
Some of the major key differences are mentioned below:
- Stock options are simply stocks that are bought and sold by one entity to the other entity with no compulsion of the time to execute just before the expiration dates. ...
- RSU, the execution of the option is restricted. ...
- After the vesting period is over in stock options, the employees have an option to buy or sell the stocks. ...
How do stock options and RSUs differ?
Key Differences
- The first key difference is shareholders’ rights. In the case of stock options, the employee receives the full right of the shareholders. ...
- The stock option offers both voting rights and dividend rights. ...
- The payment during settlement is always stock in the case of stock options. ...
- After the vesting period, the stock option becomes the common stock. ...
Are stock options or RSUs better?
Stock Options are usually better for both at an early stage company. For a later stage company, RSUs are usually better for both. The employee can get more shares from stock options than from RSUs. If the strike price is small then even the difference in value with one RSU is negligible.
Are options better than stocks?
You can limit your risk while maintaining unlimited potential gains by investing in stock options instead of stock. That doesn't means options are a better investment than stocks. It just means you have more, well, options. Every share of stock represents an equal amount of ownership in a company.
What is the best stock trading option?
Option Strategies for a Downturn
- Buying in a Downturn. Market history suggests that a contrarian approach works better. ...
- Basics of Put Options. A put option gives the buyer of that option the right to sell a stock at a predetermined price known as the option strike price.
- Put Selling in a Downturn. ...
- An Example. ...
- Drawbacks. ...
- Selling Puts Intelligently. ...
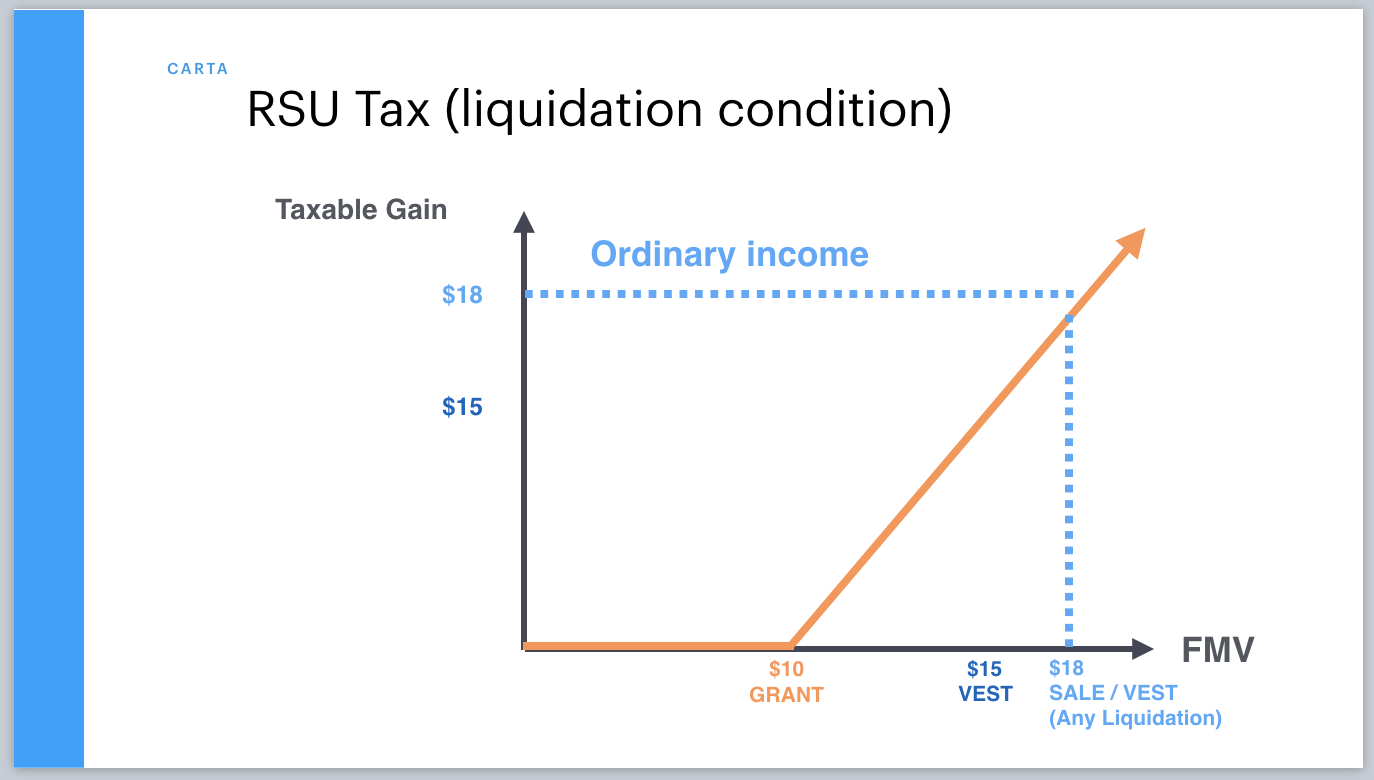
Is it better to take RSU or stock options?
Stock options are only valuable if the market value of the stock is higher than the grant price at some point in the vesting period. Otherwise, you're paying more for the shares than you could in theory sell them for. RSUs, meanwhile, is pure gain, as you don't have to pay for them.
How do RSU stock options work?
Restricted stock units are a way an employer can grant company shares to employees. The grant is "restricted" because it is subject to a vesting schedule, which can be based on length of employment or on performance goals, and because it is governed by other limits on transfers or sales that your company can impose.
What happens to RSU if you leave?
Whenever you decide to quit, the vested portion of your RSUs will stay yours. Since shares of company stock are released to you upon a vesting date, those RSUs become shares that you own outright. And since you now own company shares outright, your departure from the company has no effect on your ownership.
Can you sell RSU immediately?
In a majority of cases, the RSU selling strategy is to sell the RSUs immediately after the vesting period. However, there are exceptional cases where this may not be the go-to strategy. The company's future and your ability to bear the financial risk might make a case against selling the stock after the RSU vests.
What are the two types of stock options?
On the other hand, two types of stock options exist: non-qualified stock options (NSOs) and incentive stock options (ISOs). For NSOs, you are taxed on the difference between the market price and the grant price. This is called the spread, and it is taxed as regular income.
Why are stock options valuable?
Stock options are only valuable if the market value of the stock is higher than the grant price at some point in the vesting period. Otherwise, you’re paying more for the shares than you could in theory sell them for. RSUs, meanwhile, are pure gain, as you don’t have to pay for them.
When did restricted stock units come into use?
Restricted stock units (RSU) came in vogue in the ’90s and early 2000s. They are a bit simpler than stock options in that there is no transaction or stock pricing involved. Instead, the company simply commits to giving an employee stock in the company when a certain requirement is fulfilled.
How long do you have to work to buy stock?
This often involves a vesting schedule, where you have to work at the company for a certain period of time, often one year, before you can purchase the stock. This is to prevent people who only work at the company for a short period of time from ending up with potentially valuable stock.
Be sure you understand your rights and the tax consequences
Erin Gobler is personal finance coach and a writer with over decade of experience. She specializes in writing about investing, cryptocurrency, stocks, and more. Her work has been published on major financial websites including Bankrate, Fox Business, Credit Karma, The Simple Dollar, and more.
Which Is Right for You?
As an employee, whether you have access to RSUs or stock options will depend on the company you work for. Some companies may offer one or the other, while others may offer both.
Company Stock in Your Investment Portfolio
If your company offers either RSUs or stock options, it’s important to consider how those shares will fit into your overall investment portfolio. Allowing a single company—even the one you work for—to comprise too large a share of your portfolio could create unnecessary risk and the chance of excessive loss if the company underperforms.
The Bottom Line
RSUs and stock options are both types of equity compensation that companies may offer their employees as a way to attract and retain talent and reward them for hard work. Which you have access to will largely depend on the company you work for and your role within it.
What are the different types of stock options?
We can distinguish two types of stock options: 1 Incentive stock options or ISO. 2 Nonqualified options.
What happens if stock price rises?
The more the stock price rises, the more money you can make. The restricted stock units can also have some cons: The restricted stock units tax is an income tax. If the stock price falls, you can earn less money. You can also lose unvested shares at termination.
What is incentive stock?
The incentive is for the employee to work hard and help the company grow, so that the price of the stock goes up above the grant price. These options come in two flavors: qualified and non-qualified. Qualified options are usually called Incentive Stock Options. The important difference between the two is the way they are taxed.
What is performance share?
Performance Shares are similar to RSUs, but are tied to company performance. If the company meets the specified performance target on a specific date in the future, the employee earns the reward. These are also taxed like wages. Employee Stock Purchase Plans allow the employee to put aside some of their wages to buy company stock at a discount.
Do you pay taxes on shares purchased?
There is no tax when the shares are purchased. At the time the shares are sold part of the gain is taxed as ordinary income, and part at more favorable capital gains rates. In a divorce it is important to consider the economic treatment of rewards, as their net value can vary greatly. Let’s look at an example:
What is an RSU in stock options?
RSU, the execution of the option is restricted. As the RSUs are issued in units that do not stock format having a value attached to a specified no of shares. That means after the vesting period the employer gets the equivalent shares. These limits which work as restrictions are attached to the vesting period.
What is the difference between stock options and employee benefits?
Some of the major key differences are mentioned below: Stock options are simply stocks that are bought and sold by one entity to the other entity with no compulsion of the time to execute just before the expiration dates . When stock options are attached to the employee benefits plans that means the company has a contract to purchase ...
How long can an employee have stock options?
It means after a service of 3 years an employee can execute 30 percent of the allocated stocks in the plan. After the vesting period is over in stock options, the employees have an option to buy or sell the stocks. After the end of the vesting period, stock options behave as common stocks.
What does it mean when stock options are attached to employee benefits?
When stock options are attached to the employee benefits plans that means the company has a contract to purchase a fixed amount of shares at a fixed time with a fixed stipulated price. This is like additional incentives for the employees so that the company can attract the best employees and increase productivity.
Why are options more valuable?
If the analysis shows that the company will be doing great in the future, then stock options are more valuable because in the future the market price of the stock will be higher because of the performance of the company and the grant price at the initiation would be smaller.
Do employees have rights in restricted stock options?
In stock options, full shareholders’ rights are given to the employees. In restricted stock option units, employees have very limited rights .
Is RSU risky?
Deciding whether to go with RSU or stock options, one has to do a detailed difference between the advantages and disadvantages of both of them. Generally, the RSU is considered to be less risky because here the purchase doesn’t happen as one does not have to spend on the purchase of stocks.
What is stock option?
Stock options are the right to buy a certain number of shares at a certain price in the future , with the employee benefiting only if the stock price then exceeds the stock option price.
How do stock options work?
Stock options are normally restricted by a market standoff provision, which restricts the sale of shares for a certain period of time after an initial public offering (IPO) to stabilize the market price of the stock.
What is restricted stock?
Restricted shares and stock options are both forms of equity compensation that are awarded to employees. Restricted shares represent actual ownership of stock but come with conditions on the timing of their sale. Stock options are the right to buy a certain number of shares at a certain price in the future, with the employee benefiting only if ...
What happens to an employee's shares after a merger?
That means that an employee's shares become unrestricted if the company is acquired by another and the employee is fired in the restructuring that follows. Insiders are often awarded restricted shares after a merger or other major corporate event.
Do restricted shares have to be vested?
However, they are usually vested. That is, when restricted shares are given to an employee, it is on condition that the employee will continue working at the company for a number of years or until a particular company milestone is met. This might be an earnings goal or another financial target.
What is an RSU grant?
Unlike RSAs, when shares are “owned” by the employee on the grant date, an RSU is a promise from the company to give an employee shares at a later date. The date you actually receive your RSU shares can be a vesting date, a liquidation event, a specified date in the future, or some combination of these.
Why is restricted stock considered restricted stock?
With restricted stock, you own the shares from the day they are issued. But the stock is “restricted” stock because you still need to earn them. The most common restrictions are time-based and involve a vesting schedule, which means you earn them over time. This incentivizes employees to stay with the company.
Why is Sean's taxable gain zero?
After this window passes Sean will not be able to file the election. Sean’s taxable gain is zero at grant because the FMV is the same as what he paid ($1). By filing an 83 (b) election, Sean is choosing to recognize ordinary income tax up front. Since the taxable gain is $0, Sean pays no ordinary income tax.
When are RSA shares given?
RSA shares are given to employees on the day they are granted. RSAs are typically issued to early employees before the first round of equity financing, when the FMV of common stock is very low. RSAs provide the individual the right to purchase shares at FMV, at a discount, or at no cost on the grant date.
What happens to restricted stock when an employee leaves?
If the employee leaves, the company can repurchase the stock. There are two main types of restricted stock: Restricted Stock Awards (RSAs) and Restricted Stock Units (RSUs).
What are the two types of taxes for equity compensation?
There are two types of tax to consider with equity compensation: ordinary income tax and capital gains tax. The main thing to remember is that the capital gains tax rate is generally lower than the ordinary income tax rate.
Is a RSA eligible for 83 B?
Taxes: RSAs are eligible for 83 (b) elections. RSUs are not eligible for 83 (b) elections and are taxed when they vest. Timing is key with RSAs and RSUs – when they vest, when you sell, and when you can expect to receive them are important factors in determining the full value of these equity compensation awards.
What is an RSU?
An RSU is a promise from your employer to grant you shares of the company stock in the future if certain restrictions are met, often at no cost to you. Each grant of RSUs also typically has its own vesting schedule. Tax Implications. A major difference between NQSOs and RSUs is the way in which they are taxed.
What is a non qualified stock option?
What Are Non-Qualified Stock Options? NQSOs give you the right to buy a certain number of company shares, at a specified price (known as the exercise price) during a window of time (usu ally 10 years). Typically, your right cannot be exercised until you have satisfied the vesting requirements set forth by the company.
Do RSUs have flexibility?
RSUs offer limited flexibility in comparison to NQSOs. With NQSOs, you have some control over the timing of the exercise and thus when the taxes from the options are triggered. In the case of RSUs, however, the entire value of RSUs must be reported as ordinary income in the year of vesting.
