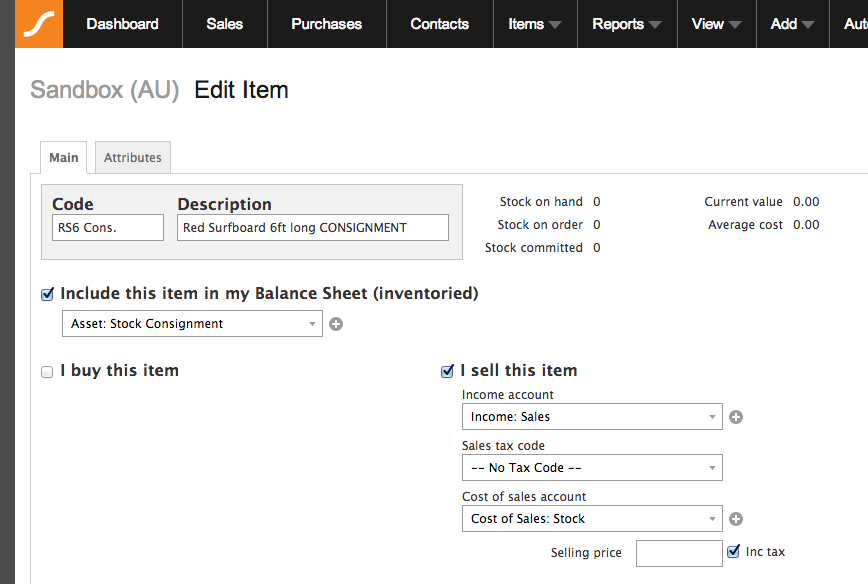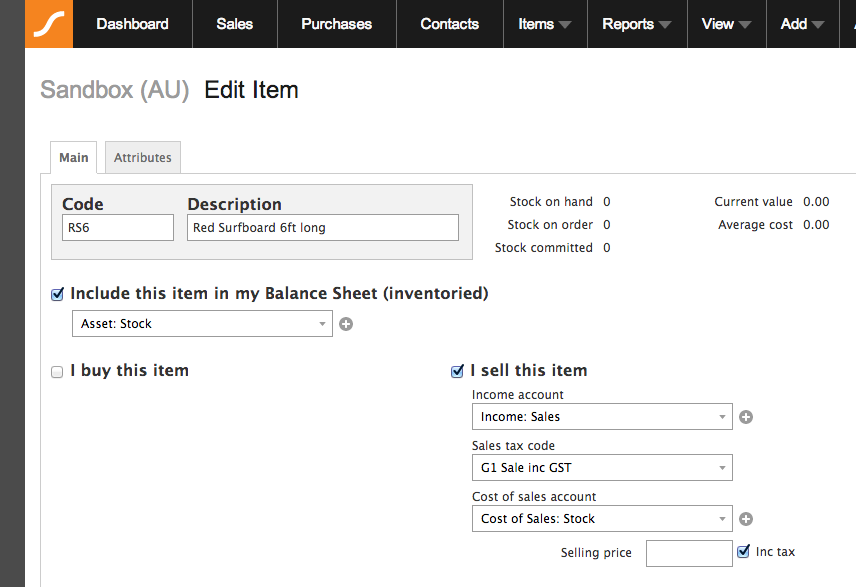
What is meant by consignment stock?
Nov 19, 2021 · Consignment inventory, otherwise known as consignment stock, is a business model. It works by a consignor (either a vendor or a wholesaler) agrees to give their goods to a consignee (typically a retailer) without the consignee paying for the goods upfront. The consignor will still be the owner of the goods, and the consignee will only pay for the goods when they …
What are the drawbacks of consignment stocks?
Just to be clear, consignment inventory is inventory that is in the possession of the retailer, but is still owned by the supplier. From an accounting point of view, such goods have neither been sold nor are a part of their owner’s inventory, which can land both parties in …
What is the stock we maintain in consignment process?
Consignment inventory is a supply chain strategy or business agreement in which the consignor (i.e., wholesaler, supplier, manufacturer) gives the goods to a consignee (i.e., the retailer) to sell. The consignor still owns the products and the consignee …
Does consignment stock have to be reported as inventory?
Jun 15, 2015 · Consignment stock is inventory that is in the retailer’s possession but is still legally owned by the supplier. It occurs where the supplier has placed some products in the retailer’s control and allows them to sell or use the goods directly from their stock. Only once the product has been consumed or resold by the retailer is the inventory then purchased from the …

What does consignment stock mean?
The consignment stock is stock legally owned by one party, but held by another, meaning that the risk and rewards regarding to the said stock remains with the first party while the second party is responsible for distribution or retail operations.
How does consignment stock work?
With consignment inventory, the producer of the stock retains ownership until the product is sold to the consumer or consumed in the business. At the same time, the retailer buys the product from the producer. The retailer or user doesn't pay for the product until it's sold.Mar 8, 2019
What are the benefits of consignment stock?
Consignment Sales - 5 Reasons to Sell on ConsignmentSave on inventory costs. This is definitely one for the retailers! ... It gets the product in front of customers. Here's one for the suppliers! ... Restock as it sells. ... Reduces risk for new products or sales channels. ... Helps nurture a better supplier / retailer relationship.Aug 19, 2013
What is consignment with example?
Consignment is an arrangement in which goods are left with a third party to sell. The party that sells the goods on consignment receives a portion of the profits, either as a flat rate fee or commission. Selling via a consignment arrangement can be a low-commission, low-time-investment way of selling items or services.
Who uses consignment stock?
Consignment inventory is a business arrangement where the consignor (a vendor or wholesaler) agrees to give their goods to a consignee (usually a retailer) without the consignee paying for the goods upfront – the consignor still owns the goods, and the consignee pays for the goods only when they actually sell.Jul 14, 2017
Who is responsible for consignment stock?
Consignment goods are stored in the warehouse of the retailer, but ownership of these goods is retained by the consignor. The responsibility for maintaining and selling them falls on the consignee. The consignor also counts these goods in their physical counts of inventory.
What is the difference between sale and consignment?
In sale, the seller sends the goods to the buyer only after getting an order from the latter. In consignment, the risk involved in the goods sent remains with the consignor till the consignee sells the goods. In the case of a sale, the risk of the goods sold is immediately transferred to the buyer.
Why do we do consignment process?
It has advantages for both sides. The consignor can establish a comprehensive long-term business relationship and the consignee can reduce the capital lock-up having at the same time immediate availability of the goods. The consignment process typically has a negotiated a long-term contract (1) as a basis.May 7, 2021
What is consignment sales process?
Consignment Process is where product are stored at the customer location but the owner of this product is still company. Customer stores the consignment stock at their own a warehouse. Customer can consume product from warehouse at any time and customer billed for product for actually quantity consumes.Feb 26, 2022
Is consignment a good idea?
However, consignment deals are a good option if your business is new and unproven. Consignment deals can also be a good opportunity to get your foot in the door with a retailer. They may not take the risk of buying your products wholesale when they're unfamiliar with them and your business.
Who owns consigned?
the consignorConsigned goods are products not owned by the party in physical possession of them. The party holding the goods (the consignee) has typically been authorized by the owner of the goods (the consignor) to sell the goods.Mar 26, 2022
How do I sell on consignment?
Here's how consignment works: The consigner will keep ownership until the product has been sold by the retailer. The retailer (consignee) will agree to sell the item for a fee at their store. If the goods are sold by the retailer, they will pay you the fair price percentage of how much it sold.Apr 26, 2021
What is consignment in retail?
The retailer sells the goods on behalf of the supplier, usually according to the supplier’s instructions. This arrangement, if handled well, can be the best of both worlds.
Why sell on consignment?
There are multiple benefits to selling goods on consignment especially if you are just starting out in the industry and getting your products off the ground. It saves holding costs (drastically) and improves cash flow for consignors.
How does consignment work?
The consignment system promotes supplier-consigned inventory, ruling out the need to coordinate shipment of inventory to the warehouse, and then having to dispatch the products to each and every one of your retailers. Consigning renders the first step unnecessary, allowing goods to reach retailers directly from the manufacturing or assembly plants. It saves time and labor, meaning that products reach retailers at a faster pace and with less hassle for wholesalers.
What is the main concern of consignment inventory?
The main concern is the lack of visibility on consignment inventory, especially slow and dead stock, for consignors. Once the goods are out of your hands, it is easy to assume that retailers will bear full responsibility and take care of the sales process moving forward, ensuring that all of your products get sold.
What can a retailer focus on?
A retailer can just focus on selling the product, instead of getting tangled up with in-house design, sourcing, and production of goods. You can zero in on just the sales process without having to worry about the production end of things, leading to greater specialization in terms of roles and job tasks.
Who is involved in a consignment deal?
Parties Involved in a consignment deal: The wholesaler - consignor. The retailer - consignee. In this supply chain management strategy, the consignor retains legal ownership of the merchandise, and the consignee is not required to pay for the goods until after they have been sold.
Is consignment better than wholesale?
And consignment margins are almost always better than margins when selling wholesale.
What is consignment inventory?
Consignment inventory is a supply chain strategy or business agreement in which the consignor (i.e., wholesaler, supplier, manufacturer) gives the goods to a consignee (i.e., the retailer) to sell.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of consignment inventory?
Consignment inventory has pros and cons for vendors and retailers alike. Let’s break them down below.
How consignment inventory works
So, how exactly can you make consignment inventory work in your store? While every arrangement will vary, strong consignment agreements typically take place when you implement these best practices.
How to manage consignment inventory
At this stage, you already have your agreement in place and are ready to sell the consigned goods in your retail store.
The bottom line
Consignment inventory can be highly beneficial to retailers and suppliers alike. When you have a mutually beneficial agreement and are using the right tools to manage inventory, your consignment efforts will have a higher chance of success.
What is consignment stock?
Consignment stock is inventory that is in the retailer’s possession but is still legally owned by the supplier. It occurs where the supplier has placed some products in the retailer’s control and allows them to sell or use the goods directly from their stock.
Why do retailers need consignment stock?
One obvious advantage to retailers of holding consignment stock is the opportunity to save on inventory costs. In not having to pay the supplier until the goods are sold, the business is able to use this capital on other projects and benefit from the increase in cash flow. The major advantage to the supplier is that they are able to get a product that they believe they can sell in front of end-users, as well as creating additional exposure within their target market.
Why is consignment inventory better?
A benefit for both the retailer and supplier when it comes to consignment inventory is that it generally reduces the lead-time on products.
Does a retailer have to tie up their capital in purchasing consignment inventory?
Only once the product has been consumed or resold by the retailer is the inventory then purchased from the supplier. So while the retailer still incurs costs related to storing and maintaining the stock, they do not have to tie up their capital in purchasing it . In the right situation, consignment inventory can have significant benefits ...
What is Consigned Inventory?
Consigned inventory is different than the traditional inventory in your business’s warehouse or stockroom.
How Does Consignment Work?
As you can see in the previous section, consignment inventory requires at least two party’s involvement to function. With multiple parties, businesses, or individuals involved, things can get complicated. However, the core idea of how consignment works is simple.
Typical Models for Consignment Inventory
Individual parties can structure their consignment deals in any way they choose. Still, two basic concepts provide the framework for these types of agreements: ownership models and tracking models. Let’s talk about them.
When Does Using Consignment Inventory Make Sense?
At this point, you may be wondering if consigning inventory is the right approach for your business. There’s no one size fits all answer, but here are some things to consider.
Pros and Cons of Consignment Inventory
In this section, we’ll break down the pros and cons of consignment inventory so you can make an informed decision about whether or not this approach is right for your business.
Best Practices for Consignment Inventory
The easiest way to avoid the cons of consignment inventory is by utilizing best practices.
Benefits of Using Inventory Management Software for Consignment Inventory
Finally, here are a few words about how inventory management software can make your consignment inventory initiative easier to manage.
What is consignment in business?
Consignment is when one business (consignee) or store sells goods on behalf of another (consignor). These two parties may be a retailer and wholesaler, two retailers, or even a retailer and an individual. Sales revenue is split according to a contract signed between the two or more parties.
What is a consignment contract?
A consignment stock contract, or consignment agreement, is a legal document outlining the agreement between a consignee and consignor in regard to consignment goods . This contract outlines the requirements for storing, transferring, and selling the consignment inventory. It also includes the amount of profits received by each party when the goods are sold.
What is the difference between vendor managed inventory and consignment inventory?
The supplier and retailer both stand to gain more in both methods by building a strong relationship. However, consignment inventory belongs to the supplier while vendor managed inventory belongs to the seller. This means suppliers have more skin in the game with a consignment model.
What is consignment inventory management?
A consignment inventory management strategy revolves around a supplier and retailer working together to sell the supplier's goods. This involves shared sales information and profit as well as the use of a dedicated consignment warehouse. The supplier must track product trends, find good bulk shipping providers if necessary, ensure stock levels are optimal for the retailer to sell.
Why is consignment important?
Sales increase when customers are offered the broadest product assortment. Consignment gives them access to a variety of unique products for minimal cost. Consignment is a great way to find products for subscription boxes as well.
What is consigned inventory?
Consigned inventory is the items held and sold by one business for another. Consigned inventory is held in warehouses intended only for inventory owned by the supplier for sale by the retailer.
Where are consignment goods stored?
Consignment goods are stored in the warehouse of the retailer , but ownership of these goods is retained by the consignor. The responsibility for maintaining and selling them falls on the consignee. The consignor also counts these goods in their physical counts of inventory.
What is consignment stock?
A consignment stock is made up of goods that are legally owned by one party called the consignor but are to be sold, shipped or held in store by an agent or consignee. This type of inventory is prevalent among manufacturing concerns.
What are the benefits of a consignment agreement?
First, the primary benefit that can be derived from a consignment agreement is that it allows the consignee to save money on inventory costs. As the consignee, you do not need to put money on the goods that you sell. You pay the consignor only after you have sold the merchandise.
Why do you pay consignors?
This could mean improved cash flow on the part of the consignee. Next, consignment can actually save you time because you do not have to wait for new inventory every time you run out of stock.
When will the person that consigned the goods replenish their inventory?
Typically, the person or company that consigned the goods will automatically replenish your inventory right after you sell some or all of the consigned goods. It is in the best interest of the consignor to keep the agent well-supplied.
Do you have to pay for goods after consignment?
Under a consignment arrangement, the consignor retains legal ownership of the merchandise, and the consignee is not required to pay for the goods until after they have been sold. The consignee can even decide to return any leftover stock without worrying about monetary repercussions.
Is a consignment stock disadvantageous?
So, a consignment stock may become disadvantageous if it brings about discrepancies in the records of both consignor and consignee. For the consignee, any misplaced item could mean paying for something ...
What is consignment inventory?
It’s called consignment inventory, and it’s an underutilized way to create a win-win partnership between suppliers and retailers as long as they’re both willing to share the risks – and rewards. To help you learn how to make consignment inventory work for you, we’ll go over what it is, what are its pros and cons, and how to implement it wisely.
Why do retailers draw upon consignment inventory?
1. Lower Cost of Ownership. Retailers are able to draw upon consignment inventory to use it without owning it , which lowers their total cost of ownership and holding costs. 2.
Why does a retailer not have to worry about excess holding costs?
The retailer doesn’t have to worry about excess holding costs since the vendor still owns the stock until it’s sold. This means the retailer can hold more consignment inventory at a lower cost and not have to worry about stockouts or buying goods that won’t sell in their store.
What happens if a retailer holds inventory longer?
The longer the retailer holds the inventory, the higher the chances of it getting damaged during normal business operations (which usually means they’re obligated to buy it). 2. Increased Chance of Stock Count Errors. Consignment inventory should be “invisible” to most employees.
What are the pros and cons of selling on consignment?
Pros for Vendors. 1. New Markets. As we pointed out in our women’s watch example, selling on consignment allows vendors to enter new markets at minimal cost to the retailers, which makes retailers more likely to carry the vendors’ inventory. 2.
What happens if a vendor offers a watch on consignment?
If the vendor offers their watches on consignment, the retailer agrees to stock the watches in their store and only pay for the ones they sell. This arrangement can be hugely beneficial for both parties, but it also carries with it some major risks.
What makes a vendor's cashflow uncertain?
Uncertain Cashflow. Vendors won’t receive payment until after some or all of the goods are sold by the retailer. Goods that aren’t sold are usually returned to the vendor. This makes cashflow uncertain and volatile since they don’t know when or how much of the goods will be sold.
What is consignment deal?
Consignment is an arrangement in which goods are left in the possession of an authorized third party to sell. Typically, the consignor receives a percentage of the revenue from the sale (sometimes a very large percentage) in the form of commission . Consignment deals are made on a variety of products, such as artwork, clothing and accessories, ...
What is a consignment arrangement?
The party that sells the goods on consignment receives a portion of the profits, either as a flat rate fee or commission. Selling via a consignment arrangement can be a low-commission, low-time-investment way of selling items or services. Most consignment shops and online dealers will offer terms, but some are willing to negotiate.
What is a consignment payment structure?
Consignment Payment Structure. A person wishing to sell an item on consignment delivers it to a consignment shop or a third party to do the selling on their behalf. Before the third party takes possession of the good, an agreement must be reached as to the revenue split when the item is sold.
What is the millennial generation known for?
The millennial generation, in particular, is known for its frugal shopping habits, which include eschewing high-end stores and designer boutiques in favor of bargains found at thrift and consignment shops.
What are some examples of consignment?
Another example of consignment would be Bethany visiting her grandmother's house and finding an old case full of clothes from the 1940s. She keeps a few pieces that she likes and decides to sell the rest. She takes the clothes to a thrift store to sell the clothes on consignment.
How many pieces of art do artists have to sell?
An artist has five large pieces of artwork to sell but has no place to showcase the work for prospective buyers. The artist decides to employ an art gallery to show and sell their works of art. The gallery does not charge the artist a fee for the wall space but will charge a sales commission for any works sold, which is incorporated into the price.
Is eBay a consignment shop?
To a certain degree, online companies such as eBay are consignment shops; for a percentage of the sale, they offer people a marketplace to exhibit and sell their wares. This removes the necessity for an individual to have to create their own website, attract customers, and set up payment processes.