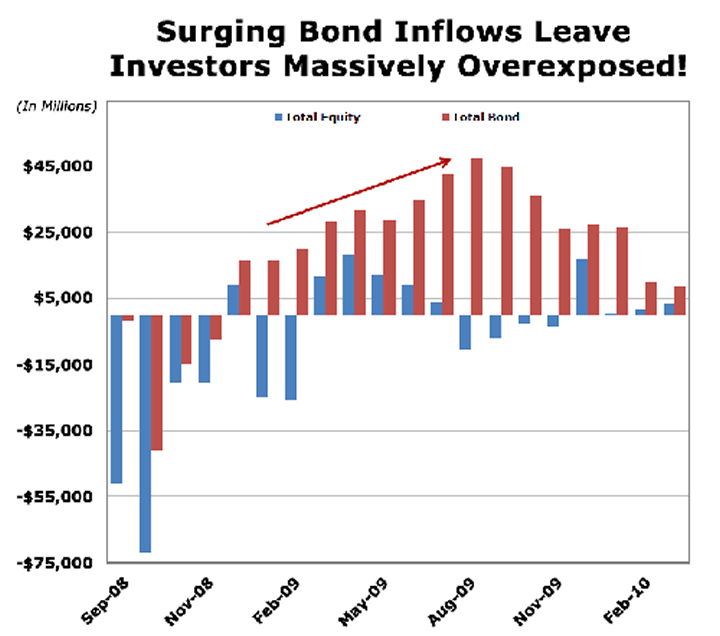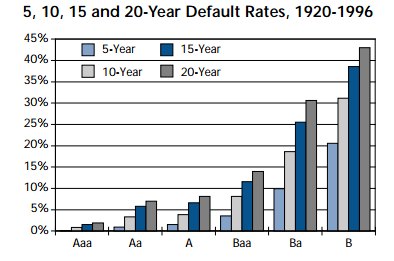
What is the difference between stocks and bonds?
Stocks are equity instruments and can be considered as taking ownership of a company. While bonds are issued by all types of entities – including governments, corporations, nonprofit organizations, etc. – stocks, on the other hand, are issued by sole proprietors, partnerships, and corporations.
How do stocks and bonds generate cash?
Stocks and bonds generate cash in different ways, too. To make money from stocks, you’ll need to sell the company’s shares at a higher price than you paid for them to generate a profit or capital gain. Capital gains can be used as income or reinvested, but they will be taxed as long-term or short-term capital gains accordingly.
What is the difference between fixed income and stocks?
Fixed-income investments are much less volatile than stocks, and also much less risky. Again, as mentioned earlier, stocks are subordinated to bonds in the event of a liquidation. However, bonds have a lower potential for excess returns than stocks do.
Where to buy stocks and bonds?
Where to Buy Stocks and Bonds Stocks are well known for being sold on various financial exchanges – in the United States, the most popular exchanges are the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), NASDAQ Stock Market, or the American Stock Exchange (AMEX).
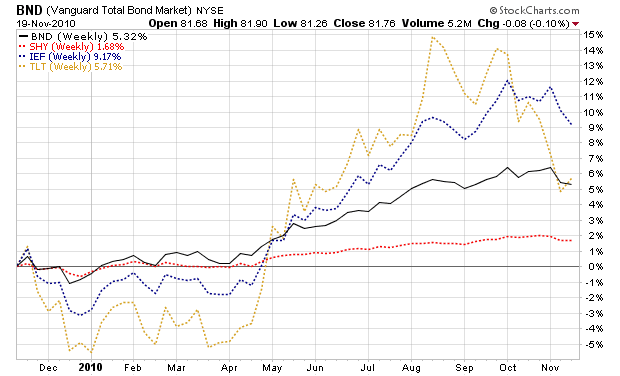
What Is Investment Income?
Investment income is money received in interest payments, dividends, capital gains realized with the sale of stock or other assets, and any additional profit made through an investment vehicle.
Understanding Investment Income
Investment income refers solely to the financial gains above the original cost of the investment. The form the income takes, such as interest or dividend payments, is irrelevant to it being considered investment income so long as the income is generated from a previous investment.
Example of Investment Income
Suppose an investor buys stock in company ABC for $50. Two weeks later, the investor sells them for $70, netting a profit of $20. This is a short-term investment, so the profit is taxed at the investor's regular earned income tax rate. (Federal tax law defines a short-term investment as one owned for less than a year.)
What are Bonds?
Bonds are debt instruments and can be considered IOUs or loans. The basic idea behind a bond is that an entity needs to raise money, and therefore, can sell a bond in return for the required funds. In return, they promise to pay back the initial amount that they borrowed, in addition to interest.
What are Stocks?
Stocks are equity instruments and can be considered as taking ownership of a company. While bonds are issued by all types of entities – including governments, corporations, nonprofit organizations, etc.
Practical Example – Bonds vs Stocks
Suppose there is a lemonade stand that recently opened. The founder of the lemonade stand is receiving much more demand than anticipated and wants to take advantage of the situation by opening a second lemonade stand. The second lemonade stand will cost around $1,000 to get up and running.
Where to Buy Stocks and Bonds
Stocks are well known for being sold on various financial exchanges – in the United States, the most popular exchanges are the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) is the largest securities exchange in the world, hosting 82% of the S&P 500, as well as 70 of the biggest , NASDAQ Stock Market, or the American Stock Exchange (AMEX).
Pros and Cons – Bonds vs Stocks
Stocks are beneficial for investors who have a higher risk appetite. Stocks are much more volatile, and there is a higher chance of losing your investment since equity holders are subordinated to debt holders if a company is forced to liquidate. However, in return for the risk, stockholders have a greater potential return.
Additional Resources
CFI is the official provider of the global Commercial Banking & Credit Analyst (CBCA)™ Program Page - CBCA Get CFI's CBCA™ certification and become a Commercial Banking & Credit Analyst. Enroll and advance your career with our certification programs and courses. certification program, designed to help anyone become a world-class financial analyst.
Stocks Represent Ownership
Stocks are simply ownership shares of corporations. When a company issues stock, it is selling a piece of itself in exchange for cash.
Bonds Represent Debt
Bonds, on the other hand, are debt. When an entity issues a bond, it is issuing debt with the promise to pay interest for the use of the money.
The Difference for Investors
Each share of stock represents an ownership stake in a corporation. That means the owner shares in the profits and losses of the company, although they are not responsible for its liabilities. Someone who invests in the stock can benefit if the company performs very well, and its value increases over time.
Which Is Right for You?
Many people invest in both stocks and bonds to diversify. Deciding on the appropriate mix of stocks and bonds in your portfolio is a function of your time horizon, tolerance for risk, and investment objectives. Typically, stocks and bonds do not fluctuate at the same time.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The recommended portion of stocks and bonds in your portfolio changes depending on your circumstances. If you start investing when you're young, you can put a larger percentage of your portfolio in stocks because of the long-term reward, which will mitigate the risk of stock volatility.
Comparing stocks and bonds
While both instruments seek to grow your money, the way they do it and the returns they offer are very different.
The upside down: When debt and equity roles reverse
There are certain types of stocks that offer the fixed-income benefits of bonds, and there are bonds that resemble the higher-risk, higher-return nature of stocks.
Intro to the Difference Between Stocks and Bonds
When people first learn about Finance, they typically hear about Stocks and Bonds soon after.
The Difference Between Stocks and Bonds: Big Picture
Before we dive into the deep end, let’s begin here with a big picture view of Stocks versus Bonds.
Difference Between Stocks and Bonds: Bonds
A Business’ Debt usually consists of Loans or Bonds. Since most people are familiar with Bonds that they can buy and sell, we’ll focus on Bonds here.
Difference Between Stocks and Bonds: Stocks
To initially fund a private Business, the investors (or ‘ Shareholders ‘) invest through an Equity Contribution and gain ownership (or ‘ Equity ‘) proportional to their investment.
Typical Stock and Bond Investors
Once a Business publicly lists its Stocks and Bonds, Investors can buy and sell every day.
Wrap-Up: The Difference Between Stocks and Bonds
In summary, Stocks and Bonds differ in that one reflects ownership (or ‘ Equity ‘) and the other reflects Borrowing (or ‘ Debt ‘).
Stocks vs Bonds: Full Animated Explainer Video
If you enjoyed this article, definitely check out our full Animated Explainer Video below on the differences between Hedge Funds and Mutual Funds.
The Three Primary Types of Income
To make an even sharper distinction between portfolio income and other forms of income, let’s examine portfolio income versus passive income and earned income.
Tips on Boosting Portfolio Income
Once you’ve come to grips with portfolio income and know how it works, put that knowledge to good use with these portfolio income amplification tips, which are especially helpful for long-term investors:
The Takeaway on Portfolio Income
Any investor interested in growing the value of his or her investment portfolio should know that portfolio income is a critical driver of total return.
No Special Tax Treatment
Investors don’t typically look to bonds to outperform stocks, although this happens from time to time (and many an experienced bond trader would beg to differ). However, most investors see the function of maintaining bonds in their portfolio as a way to help achieve stability and income.
Bond Types and Taxes
Bonds can have immediate tax consequences because you typically receive income from them twice a year. Here’s how the tax situation breaks down per bond type:
Do the Math
There's a quick way to look at how a municipal bond compares with a stock on an after-tax basis—which, after all, is the only basis that matters. You can compute the taxable equivalent of a municipal bond’s return using this formula:
Conclusion
Of course, stocks have always outperformed bonds over the long term. However, if you're looking for relatively secure income at a reasonable return, municipal bonds are worth a look for their tax benefits. Depending on your goals, you may find a place for them in your portfolio as part of a diversification strategy.
Summary
When an investor buys a stock, part ownership in the form of a share is bought.
What is a Stock?
When an investor buys a stock, part ownership in the form of a share is bought. If the business or enterprise happens to do well, the investor benefits by seeing an increase in the value of the share.
What is a Bond?
Bonds are a type of investment designed to aid governments and corporations to raise money. It can be viewed as a type of loan. There is no stock ownership and dividends, but investors who purchase bonds do receive payment in the form of interest.
Stock vs. Bonds
When bonds and stocks are compared, bonds are considered to be a safer investment.
Mutual Funds
Stocks and bonds are characterized by asset classes. On the other hand, mutual funds are pooled investment vehicles. In a mutual fund, money collected from various investors is taken together to buy a large variety of securities. A mutual fund gives an investor instant diversification.
Key Takeaways
Investors do not decide between stocks and bonds but decide on the proportion of the two in their portfolio. As stocks and bonds come with their own pros and cons, an investor will decide on the proportion according to the desired goals and risk tolerance.
More Resources
Thank you for reading CFI’s guide on Stocks, Bonds, and Mutual Funds. In order to help you become a world-class financial analyst and advance your career to your fullest potential, these additional resources will be very helpful: