Inverted Market
- Understanding Inverted Markets. An inverted market may arise for multiple reasons, including a short-term supply decrease, which causes prices to be higher in the short term.
- Causes for Inverted Markets. ...
- Contango and Backwardation. ...
- Inverted Market Examples. ...
What does yield curve inversion mean for investors?
A yield curve inversion has the greatest impact on fixed-income investors. In normal circumstances, long-term investments have higher yields; because investors are risking their money for longer periods of time, they are rewarded with higher payouts.
What happens to stocks after a market inversion?
In the year immediately following an inversion, stocks showed a very robust average return of 8.8%, and in the next year after that, they returned an even better 9.6%.
What is the difference between inversion and backwardation?
Inversion and backwardation are more commonly seen together, which is why sometimes, erroneously, the two terms are used interchangeably. An inverted market can occur in either a backwardation or contango market. Inverted markets aren't "normal," although they are rather common.
What are bond inversions and why do they matter?
One reason inversions happen is because investors are selling stocks and shifting their money to bonds. They’ve lost confidence in the economy and believe the meager returns that bonds promise might be better than potential losses they could incur by holding stocks into a recession.
What does an inverted yield curve mean for stocks?
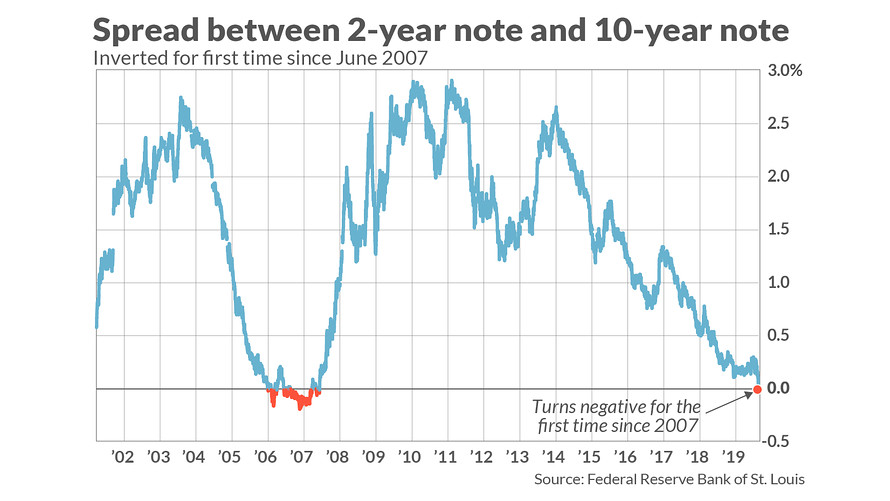
Many economists say an inverted yield curve signals an economic downturn is coming. So what is it? An inverted yield curve occurs when short-term Treasury yields exceed long-term yields. In recent days two-year yields have often topped 10-year yields.
What happens when yield curve inverts?
Yield curve inversion takes place when the longer term yields falls much faster than short term yields. This happens when there is a surge in demand for long term Government bonds (e.g. 10 year US Treasury bond) compared to short term bonds.
Why does an inverted yield curve indicate recession?
The yield curve does not cause recessions, even though it often predicts recessions. The usual mechanism for inversion is that the Federal Reserve tightens, meaning they push up short-term interest rates. Long-term interest rates are less sensitive to Fed actions and thus rise less than short-term rates.
When was the last time the yield curve inverted?
And when inflation expectations are stripped out, the yield curve hasn't inverted, and has kept its upward slope. A quick comparison to the past three inversions—which were all followed by recessions—shows that the “real yield” curve was fully inverted in 2019 and 2006, and almost perfectly flat in 2000.
What is the most likely explanation for an inverted yield curve?
An inverted yield curve occurs when short-term debt instruments have higher yields than long-term instruments of the same credit risk profile. An inverted yield curve is unusual; it reflects bond investors' expectations for a decline in longer-term interest rates, typically associated with recessions.
How long do recessions last?
11 monthsOn average, recessions last 11 months, according to Lindsey Bell, chief markets and money strategist for Ally. The shortest recession on record is the 2020 pandemic-induced recession, which lasted just three months.
How long after inverted yield curve does recession happen?
You Can't Exactly Set Your Watch by Inversions Going back to 1900, the lag between a yield curve inversion and the start of a recession has averaged about 22 months, Gaggar says. Over the past six recessions, however, that lag has ranged from as little as six months to as long as three years.
What yield curve tells us?
A yield curve is a line that plots yields (interest rates) of bonds having equal credit quality but differing maturity dates. The slope of the yield curve gives an idea of future interest rate changes and economic activity.
Do interest rates go up during recession?
While interest rates usually fall early in a recession, credit requirements are often strict, making it challenging for some borrowers to qualify for the best interest rates and loans. Consider the worst-case scenario: You lose your job and interest rates rise as the recession starts to abate.
How accurate is yield curve inversion?
An inverted yield curve in U.S. Treasuries has predicted every recession since 1955, with only one false signal during that time. 12 It even "predicted" the economic downturn that followed the COVID-19 pandemic (although most economists attribute this to luck, and not the fact that it can predict natural disasters).
Which fund has higher interest rate risk?
Interest rate risk is present in all debt funds but the degree could vary. Gilt funds with longer maturity, carry higher interest rate while it is negligible or very low in liquid funds, which invest in securities of up to 91 days maturity.
How many times have we had an inverted yield curve?
The U.S. curve has inverted before each recession since 1955, with a recession following between six and 24 months, according to a 2018 report by researchers at the Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco. It offered a false signal just once in that time.
How the Yield Curve Works
Below is a chart of the yield curve. I used the 10-year minus the 2-year interest rate, which looks at the difference between the 10-year interest rate minus the 2-year rate.
What Does the Inverted Yield Curve Mean for the Economy?
Imagine if you could borrow for ten years at 2%, but if you wanted to borrow for two years it would cost 3%. This would lock in a loss of 1% for any business that borrows long and lends short, i.e., banks.
The Yield Curve in 2022 – Outside the Normal Pattern
Here’s a picture of the yield curve again. The data goes back to 1989 and all the way up to the beginning of 2022.
What Should Traders Do?
The yield curve doesn’t lie. But when we see a pattern in the yield curve that is unprecedented, we’ll need to be prepared to react differently than we have in the past. Here are some actions traders can take.
How long will the inverted yield curve last in 2021?
A Credit Suisse analysis shows recessions follow inverted yield curves by an average of about 22 months — that would bring us to June 2021 — and that stocks continue to do well for 18 months — through February 2021. An inverted yield curve, like most other indicators, is not perfect and doesn’t mean a recession is imminent.
Why is the Squawk Box inverted?
A brief inversion could be just an anomaly. In fact, some inversions have not preceded recessions. The curve may also have inverted because of the Federal Reserve.
Why is yield curve inversion important?
In normal circumstances, long-term investments have higher yields; because investors are risking their money for longer periods of time, they are rewarded with higher payouts. An inverted curve eliminates the risk premium for long-term investments, allowing investors to get better returns with short-term investments .
What happens when the yield curve is inverted?
When the yield curve becomes inverted, profit margins fall for companies that borrow cash at short-term rates and lend at long-term rates , such as community banks. Likewise, hedge funds are often forced to take on increased risk in order to achieve their desired level of returns.
What happens to the yield curve when the spread between short term and long term interest rates narrows?
This is referred to as a normal yield curve. When the spread between short-term and long-term interest rates narrows, the yield curve begins to flatten.
Why do investors demand higher yields at the long end of the curve?
In a growing economy, investors also demand higher yields at the long end of the curve to compensate for the opportunity cost of investing in bonds versus other asset classes, and to maintain an acceptable spread over inflation rates.
When will inverted yield curves form again?
Considering the consistency of this pattern, an inverted yield will likely form again if the current expansion fades to recession.
Do inversions last forever?
For your short-term income needs, do the obvious: choose the investment with the highest yield, but keep in mind that inversions are an anomaly and they don't last forever. When the inversion ends, adjust your portfolio accordingly. Take the Next Step to Invest. Advertiser Disclosure.
Does an inverted yield curve precede a recession?
Despite their consequences for some parties, yield-curve inversions tend to have less impact on consumer staples and healthcare companies, which are not interest-rate dependent. This relationship becomes clear when an inverted yield curve precedes a recession.
Research On Yield Curve Inversion
The ability of the U.S. yield curve to predict recessions is reasonably well studied by academics. This paper find that the term spread, or the difference between 3-month and 10-year U.S. Treasury yields has historically been predictive of future U.S. economic growth.
A Recession Predictor
Perhaps even more powerfully, this paper shows that the U.S. yield curve inverting has predicted all but one of recent U.S. recessions since the 1970s, and without any obvious false positives. The exception was the recession of 1990, though the yield curve was still relatively flat before the recession.
Important Caveats
There are however, some important caveats. The first is perhaps that the slope of the yield curve is now a very well-monitored indicator. That may reduce its forecasting power.
How The Yield Curve Works
What Does The Inverted Yield Curve Mean For The Economy?
- Imagine if you could borrow for ten years at 2%, but if you wanted to borrow for two years it would cost 3%. This would lock in a loss of 1% for any business that borrows long and lends short, i.e., banks. When the yield curve is inverted, it is almost impossible for banks to make money. It’s no different than buying hot dogs for $2 and selling the...
The Yield Curve in 2022 – Outside The Normal Pattern
- Here’s a picture of the yield curve again. The data goes back to 1989 and all the way up to the beginning of 2022. The pattern is cyclical. Every test of the lower yellow band results in a snapback test of the upper yellow band. This has happened 3 times in the past 30 years. Each time the drop into the lower yellow band resulted in a market crash and a recession. Every time t…
What Should Traders do?
- The yield curve doesn’t lie. But when we see a pattern in the yield curve that is unprecedented, we’ll need to be prepared to react differently than we have in the past. Here are some actions traders can take. 1. Be prepared to day trade more often due to higher volatility 2. Accept that the easy uptrend is over for now 3. Trade both sides of the market long and short And most importa…