
For RSUs, the cost basis should be the fair market value (FMV A full motion video (FMV) is a video game narration technique that relies upon pre-recorded video files (rather than sprites, vectors, or 3D models) to display action in the game. While many games feature FMVs as a way to present information during cutscenes, games that are primarily presented through FMVs are referred to as full-motion video games or interactive movies.Full motion video
What is the cost basis for selling RSU shares?
When you sell the remaining shares, use $30.53 per share as your cost basis. Reply SGKsays March 14, 2012 at 3:28 pm Great article on RSU’s.
Are restricted stock units (RSUs) worth anything?
Restricted Stock Units: The Essential Facts 1 Restricted stock units (RSUs) are a way your employer can grant you company shares. 2 RSUs are nearly always worth something, even if the stock price drops dramatically. 3 RSUs must vest before you can receive the underlying shares. Job termination usually stops vesting. More ...
How are RSU stock awards taxed?
Stock awarded as part of an RSU plan is taxed as ordinary income at the time the award, as determined by the vesting schedule. For tax purposes, the stock is assigned a fair market value at the time they become vested.
What is the difference between stock options and an RSU?
RSUs are also less risky than stock options. Stock options require an increase in a company’s stock price to have value. With a stock option, if the price of the shares stays at the grant price or even drops in value, your options will be worth nothing.
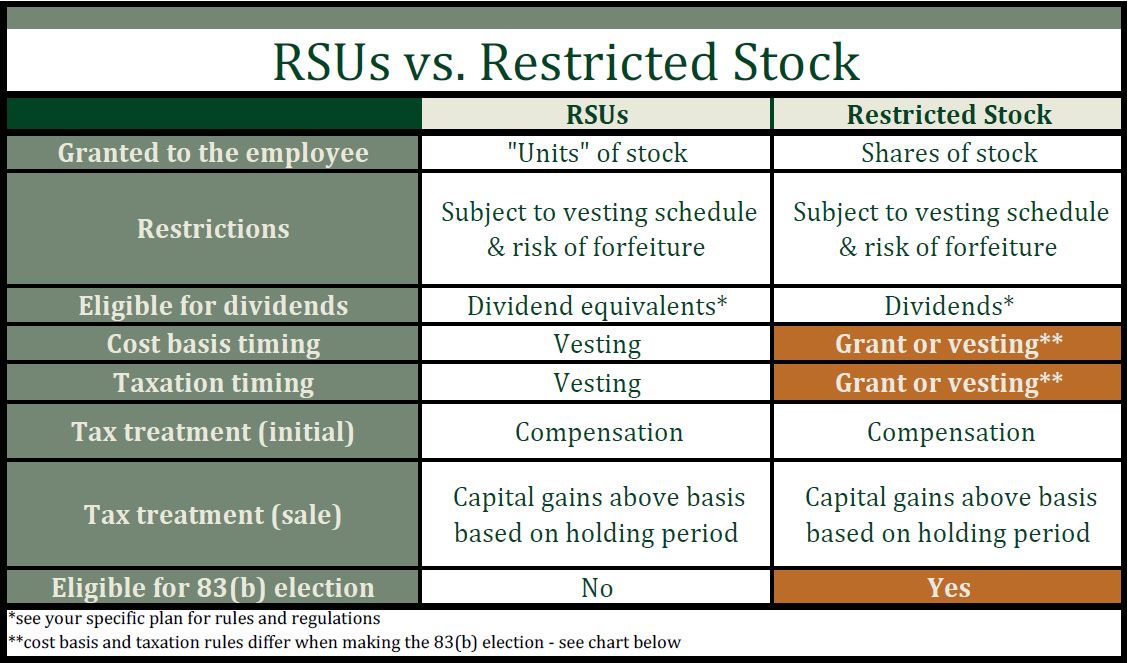
Do I need to adjust cost basis for RSU?
Restricted Stock Units (RSUs) Non-covered: cost basis not reported to IRS FMV* You will not need to adjust your cost basis, but you will need to use Form 8949 to report cost basis and the proceeds for these transactions.
How are RSUs taxed when sold?
RSUs are taxed as income to you when they vest. If you sell your shares immediately, there is no capital gain tax, and you only pay ordinary income taxes. If instead, the shares are held beyond the vesting date, any gain (or loss) is taxed as a capital gain (or loss).
Why are RSU taxed twice?
Are RSUs Taxed Twice? No, RSUs are not taxed twice. However, it can seem like RSUs are taxed twice if you hold onto the stock and it increases in value before you sell it. RSUs are taxed at the ordinary income tax rate when they are issued to an employee, after they vest and you own them.
How are capital gains calculated on RSU?
You can calculate capital gain by deducting the market value of your RSU shares on the vesting date from the selling price. For instance, you sold your 200 shares above which were valued at $10 on the vesting date at $15.
How do I avoid capital gains tax on RSU?
The first way to avoid taxes on RSUs is to put additional money into your 401(k). The maximum contribution you can make for 2021 is $19,500 if you're under age 50. If you're over age 50, you can contribute an additional $6,000.
Why are RSU taxed so high?
Taxes are usually withheld on income from RSUs. Since RSUs amount to a form of compensation, they become part of your taxable income, and because RSU income is considered supplemental income, the withholding rate can vary from 22% to 37%.
Should you sell RSU as soon as they vest?
Sell Them As Soon As They Vest Because RSUs are taxed at the time they vest, there's no tax advantage for holding on to them. Moreover, investments that are diversified—spread out over many different stocks or bonds—perform better, on average, than investments that are concentrated in one stock.
What should I do with my restricted stock units?
Once the grant vests you own the shares outright, at least in a public company. You can hold, sell, donate, or gift the shares as you wish (though you always need to avoid insider trading by not selling when you know important nonpublic information about the company).
Are RSU taxes reported on W-2?
RSUs are considered part of your wages, so they're also already included in Box 1 of your W-2, which reports your wages.
How do you calculate cost basis for restricted stock units?
Your cost basis is the amount your employer included on your W-2, which is the closing price on the vesting date times the number of shares vested.
How much are RSUs taxed when vested?
To cover the tax payment when the RSUs vest, your employer must withhold taxes on your behalf: Federal income tax: 22% (37% once your supplemental wages exceed $1,000,000) California income tax: 10.23%
How much tax do you pay on vested shares?
In other words, any share-price appreciation that occurs between when the restricted shares are awarded to you and when they become vested will be taxed at your regular federal rate, which under the current rules could be as high as 37% plus 3.8% for the Medicare employment tax on compensation income plus state income ...
Why is there no 1099B?
The reason there is no 1099B is because the stock wasn't sold, as you indicate, but was "withheld" by your employer. That amount is divided in some ratio and is put in different buckets, like Federal, State, Medicare etc withholding.
Can you use 1099-B for stock sale?
If not use ' Short Term'. This should be on your 1099-B. If you determine your correct Cost Basis, you can enter your 1099-B as a regular stock sale.
How are RSUs taxed?
With RSUs, you are taxed when the shares are delivered, which is almost always at vesting. Your taxable income is the market value of the shares at vesting. You have compensation income subject to federal and employment tax (Social Security and Medicare) and any state and local tax. That income is subject to mandatory supplemental wage withholding. Withholding taxes, which for U.S. employees appear on Form W-2 along with the income, include the following: 1 federal income tax at the flat supplemental wage rate, unless your company uses your W-4 rate 2 Social Security (up to the yearly maximum) and Medicare 3 state and local taxes, when applicable
What is restricted stock unit?
Restricted stock units (RSUs) are a way your employer can grant you company shares. RSUs are nearly always worth something, even if the stock price drops dramatically. RSUs must vest before you can receive the underlying shares. Job termination usually stops vesting.
How long does a vesting schedule last?
Example: You are granted 5,000 RSUs. Your graded vesting schedule spans four years, and 25% of the grant vests each year.
Is a RSU worth anything?
Unlike stock options, which can go "underwater" and lose all practical value with a falling stock price, RSUs are almost always worth something, even if the stock price drops dramatically.
What is an RSU?
An RSU is only one of many types of compensation that a company might use as an employee incentive. Some companies may elect to use RSUs, while others may choose stock grants or another form of equity compensation. It is up to you to decide which form is best for your company and your employees.
What is an RSU plan?
With an RSU plan, the company offers the employee an economic interest in the company stated as a specific number of shares of company stock. The stock is not immediately given out to the employee, however, but is instead awarded at a future time upon completion of a stated goal or on reaching a stated date.
What are the disadvantages of using RSUs?
They include: Your stock may not increase in value sufficiently to reward employees. RSUs are not always a sufficient incentive to attract the right talent.
What is graduated vesting?
Graduated vesting refers to vesting schedules under which stock to be awarded as part of an RSU plan vests in stated amounts at stated intervals throughout the vesting period. As an illustration, if an RSU plan calls for the employee to become 100% vested after five years of employment, he or she may become partially vested at stated intervals during the five year period, as laid out in the RSU plan. For example, the RSU plan may call for graduated vesting as follows: 10% after one year; 30% after two years; 50% after three years; 80% after four years; 100% after five years.
Why are RSUs important?
RSUs are a great tool for companies seeking to hire highly talented and in-demand employees by offering them the additional incentive of taking part in the company’s growth. Additionally, RSUs are converted to stock at a future date according to a vesting schedule, and therefore provide the company with a level of security in terms of retaining top employees because those employees are likely to remain with the company until the stock benefit is fully vested.
How long does a RSU vest?
The value of the stock may not be as great as anticipated. RSUs typically do not fully vest for five years, meaning that if you leave the company before that time, you will lose your ability to claim some or all of the stock shares under your RSU plan.
What is stock grant?
Stock grants refer to the issuance of an award, such as a stock option, that is provided to key employees as part of a stock plan. Stock grants allow the employee to purchase a specific number of shares of company stock at a specific price (known as the grant price) as stated in the grant. Restricted stock awarded to employees is a form ...
How does an RSU work?
An RSU is offered to an employee, generally as an incentive to stay with the company and help the company perform better. If the company does well, the stock price will increase, which helps the employee’s RSUs increase in value. It’s a win-win.
Why do companies give restricted stock units?
RSUs are a compensation and retention tool for employers. The benefits of a company issuing these is that employees who have shares in the company they work for are more likely to perform in a way that would help the company grow and do better, and in turn that would make their shares do better.
What are the advantages of restricted stock units?
The advantages of a restricted stock unit is that the employee gets to share in the growth of the company they spend their time working for. As the shares vest, the employee can then either keep them or sell them.
What are the disadvantages of restricted stock units?
One disadvantage of having RSUs as a form of compensation is that the money is not yours until the shares vest. If you leave the company or are fired before your shares are fully vested, then those shares go back to the company. You can’t count on the money in the RSU account until it is vested.
How do RSUs differ from stock options?
Stock options give an employee the right to purchase company stock at a determined price within a specified window of time. If the company stock increases from the time of offer to the time the stock options vests, an employee may be able to purchase the stock at a discounted price from the actual market value at time of purchase.
Is it better to take RSU or stock options?
This really depends on the situation. There are pros and cons to both stock options and RSUs.
What should I do with my restricted stock units?
This depends. If you are vested in the RSUs, that means you own the stock. In general, owning a high concentration of one company in your portfolio puts you at higher risk than a diversified portfolio would. If your RSUs are a large part of your portfolio, selling some to diversify may be a good idea.
