
Jump To
- Implied volatility uses options to forecast the likely future movement of a security’s price
- IV can help predict future price movements caused by upcoming earnings, economic data and interest rates.
- Historical volatility measures past moves in a stock’s price over a predetermined time frame
How do you calculate implied volatility?
The factors are as follows:
- The market price of the option
- The underlying stock price
- The strike price
- The time to expiration
- The risk-free interest rate
What is considered a high implied volatility?
- Quantifies market sentiment, uncertainty
- Helps set options prices
- Determines trading strategy
How to measure implied volatility?
- Time until expiration — $2
- Distance between the strike price and current stock price — $2
- Implied volatility — $1
What is a good implied volatility percentage?
- Stocks tend to have a “smirk”, where the OTM puts have much higher implied volatilities (relative to the ATM Ivol. ...
- This is due to the fear-greed of market players. Fear in stocks is when they go down.
- Commodities, on the other hand, have a “floor” in price. The option skew for commodities will show OTM calls hav
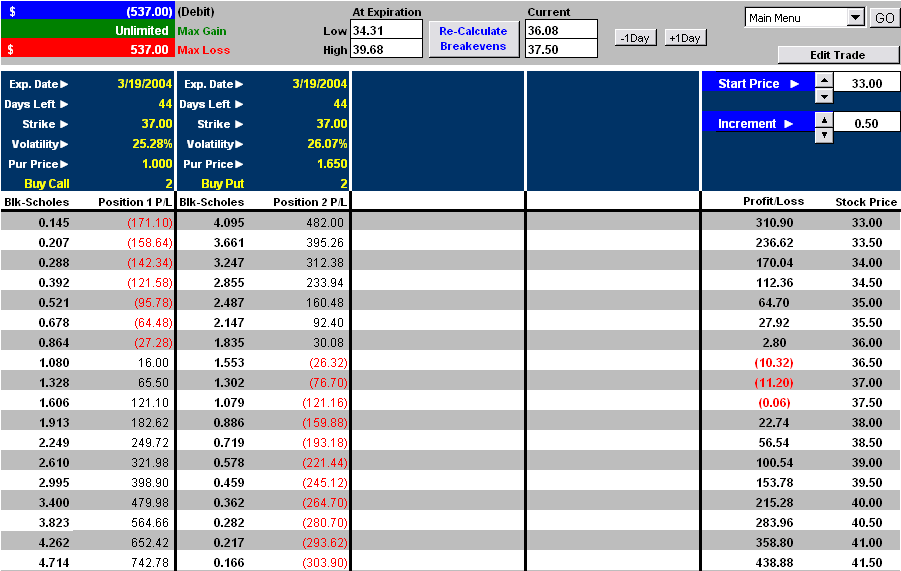
What is a good implied volatility for options?
Around 20-30% IV is typically what you can expect from an ETF like SPY. While these numbers are on the lower end of possible implied volatility, there is still a 16% chance that the stock price moves further than the implied volatility range over the course of a year.
What is implied volatility in options example?
For example, imagine stock XYZ is trading at $50, and the implied volatility of an option contract is 20%. This implies there's a consensus in the marketplace that a one standard deviation move over the next 12 months will be plus or minus $10 (since 20% of the $50 stock price equals $10).
What is considered a high implied volatility?
When a stock that normally trades in a 1% range of its price on a daily basis suddenly trades 2-3% of its price, it's considered to be experiencing “high volatility.”
Is 80% implied volatility high?
Put simply, IVP tells you the percentage of time that the IV in the past has been lower than current IV. It is a percentile number, so it varies between 0 and 100. A high IVP number, typically above 80, says that IV is high, and a low IVP, typically below 20, says that IV is low.
Is higher implied volatility better?
Options that have high levels of implied volatility will result in high-priced option premiums. Conversely, as the market's expectations decrease, or demand for an option diminishes, implied volatility will decrease. Options containing lower levels of implied volatility will result in cheaper option prices.
Is high IV good for options?
High IV (or Implied Volatility) affects the prices of options and can cause them to swing more than even the underlying stock. Just like it sounds, implied volatility represents how much the market anticipates that a stock will move, or be volatile.
Can implied volatility be greater than 100?
The short answer to this question is: Yes, volatility can be over 100%. Volatility can theoretically reach values from zero (no volatility = constant price) to positive infinite.
How do you know if options are cheap?
When it comes to the price of an option, the amount of time that the option has until expiration and the level of its implied volatility are two of the main factors that play into whether the option's price is actually cheap or expensive.
What Delta is good in options?
Call options have a positive Delta that can range from 0.00 to 1.00. At-the-money options usually have a Delta near 0.50. The Delta will increase (and approach 1.00) as the option gets deeper ITM. The Delta of ITM call options will get closer to 1.00 as expiration approaches.
How do you profit from volatility?
10 Ways to Profit Off Stock VolatilityStart Small. The saying 'go big or go home,' while inspirational, is not for beginning day traders. ... Forget those practice accounts. ... Be choosy. ... Don't be overconfident. ... Be emotionless. ... Keep a daily trading log. ... Stay focused. ... Trade only a couple stocks.More items...
Which option strategy is most profitable?
The most profitable options strategy is to sell out-of-the-money put and call options. This trading strategy enables you to collect large amounts of option premium while also reducing your risk. Traders that implement this strategy can make ~40% annual returns.
How do you know if implied volatility is high or low?
One simple method involves comparing the IV for your option against the stock's historical volatility (HV) for a comparable time period. For example: If you're considering a November-dated option that expires in about two months, compare the contract's IV level against the security's two-month HV.
Is a higher implied volatility good?
Higher levels of IV (implied volatility) result in higher option premiums. Therefore, if you are selling options, a higher IV means a higher reward...
Do I want implied volatility to be high or low?
Determining the ideal level of IV will depend on your options trading strategy. Generally, option sellers prefer a high IV when entering trades, an...
What is the difference between volatility and implied volatility?
Volatility, also known as historical volatility, represents the past volatility of a stock, ETF, or index. Implied volatility represents the future...
How does implied volatility affect the market?
Implied volatility is directly influenced by the supply and demand of the underlying options and by the market's expectation of the share price's direction. As expectations rise, or as the demand for an option increases, implied volatility will rise.
What happens to implied volatility?
Options that have high levels of implied volatility will result in high-priced option premiums. Conversely, as the market's expectations decrease, or demand for an option diminishes, implied volatility will decrease. Options containing lower levels of implied volatility will result in cheaper option prices.
What happens when implied volatility is relatively low?
Conversely, if you determine where implied volatility is relatively low, you might forecast a possible rise in implied volatility or a reversion to its mean.
Why are options less expensive?
As implied volatility decreases, options become less expensive. As implied volatility reaches extreme highs or lows, it is likely to revert to its mean. 2. If you come across options that yield expensive premiums due to high implied volatility, understand that there is a reason for this.
Why is implied volatility important?
This is important because the rise and fall of implied volatility will determine how expensive or cheap time value is to the option , which can, in turn, affect the success of an options trade.
What is time value in options?
Time value is the additional premium that is priced into an option, which represents the amount of time left until expiration. The price of time is influenced by various factors, such as the time until expiration, stock price, strike price, and interest rates. Still, none of these is as significant as implied volatility.
Which option is more sensitive to volatility?
Options with strike prices that are near the money are most sensitive to implied volatility changes, while options that are further in the money or out of the money will be less sensitive to implied volatility changes. Vega —an option Greek can determine an option's sensitivity to implied volatility changes.
Determine Whether Implied Volatility Is High Or Low
Determine whether IV is high or low, rising or falling, by looking at a metrics that shows the IV rank.
Research Why Some Options Yield Higher Premiums
There will always be a reason why some options yield higher premiums due to high implied volatility. It could be a product approval, or news about a merger or acquisition.
Identifying Options With High Implied Volatility For Short Premium Strategies
After you’ve done your research, you could identify options with high implied volatility that you might consider selling. You can sell options and still be bullish or neutral.
Identifying Options With Low Implied Volatility For Long Premium Strategies
When the implied volatility is low and the premiums are low-priced, it’s typically a buyers’ market. In a low IV environment, you can consider options buying strategies such as:
What is volatility in stock market?
By definition, volatility is simply the amount the stock price fluctuates, without regard for direction. As an individual trader, you really only need to concern yourself with two forms of volatility: historical volatility and implied volatility.
What would happen if there were no options traded?
In fact, if there were no options traded on a given stock, there would be no way to calculate implied volatility. Implied volatility and option prices. Implied volatility is a dynamic figure that changes based on activity in the options marketplace.
What is at the money option?
Usually, at-the-money option contracts are the most heavily traded in each expiration month. So market makers can allow supply and demand to set the at-the-money price for at-the-money option contract. Then, once the at-the-money option prices are determined, implied volatility is the only missing variable.
Why do options change time value?
The reason the options’ time value will change is because of changes in the perceived potential range of future price movement on the stock. Implied volatility can then be derived from the cost of the option. In fact, if there were no options traded on a given stock, there would be no way to calculate implied volatility.
Is implied volatility good or bad?
So when implied volatility increases after a trade has been placed, it’s good for the option owner and bad for the option seller. Conversely, if implied volatility decreases after your trade is placed, the price of options usually decreases. That’s good if you’re an option seller and bad if you’re an option owner.
Can you calculate implied volatility?
However, you can’t calculate implied volatility without knowing the prices of options. So some traders experience a bit of “chicken or the egg” confusion about which comes first: implied volatility or option price. In reality, it’s not that difficult to understand.
What is Implied Volatility?
Implied Volatility Definition: The market’s predictive forecast of a likely price movement.
Implied Volatility and Extrinsic Value
An option’s premium consists of extrinsic and/or intrinsic value. When we’re talking implied volatility, we are focusing only on the extrinsic value of an options price.
Implied Volatility vs Historical Volatility
Historical Volatility Definition: A statistical indicator that measures the historical return distribution for a security over a predetermined period of time.
Implied Volatility and Probability
When you look at an options chain, you will see that every option expiration cycle has an implied volatility (IV) level associated with it.
Implied Volatility is Annualized
Implied volatility is expressed as an annual percentage (Optiver). Even if the options on your chain expire in 30 days, the IV number is still annualized.
Expected Range Formula
In the stock market, this mean/average is the current price of a stock. Here is the formula to compute this:
1 Standard Deviation Explained
The above chart shows a $100 stock with 25% implied volatility. 68% of the area under the curve falls between $75 and $125, indicating that the market is implying a 68% probability that the stock price is between these two levels one year from today.
What is implied volatility?
The implied volatility definition is this: implied volatility is a statistical measure of how an asset has performed over the past and how it is expected to perform in the future. There are two types of volatility: the implied volatility, which tries to measure future fluctuations, and the second one, historical volatility, ...
Why is implied volatility important?
The reason why implied volatility in options is so important is because it will directly affect to the option premiums of the contracts. Along with the relationship between the underlying price and the strike price, the implied volatility will determine the option premium.
What does it mean when a stock has high volatility?
For example, a high volatility means that the stock is expected to vary its price much more than a low volatility stock. Amazon is a high volatility company because its stock prices fluctuate over 100$ in a single day. Starbucks stock is a low implied volatility company because the fluctuations of its prices are relatively small.
Is Starbucks a low volatility stock?
Starbucks stock is a low implied volatility company because the fluctuations of its prices are relatively small. As a general rule, those stocks that have a higher stock trading volume tend to have a higher volatility, but this is not always the case with options.
Can implied volatility be negative?
No, implied volatility cannot be negative. It can be very low, but not negative. The reason is simple. As implied volatility is the one that shows us how much the price is going to fluctuate in the future, a negative implied volatility would not make any sense at all.
What does higher implied volatility mean?
Higher implied volatility indicates a higher premium for the option. Conversely, a lower implied volatility indicates a lower premium. It is important to note that implied volatility does not predict which direction the security’s price will go.
Why is implied volatility important?
In contrast, a longer amount of time remaining leads to a higher implied volatility. Implied volatility is an important concept that contributes to the pricing of options. Understanding how implied volatility affects the price of options is crucial in an investor’s success when buying or selling option contracts.
What factors affect implied volatility?
A factor that affects implied volatility is supply and demand. When there is high demand for a security, the price will rise and so will the implied volatility. This leads to a higher premium for the option contract. Conversely, when there is more supply than demand for a security, the price will fall and so will implied volatility.
What does it mean when a security has high implied volatility?
High implied volatility means that the security is expected to have large fluctuations in its price, or that there is uncertainty related to the security. Low implied volatility means that the security is not expected to have large fluctuations in its price, or that there is little uncertainty related to the security.
What is an option contract?
Options are a contract that give the opportunity to buy or sell a security at a specific price before, or on, a pre-determined expiration date. A buyer pays a premium for the option contract to a seller. This premium is affected by implied volatility. Higher implied volatility indicates a higher premium for the option.
How Implied Volatility (IV) Works
- Implied volatility is the market's forecast of a likely movement in a security's price. It is a metric used by investors to estimate future fluctuations (volatility) of a security's price based on certain predictive factors. Implied volatility is denoted by the symbol σ (sigma). It can often be thought t…
Implied Volatility and Options
- Implied volatility is one of the deciding factors in the pricing of options. Buying options contracts allow the holder to buy or sell an assetat a specific price during a pre-determined period. Implied volatility approximates the future value of the option, and the option's current value is also taken into consideration. Options with high implied volatility have higher premiums and vice versa. Kee…
Implied Volatility and Option Pricing Models
- Implied volatility can be determined by using an option pricing model. It is the only factor in the model that isn't directly observable in the market. Instead, the mathematical option pricing model uses other factors to determine implied volatility and the option's premium.
Factors Affecting Implied Volatility
- Just as with the market as a whole, implied volatility is subject to unpredictable changes. Supply and demandare major determining factors for implied volatility. When an asset is in high demand, the price tends to rise. So does the implied volatility, which leads to a higher option premium due to the risky nature of the option. The opposite is also true. When there is plenty of supply but no…
Pros and Cons of Using Implied Volatility
- Implied volatility helps to quantify market sentiment. It estimates the size of the movement an asset may take. However, as mentioned earlier, it does not indicate the direction of the movement. Option writers will use calculations, including implied volatility, to price options contracts. Also, many investors will look at the IV when they choose an investment. During perio…
Real-World Example
- Traders and investors use charting to analyze implied volatility. One especially popular tool is the Cboe Volatility Index (VIX). Created by the Cboe Global Markets, the VIX is a real-time market index. The index uses price data from near-dated, near-the-money S&P 500 index options to project expectations for volatility over the next 30 days.4 Investors can use the VIX to compare …