- The expected return is the amount of profit or loss an investor can anticipate receiving on an investment.
- An expected return is calculated by multiplying potential outcomes by the odds of them occurring and then totaling these results.
- Expected returns cannot be guaranteed.
How do I calculate the expected return of a stock?
- Find the initial cost of the investment
- Find total amount of dividends or interest paid during investment period
- Find the closing sales price of the investment
- Add sum of dividends and/or interest to the closing price
- Divide this number by the initial investment cost and subtract 1
How to calculate expected total return for any stock?
The ‘quick and easy’ way to find total return is to:
- Calculate return from change in price-to-earnings multiple
- Add in current dividend yield
- Add in expected business growth rate on a per share basis
How does the expected return affect a stock price?
Key Points
- A company that is publicly traded must announce its earnings reports quarterly. ...
- Beta is a metric used to signal the risk in a particular stock. ...
- Analysts constantly assess the health of public companies to assess the value of its equity and debt instruments, and their outlook affects stock and bond prices in secondary markets.
What does return on investment tell us about a stock?
The return on a stock market is the sum of the average capital gain and the average dividend yield. In the short term, a stock market can provide a negative rather than a positive return if the effect of falling share prices outweighs the dividend yield.
What is expected return theory?
that can take any values within a given range. The expected return is based on historical data, which may or may not provide reliable forecasting of future returns. Hence, the outcome is not guaranteed.
Is expected return a predictor of stock performance?
Although not a guaranteed predictor of stock performance, the expected return formula has proven to be an excellent analytical tool that helps investors forecast probable investment returns and assess portfolio risk and diversification.
What is expected return?
The expected return of an investment is the rate of return an investor can reasonably expect, based on historical performance. You can use an expected-return formula to estimate the profit or loss on a specific stock or fund.
Why is expected return important?
Expected return can be an effective tool for estimating your potential profits and losses on a particular investment. Before diving in, it’s important to understand the pros and cons. Pros. Helps an investor estimate their portfolio’s return. Can help guide an investor’s asset allocation.
What does it mean when a stock has a low standard deviation?
When a stock has a low standard deviation, its price stays relatively stable, and returns are usually close to the average. A high standard deviation indicates that a stock can be quite volatile.
Is expected return based on historical performance?
The expected return is based entirely on historical performance. There’s no guarantee that future returns will compare. It also doesn’t take into account the risk of each investment. The expected return of an asset shouldn’t be the only factor you consider when deciding to invest.
Can you use expected and required return in tandem?
You can use the required return and expected return in tandem. When you know the required rate of return for an investment , you can use the expected return to decide if it’s worth your while.
ABSTRACT
We derive a formula for the expected return on a stock in terms of the risk-neutral variance of the market and the stock's excess risk-neutral variance relative to that of the average stock. These quantities can be computed from index and stock option prices; the formula has no free parameters.
I. Theory
Our starting point is the gross return with maximal expected log return: call it , so for any gross return . This growth-optimal return has the special property, unique among returns, that is a stochastic discount factor (SDF).
II. Three Measures of Risk-Neutral Variance
The risk-neutral variance terms that appear in our formulas can be calculated from option prices using the approach of Breeden and Litzenberger ( 1978 ). Our measure of market risk-neutral variance, SVIX t 2, is determined by the prices of index options:
III. Testing the Model
In this section, we use SVIX t 2, SVIX i , t 2, and SVIX ¯ t 2 to test the predictions of our model using full-sample information. But before turning to formal tests, we conduct a preliminary exploratory exercise.
IV. Risk Premia and Stock Characteristics
The results of the previous section show that the model performs well in forecasting stock returns.
V. Out-of-Sample Analysis
Formulas 16 and 17 have no free parameters, so it is reasonable to hope that they may be well suited to out-of-sample forecasting. In this section, we show that they are. This fact is particularly striking given the substantial variability of the forecasts both in the time series and in the cross section.
VI. Conclusion
We conclude by highlighting some distinctive features of our approach to the cross section of expected stock returns.
Expected Return
Expected return is an estimate of the long-term returns a stock investment is likely to generate, assuming it's purchased at its current stock price. This estimation is also based on how long you expect to hold the stock.
Discounted Cash Flow Model
In many cases, the discounted cash flow (DCF) model is the most accurate approach to estimating a company's intrinsic/fair value, at which a company is worth buying. In other words, the DCF model will provide you with a buy price range in which the company will be considered "undervalued" and potentially worth buying.
How to Estimate Expected Return
Now, I will show you how to estimate the expected return for Texas Instruments, continuing with the example above.
The Bottom Line
In summary, you can estimate the expected return of a stock investment by using the discounted cash flow (DCF) model, applying the most likely growth rate for free cash flow (FCF), and altering the discount rate (required rate of return) until it hits the stock's current stock price.
How to calculate expected return?
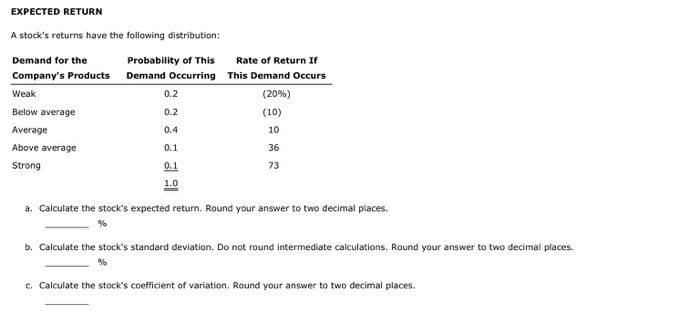
The formula for expected return for investment with different probable returns can be calculated by using the following steps: 1 Firstly, the value of an investment at the start of the period has to be determined. 2 Next, the value of the investment at the end of the period has to be assessed. However, there can be several probable values of the asset, and as such, the asset price or value has to be assessed along with the probability of the same. 3 Now, the return at each probability has to be calculated based on the asset value at the beginning and at the end of the period. 4 Finally, the expected return of an investment with different probable returns is calculated as the sum product of each probable return and corresponding probability as given below –#N#Expected return = (p1 * r1) + (p2 * r2) + ………… + (pn * rn)
Why is it important to understand the concept of a portfolio's expected to return?
It is important to understand the concept of a portfolio’s expected to return as it is used by investors to anticipate the profit or loss on an investment. Based on the expected return formula, an investor can decide whether to invest in an asset based on the given probable returns.
What is Dave Ramsey's projection of future returns?
Dave Ramsey has one of the most optimistic projections for future returns. He has been stating for years that investors should expect a 12% return on their stock investments. It’s part of Dave Ramsey’s Financial Peace University course that has been taken by millions. Dave argues that his 12% projection of future investment returns is based on ...
Can you predict the future?
Of course, no one can predict the future. Investment returns could be really good, average, or really bad in the future. You should plan your retirement savings using conservative projections to ensure that you’ll be able to meet your retirement goals even if the market has returns lower than the historical average.
Is real return better than nominal return?
Real returns is a better metric than nominal returns in retirement planning. If you use nominal returns, then you have to adjust your projected spending in retirement by the inflation rate.
Did investors take inflation into their return estimates?
It’s unclear whether investors did not take into account inflation into their return estimates. Regardless, it is promising that financial advisors, at least when responding to a survey, appearing to be using historical data to guide their estimates of the future returns they can deliver to their clients.
How to calculate expected return on stock?
Follow these steps to calculate a stock’s expected rate of return in Excel: 1. In the first row, enter column labels: 2. In the second row, enter your investment name in B2, followed by its potential gains and probability of each gain in columns C2 – E2*. 3.
What is the rate of return?
The money that you earn on an investment is known as your return. The rate of return is the pace at which money is earned or lost on an investment. If you’re going to invest, you may want to consider how much money that investment is likely to earn you.
What is required rate of return?
The required rate of return is a concept in corporate finance. It’s the amount of money, or the proportion of money received back from the money invested, that a project needs to generate in order to be worth it for the investor or company doing it.
Why is the real rate of return negative?
This matters because the reason to invest in assets like stocks, bonds, property and so on is to generate money to buy things — and if the cost of things is going up faster than the rate of return on your investment, then the “real” rate of return is actually negative.
Why is compound annual growth rate useful?
This can be useful because it’s a way of comparing investments over annual timespans.
Is expected return a prediction?
Expected return is just that: expected. It is not guaranteed, as it is based on historical returns and used to generate expectations, but it is not a prediction.
Do expected returns take volatility into account?
For instance, expected returns do not take volatility into account. Securities that range from high gains to losses from year to year can have the same expected returns as steady ones that stay in a lower range.
Can expected returns be dangerous?
So it could cause inaccuracy in the resultant expected return of the overall portfolio. Expected returns do not paint a complete picture, so making investment decisions based on them alone can be dangerous. For instance, expected returns do not take volatility into account.