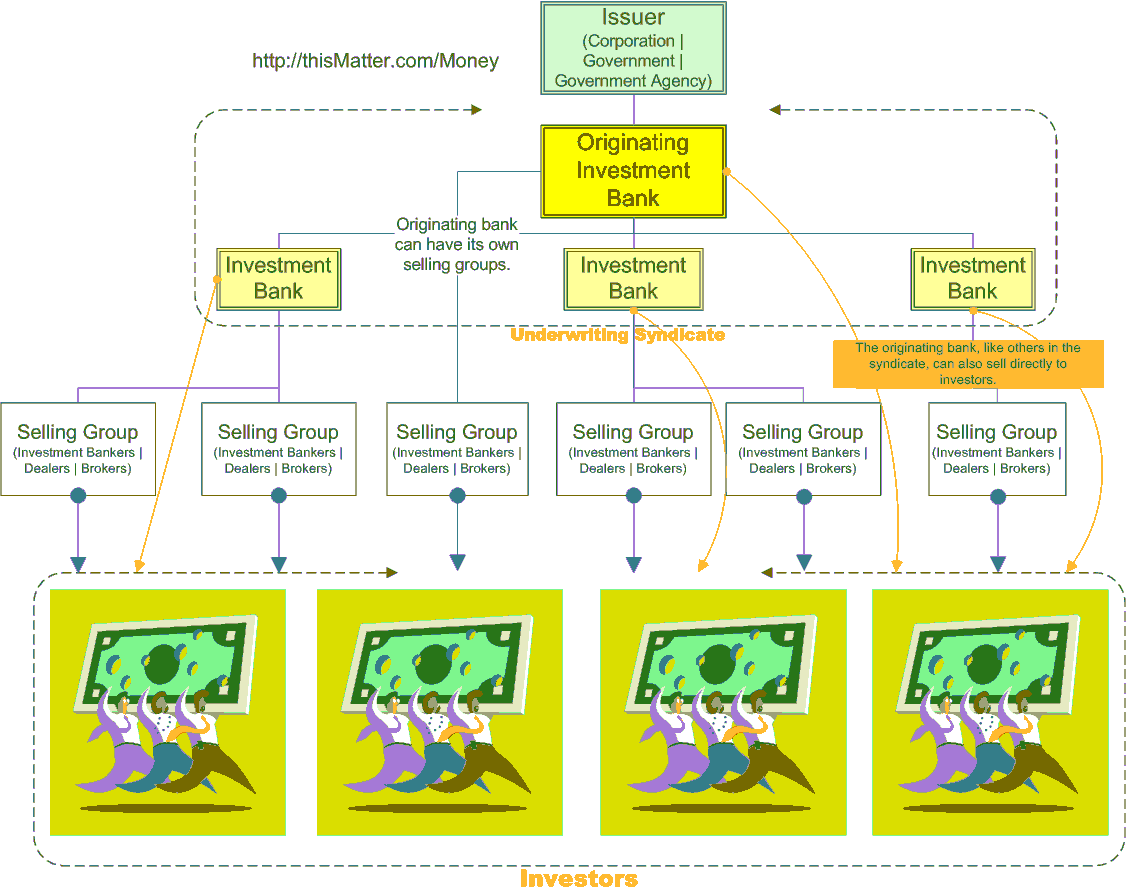
What happens when there is a public offering of Common Stock? A public offering is the sale of equity shares or other financial instruments such as bonds to the public in order to raise capital. The capital raised may be intended to cover operational shortfalls, fund business expansion, or make strategic investments.
What is the importance of offering shares to the public?
Apr 21, 2020 · Offerings. Common stocks are ordinary shares that companies issue as an alternative to selling debt or issuing a different class of shares known as preferred stock. The first time that a company issues common stock into the public markets, it does so via an initial public offering. Click to see full answer. Thereof, is a stock offering good or bad?
Should public companies offer shares to the public?
Nov 19, 2003 · Common stock is a security that represents ownership in a corporation. In a liquidation, common stockholders receive whatever assets remain after creditors, bondholders, and preferred stockholders...
What is the current price of common stock?
What does closing of common stockpublic offering means?

What does a public offering do to stock price?
When a public company increases the number of shares issued, or shares outstanding, through a secondary offering, it generally has a negative effect on a stock's price and original investors' sentiment.
Is a public offering of common stock good?
Issuing common stock helps a corporation raise money. That capital can be used in a number of ways to help the business grow, such as to acquire another company, pay debts or to simply have access to more cash for general corporate reasons.
What does offering of common stock mean?
Common Stock Offering means the sale and issuance for cash by the Corporation to persons other than the Corporation or any of its subsidiaries after the Original Issue Date of shares of Common Stock (other than any such sales and issuances made pursuant to agreements or arrangements entered into, or pursuant to ...
What are public stock offerings?
A public offering is a sale or equity shares or debt securities by an organization to the public in order to raise funds for the company.
Why do stocks drop after public offering?
The money raised by a public offering is not earnings. Dilution occurs when new shares are offered to the public, because earnings must be divvied up among a larger number of shares. Dilution therefore lowers a stock's EPS ratio and reduces each share's intrinsic value.Jan 28, 2019
What happens when a company does a public offering?
Generally, the securities are to be listed on a stock exchange. In most jurisdictions, a public offering requires the issuing company to publish a prospectus detailing the terms and rights attached to the offered security, as well as information on the company itself and its finances.
What happens when a company issues common stock?
Reduces Debt: When a company issues common stock, they ask people to buy a part of the company. Owning stocks of the company implies that the investor owns a particular share of the company. This does not need to be repaid by the company itself, and therefore there is no interest expense attached to it.
Why do companies issue common stock?
Companies issue shares to raise money from investors who tend to invest their money. This money is then used by companies for the development and growth of their businesses.
What happens when common stock is issued?
In issuing its common stock, a company is effectively selling a piece of itself. The stock purchasers give up cash and in exchange receive a small ownership stake in the business. The holders of common stock's ownership position is known as equity.Feb 14, 2022
How do you get the public offering of common stock?
To purchase IPO shares, you must open an account with TD Ameritrade, then complete a personal and financial profile, and read and agree to the rules and regulations affecting new issue investing. Each account being registered must have a value of at least $250,000, or have completed 30 trades in the last 3 months.
How does an IPO raise money?
Through an initial public offering (IPO), a company raises capital by issuing shares of stock, or equity, in a public market. Generally, an IPO is a company's first issue of stock. But there are ways a company can go public more than once. The IPO process is the locomotive of capitalism.
What is common stock?
Common stock is a security that represents ownership in a corporation. In a liquidation, common stockholders receive whatever assets remain after creditors, bondholders, and preferred stockholders are paid. There are different varieties of stocks traded in the market. For example, value stocks are stocks that are lower in price in relation ...
What is an IPO?
An IPO is a great way for a company, seeking additional capital, to expand. To begin the IPO process, a company must work with an underwriting investment banking firm, which helps determine both the type and pricing of the stock.
Why are stocks important?
They bear a greater amount of risk when compared to CDs, preferred stock, and bonds. However, with the greater risk comes the greater potential for reward. Over the long term, stocks tend to outperform other investments but are more exposed to volatility over the short term.
Who is James Chen?
James Chen, CMT, is the former director of investing and trading content at Investopedia. He is an expert trader, investment adviser, and global market strategist. Gordon Scott has been an active investor and technical analyst of securities, futures, forex, and penny stocks for 20+ years.
What is the largest stock exchange in the world?
NYSE had a market capitalization of $28.5 trillion in June 2018, making it the biggest stock exchange in the world by market cap. There are also several international exchanges for foreign stocks, such as the London Stock Exchange and the Tokyo Stock Exchange.
What is the difference between growth and value stocks?
There are also several types of stocks. Growth stocks are companies that tend to increase in value due to growing earnings. Value stocks are companies lower in price in relation to their fundamentals. Value stocks offer a dividend, unlike growth stocks.
Is common stock riskier than debt?
This makes common stock riskier than debt or preferred shares. The upside to common shares is they usually outperform bonds and preferred shares in the long run. Many companies issue all three types of securities. For example, Wells Fargo & Company has several bonds available on the secondary market.
What is public offering?
A public offering is a corporation’s sale of stock shares to the public. The effect of a public offering on a stock price depends on whether the additional shares are newly created or are existing, privately owned shares held by company insiders. Newly created shares typically hurt stock prices, but it’s not always a sure thing.
Why are secondary offerings non-dilutive?
Some secondary offerings are non-dilutive because they don’t involve the creation of new shares. Frequently, when a company offers public shares for the first time (an initial public offering, or IPO), corporate insiders such as founders, directors and venture capitalists are barred from participating. Instead, they must wait a certain amount of ...
Why does dilution occur?
Dilution occurs when new shares are offered to the public, because earnings must be divvied up among a larger number of shares. Dilution therefore lowers a stock’s EPS ratio and reduces each share’s intrinsic value.

What Is A Public Offering?
Public Offering Explained
- Generally, any sale of securities to more than 35 people is deemed to be a public offering, and thus requires the filing of registration statements with the appropriate regulatory authorities. The issuing company and the investment bankers handling the transaction predetermine an offering pricethat the issue will be sold at. The term public offering is equally applicable to a company's i…
Initial Public Offerings and Secondary Offerings
- An initial public offering (IPO) is the first time a private company issues corporate stock to the public. Younger companies seeking capital to expand often issue IPOs, along with large, established privately owned companies looking to become publicly traded as part of a liquidity event. In an IPO, a very specific set of events occurs, which the selected IPO underwriters facilita…
Understanding Dilutive Offerings
- Stock shares represent a partial ownership of the company. The more shares you hold, the bigger the slice of the company you own. As an owner, you are entitled to vote at corporate meetings and to participate in the growth of the company through dividends and higher share prices. One measure of share value is earnings per share (EPS), which is the ...
Dilutive Offering Example
- Suppose a company had previously issued 1 million shares and earned a profit of $50M this year. The EPS is therefore $50M/1M, or $50. The price per share happens to be $180 before a new offering, at which time the company issues 100,000 new shares, creating a an EPS of $45.45 ($50M/1.1M). The price/earnings ratio before the sale is $180/$50, or 3.6. To maintain the same …
Exploring Non-Dilutive Offerings
- Some secondary offerings are non-dilutive because they don’t involve the creation of new shares. Frequently, when a company offers public shares for the first time (an initial public offering, or IPO), corporate insiders such as founders, directors and venture capitalists are barred from participating. Instead, they must wait a certain amount of time, called a lockup period, before the…
A Word of Caution
- A dilutive stock offering should lower prices, assuming the demand remains unchanged. However, that isn’t always a safe assumption. For example, a company known as CRISPR Therapeutics A.G. saw stock prices rise 17 percent on the day it announced a dilutive secondary offering in January 2018. This can only be due to an increase in demand. While the reasons aren't always be certain…