What is the Dow Theory?
- Dow theory trading strategy is primarily based on the ideas about stock price movement put forth by Charles H. ...
- It mainly states that multiple indices should provide the same signal to confirm a trend.
- It lists a set of fundamental tenets. ...
- It is the core principle of modern technical analysis. ...
What are the basic principles of Dow's theory?
How the Dow Theory Works
- The Market Discounts Everything. The Dow theory operates on the efficient markets hypothesis (EMH), which states that asset prices incorporate all available information.
- There Are Three Primary Kinds of Market Trends. Markets experience primary trends which last a year or more, such as a bull or bear market. ...
- Primary Trends Have Three Phases. ...
What does the Dow measure exactly?
What Does the Dow Jones Measure?
- Purpose of the Dow. The Dow is a stock index that is based on 30 of the largest publicly owned corporations in the United States.
- Calculating the Dow. The Dow is calculated by adding up the share prices of all 30 stocks that it follows and then dividing by a value known as the ...
- Problems With the Dow. ...
- Modern Relevance. ...
How does the Dow theory work?
- The History of Dow Theory
- How Does Dow Theory Work?
- The Six Dow Theory Principles The Market Discounts Everything There are Three Types of Trends Primary Trends Transition Through Three Phases Trends Require Index Confirmation Trends Require Volume Confirmation Trends ...
- Dow Theory and Closing Prices
- Is Dow Theory Still Relevant?
- Dow Theory Downsides
What does Dow theory say?
The 6 Tenets of Dow Theory
- The Market discounts everything. This Dow theory principle has been taken from the efficient market hypothesis. ...
- There are 3 kinds of market trends. ...
- Primary trends have three phases. ...
- Indices must confirm each other. ...
- Volume must confirm the trend. ...
- Trends persist until there is a clear reversal. ...
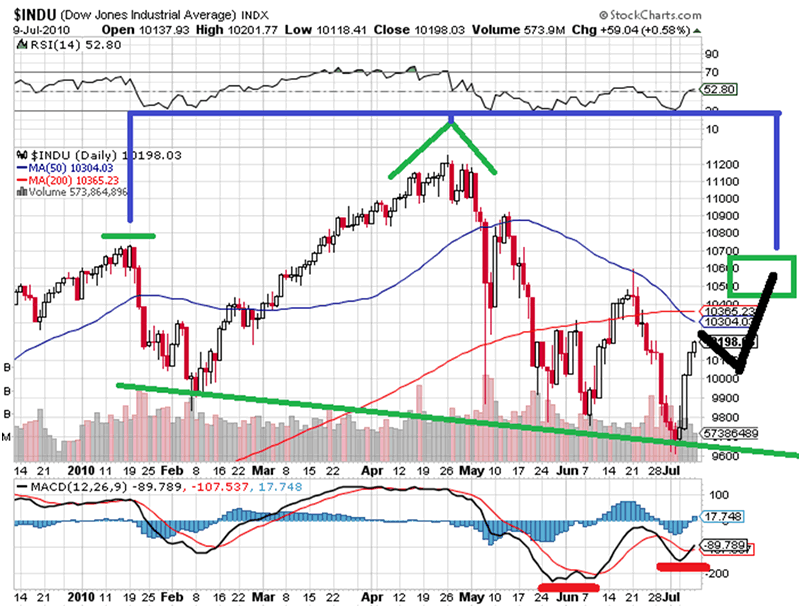
How does the Dow Theory determine the market?
Steps to determine the market trend using Dow Theory, Take the data of approx 2 years and plot it into line chart. Mark the tops and bottoms. Qualify the tops and bottoms (ex :- Bottom, Higher Bottom, Top, higher Top) Look for a sequence to find the trend.
What is the Dow Theory Buy Signal?
The classic Buy signal is developed as follows: After the low point of a primary downtrend in a Bear market is established, a secondary uptrend (this is the most often debated part of the Theory) bounce will occur.
How accurate is the Dow Theory?
For those questioning how accurate the Dow Theory could be, after more than 100 years in practice, Blay said the average annual gain for the indicator would have been 11.22% since 1953, compared with a 10.8% gain with a buy-and-hold strategy.
What is the Dow explained?
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) is a widely-watched benchmark index in the U.S. for blue-chip stocks. The DJIA is a price-weighted index that tracks 30 large, publicly-owned companies trading on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the Nasdaq.
What is Dow Theory in simple words?
The Dow theory is a financial theory that says the market is in an upward trend if one of its averages (i.e. industrials or transportation) advances above a previous important high and is accompanied or followed by a similar advance in the other average.
What is the goal of the Dow Theory?
The goal of the theory is to determine changes in the primary, or major, movement of the market. Once a trend has been established, it is assumed to exist until a reversal is proved. Dow theory is concerned with the direction of a trend and has no forecasting value as to the trend's ultimate duration or size.
Is Dow Theory still relevant?
Conclusion. Even though it is more than a hundred years old, the Dow Theory is still relevant in the current trading market. This is because by understanding Dow Theory, traders can benefit from spotting and exploiting trends in the market.
How many principles are there in the Dow Theory?
six principlesThe Dow Theory has six principles which when put together gives a complete picture for the markets.
Who developed Dow Theory?
The Dow Theory was introduced to the world by Charles H. Dow, who also founded the Dow-Jones financial news service (Wall Street Journal). During his time, he wrote a series of articles starting from the 1900s which in the later years was referred to as 'The Dow Theory'.
Why is Amazon not in the Dow?
Amazon ($2,837.06) has far too high a price tag and would drastically throw off the index. The same is true of Alphabet ($2,519.02). There is, of course, a better solution: The Dow could forget tradition and turn into a float capitalization-weighted index like the S&P 500.
Why is the Dow Jones so important?
In addition to representing 30 of the most highly capitalized and influential companies in the U.S. economy, the Dow is also the financial media's most referenced U.S. market index and remains a good indicator of general market trends.
How do you use Dow Jones?
The DJIA as a Dollar Value To figure out how a change in any particular stock affects the index, divide the stock's price change by the current divisor. For example, if Walmart (WMT) is up $5, divide five by the current divisor (0.147), which equals 34.01.
Dow Theory Explained
The Dow theory developed from the market price action analysis, views on speculation, etc., put forth by Charles H. Dow formed a foundational step for technical analysis when the software’s aided technical analysis like today didn’t exist.
How Does Dow Theory Work in Technical Analysis?
The Dow theory was fundamental to technical stock market analysis and acted as the underlying principle for its continued advancement.
Example
The technical analysis in line with the theory confirms a particular trend and validates the buy or sell signal if both averages confirm each other. If one average is moving towards a new high or low, then the other must soon follow.
Recommended Articles
This has been a Guide to Dow theory and its meaning. Here we explain how does Dow theory works in technical analysis and paradigms, along with an example. You can learn more from the following articles –
What is the Dow Theory?
While there are those who may think that the market is different now, a read through Rhea's book, The Dow Theory, will attest that the stock market behaves the same today as it did almost 100 years ago.
How does Dow Theory work?
The theory centers around identifying the trend for the Dow Jones Rail (now Transportation) Average and the Dow Jones Industrial Average, and using volume to confirm those trends. If both Dow Jones averages are trending in the same direction, then the entire market can be said to be trending in that direction as well. Investors can use these signals to identify the primary market trend, and then trade with that trend.
How to identify the primary trend?
The first step in identifying the primary trend is to identify the individual trends of the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), and Dow Jones Transportation Average (DJTA). Hamilton used peak and trough analysis in order to ascertain the identity of the trend. An uptrend is defined by prices that form a series of rising peaks and rising troughs (higher highs and higher lows). In contrast, a downtrend is defined by prices that form a series of declining peaks and declining troughs (lower highs and lower lows).
Why is Dow Theory important?
Dow Theory helps investors identify facts, not make assumptions or forecast. It can be dangerous when investors and traders begin to assume. Predicting the market is a difficult, if not impossible, game. Hamilton readily admitted that Dow Theory was not infallible. While Dow Theory may be able to form the foundation for analysis, it is meant as a starting point for investors and traders to develop analysis guidelines that they are comfortable with and understand.
What are the three types of price movements?
Dow and Hamilton identified three types of price movements for the Dow Jones Industrial and Rail averages: primary movements, secondary movements and daily fluctuations. Primary moves , which can last from a few months to many years, represent the broad underlying trend of the market. Secondary (or reaction) movements, which can last from a few weeks to a few months, move counter to the primary trend. Daily fluctuations can move with or against the primary trend and last from a few hours to a few days, but usually not more than a week.
How many times a year can you trade on the Dow?
According to Hamilton (writing in the early part of the 20th century), those who successfully applied Dow Theory rarely traded more than four or five times a year. Remember that intraday, day-to-day and possibly even secondary movements can be prone to manipulation, but the primary trend is immune from manipulation.
Is Coca Cola a primary or secondary trend?
The chart below of Coca-Cola (KO) is a relatively recent example of the primary trend remaining intact. The downtrend for Coca-Cola began with the sharp fall from above 90. The stock rallied with the market in October and November 1998, but by December started to decline again. According to Dow Theory, the October/November rally would be called a secondary move (against the primary trend). It is likely that the stock was caught up in the general market advance at the time. However, when the major indices were hitting new highs in December, Coca-Cola was starting to flounder and resume its primary trend.
What is Dow Theory?
The Dow Theory is a theory based on observations of Mr Charles Dow. These observations are known as tenets of the Dow Theory. Using this theory, you could easily understand what phase the market is in and make predictions about what is going to happen next.
History of Dow Theory
Mr Charles Dow introduced the Dow Theory to the world in 1896. He was the founder of Dow Jones & Company. He along with his friends Charles Bergstresse and Edward Jones co-founded the Wall Street Journal where he used to publish small portions of the Dow Theory.
Six Tenets of Dow Theory
This is one of the key assumptions of technical analysis. It believes that we humans behave in a similar way in different situations. So, when there is panic in the markets, investors tend to get fearful and sell their holdings.
What is the Dow Theory?
Share. The Dow Theory, a financial markets theory developed by Charles H. Dow, rests on six basic tenets that were a precursor to modern-day technical analysis. Charles Dow believed that the stock market as a whole was a reliable measure of global economic conditions and that by analysing the global market, it was possible to accurately assess ...
Why is Dow's theory important?
According to the Dow theory, the importance of these upward and downward movements is their position in relation to previous fluctuations. This method teaches investors to read a trading chart and to better understand what is happening with any asset at any given moment. With this simple analysis, even the most inexperienced can identify the context in which a financial instrument is evolving.
Why did Charles Dow create the Dow Jones Industrial Index?
Charles Dow created these indices as he believed that they would provide an accurate reflection of the economic and financial conditions ...
What does Charles Dow believe?
Furthermore, Charles Dow supported the common belief among all traders and technical analysts that an asset price and its resulting movements on a trading chart already have all necessary information already available and forecasted in order to make accurate predictions.
Is the Dow theory controversial?
This is one of the more controversial elements of Dow theory. Indeed, reversals in primary trends can easily be confused with the emergence of secondary trends. The Dow Theory therefore advocates caution, as it is difficult to distinguish between the two until after the event.
Who created the Dow Jones Industrial Average?
However, more than a century later, the Dow Jones Industrial Average market index, created by the American journalist to illustrate his theory, is probably now the most followed index on the planet.
Can two opposing primary trends coexist?
This last tenet, that two opposing primary trends cannot coexist on two different market indices, was doubtless the most important to Charles H. Dow. In other words, the primary trend discovered on a market index must always be confirmed by a similar trend on another market index and vice versa.
What is the Dow theory?
On January 31st,1901 Charles H. Dow compared the stock market to the tides of the ocean when he wrote in the Wall Street Journal " A person watching the tide coming in and who wishes to know the exact spot which marks the high tide, sets a stick in the sand at the points reached by the incoming waves until ...
When was the Dow Theory first developed?
The following record is for the original Dow Theory discussed above. Since the Dow Theory was first developed in the early 1900s, I have added to its usefulness; that evolution, interpretation, and subsequent record as outlined in my book " Dow Theory for the 21st Century ", is available for Subscribers only, along with the current status.
What is a bear market sell signal?
A Bear market Sell signal is determined in much the same way, but opposite to a Buy Signal. When a Bull market tops and sets back, and the subsequent rally that goes back up (again, over 3%) and falls short of reaching the previous high and then penetrates the recent lows on the next decline as measured by both the Industrial and Transportation Averages, a SELL Signal is generated indicating a Bear market. This is the must usual SELL signal (S-1):
Is the theory of averages infallible?
The theory is not infallible. The "definite theorems": There are three movements of the averages. The first, and most important, is the primary trend. The second, and most deceptive is the secondary reaction. The third, and usually unimportant, is the daily movement.
Is confirmation by both a part of Dow Theory?
Confirmation by both is an integral part of the Dow Theory. Manipulation is possible day-to-day but the primary trend cannot be manipulated. The Averages discount everything (except acts of God). The theory is not infallible. The "definite theorems": There are three movements of the averages.
What is Dow Theory?
Out of this company and, more particularly, out of the mind of Dow came the theories that form most of the basis of technical analysis today. In 1884 Charles Dow published the first-ever stock index, the Industrial Average consisting of 11 companies. In 1897 Charles Dow created a Rail Index or what is now known as the Transport Index . In 1928 the Industrial Average grew to 30 stocks, the famous DJ-30.
What is phase 3 of the stock market?
Phase 3 – Distribution . Far-sighted investors start to sell as they see Stock Price growth is unsustainable compared to company earnings or economic climate.
What was the first stock index?
In 1884 Charles Dow published the first-ever stock index, the Industrial Average consisting of 11 companies. In 1897 Charles Dow created a Rail Index or what is now known as the Transport Index .
When should the market discount?
As soon as news is made available to the market, it should discount (or appreciate) the prices accordingly. The market participants discount everything, including past information, present information, and future expectation. Also built-in are emotions, fads, and trends.
Has the stock market recovered since March 2009?
Volume. Since the market bottom in March 2009, stocks have recovered, but volume has been decreasing. This trend continued for the next 6 years as my independent investors refused to re-enter the market after being burned so badly in this crash.
Does the market theory still work today?
This theory still works today on many levels, and we can compare many different markets.
Is volume analysis important in Dow's era?
Of course, Dow suggested this is not as important a rule as the previously stated tenets; however, you will see in future chapters a whole area of volume analysis has been developed since Dow’s era that will give you much further insight into the role of volume in markets.
Dow Theory Explained
How Does Dow Theory Work in Technical Analysis?
- The Dow theory was fundamental to technical stock market analysis and acted as the underlying principle for its continued advancement. The technical framework of the analysis emphasizes the need to pay close attention to market data to discern trends, reversals and determine when to buy or sell an asset for maximum profit since the market is the in...
Example
- The technical analysis in line with the theory confirms a particular trend and validates the buy or sell signal if both averages confirm each other. If one average is moving towards a new high or low, then the other must soon follow. To further illustrate how Dow’s theory work, check the following chart that shows the relationship between the industrial and transports indices and wh…
Recommended Articles
- This has been a Guide to Dow theory and its meaning. Here we explain how does Dow theory works in technical analysis and paradigms, along with an example. You can learn more from the following articles – 1. Fundamental Analysis vs Technical Analysis 2. Security Analysis 3. Trend Trading