Why would a stock have no par value?
Jan 02, 2022 · In common stock trading, par value usually plays a negligible part. Companies set a par value for their common stock because they are often legally required to do so. In case of …
What does par value per share of common stock represent?
Feb 09, 2022 · As with bonds and preferred stock, the final market value of a common stock has no relationship to its par value. For example, the par value of common stock from Apple is …
What does "par value" mean in stocks?
What is the current price of the common stock?
How is par value of common stock determined?
What does $1 par value mean?
What is a good par value for stock?
What does $10 par value mean?
Is closing price a stock or bond?
Why would a stock have no-par value?
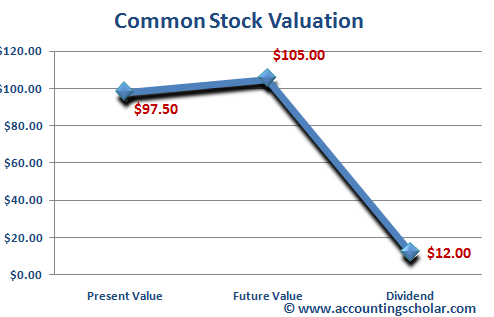
Is par value the same as future value?
Why is par value low?
What is par value stock?
Par value stock is a type of common or preferred stock having a nominal amount (known as par value) attached to each of its share. Par value is the per share legal capital of the company that is usually printed on the face of the stock certificate. It is also known as stated value and face value. A company is free to choose any amount as ...
How many ways can a stock be issued at par value?
The par value stock can be issued in three ways – at par, above par and below par. A brief explanation and journal entries for all the situations are given below:
What does it mean when a stock is issued below par?
When stock is issued at a price lower than its par value, it is said to have been issued below par. In such an issue, the cash account is debited with the total amount of cash received, discount on issue of capital stock account is debited with the difference between amount received and the par value of shares issued and the common stock account is credited with the par value of the shares issued. The journal entry for such an issue is given below:
What happens when stock is issued above par?
When stock is issued at a price higher than its par value, it is said to have been issued above par. When stock is issued above par, the cash account is debited with the total amount of cash received , capital stock account is credited with the total par value of shares issued and an account known as additional paid-in capital or capital in excess of par is credited with the difference between cash received and the par value of shares issued. This information is summarized in the form of the following journal entry:
What is par value in stocks?
Par value is the face value of a security. Both stocks and bonds have a par value, which is set by the issuer of the security. Par value remains fixed for the life of a security, unlike market value, which fluctuates regularly. Because it influences interest and dividend payments, it’s a key factor for understanding your return on investment in ...
What is preferred stock par value?
Par Value for Preferred Stock. It’s helpful to think of preferred stock as a hybrid of bonds and common stock. Preferred stock represents equity in a company—a portion of ownership, like common stock. In addition, though, you are entitled to fixed dividend payments, like a bond’s fixed interest payments.
Why is par value important?
Par value remains fixed for the life of a security, unlike market value, which fluctuates regularly. Because it influences interest and dividend payments, it’s a key factor for understanding your return on investment in bonds and preferred stock.
What happens when you buy a bond?
When you buy bonds, you’re lending money for a set amount of time to an issuer, like a government, municipality or corporation. The issuer promises to repay your initial investment—known as the principal—once the term is over, as well as pay you a set rate of interest over the life of the bond. The principal in a bond investment may ...
What is YTM in bond?
YTM factors in the market price of a bond, its par value as well as any interest you may earn along the way. The YTM rate is often presented as a percentage. For example, a bond’s YTM may be 10%, meaning you can expect your money to grow by 10% when you consider the interest you’ll earn as well as the return of the par value.
What is preferred stock?
It’s helpful to think of preferred stock as a hybrid of bonds and common stock. Preferred stock represents equity in a company—a portion of ownership, like common stock. In addition, though, you are entitled to fixed dividend payments, like a bond’s fixed interest payments.
Does common stock pay dividends?
In addition, common stock’s par value has no relationship to its dividend payment rate. Instead, common stock dividends are generally paid as a certain dollar value per share you own. Many people will then divide this value by the cost of a share to create its dividend yield.
What is no par value stock?
No Par Value Stock. Some states allow corporate stock to be issued with no par value. In this event, "no par value" should be printed on the stock certificates. Purchasers of no par value shares don't have to worry about being liable to corporate creditors if they pay too little for the shares. For accounting purposes, the entire purchase price ...
Why is par value misleading?
The term par value can be misleading because it has nothing to do with how much a corporation's shares are actually worth. It is only a minimum legal value. A corporation's board of directors may require investors to pay far more than par value for the corporations' shares.
What is par value of shares?
What is Par value of Share? Par value of shares also known as the stated value per share is the minimal shares value as decided by the company which is issuing such shares to the public and the companies then will not sell such type of shares to the public below the decided value.
What does "no par value" mean?
That means corporations are not having any kind of legal obligations to their debt holders. Though the par value usually is so low that no par value also won’t provide much of the difference.
What is shareholder equity?
The broad classification Shareholder’s equity is that the first one is “ paid in capital. Paid In Capital Paid in Capital is the capital amount that a Company receives from investors in exchange for the stock sold in the primary market, including common or preferred stock.
Step 1
Look through the company's financial statements for the balance sheet. It should have three sections: assets, liabilities and shareholders' equity. Go to the shareholders' equity section of the balance sheet. Sometimes the company uses the term "stockholders' equity," which means the same thing.
Step 2
Identify the line referring to the company's issuance of common stock. It will say something such as "book value of common shares outstanding" or "book value of common shares." This line will also provide the number of shares outstanding and the par value of the common stock, if any.
Step 3
If the par value is not explicitly stated, divide the book value of the common shares outstanding by the number of common shares outstanding. The result is the par value for one share of that company's common stock.
What is Par Value for Stock?
Par value is the stock price stated in a corporation’s charter. The intent behind the par value concept was that prospective investors could be assured that an issuing company would not issue shares at a price below the par value.
What is Par Value for Preferred Stock?
The par value of a share of preferred stock is the amount upon which the associated dividend is calculated. Thus, if the par value of the stock is $1,000 and the dividend is 5%, then the issuing entity must pay $50 per year for as long as the preferred stock is outstanding.
What is Par Value for Bonds?
The par value of a bond is usually $1,000, which is the face amount at which the issuing entity will redeem the bond certificate on the maturity date. The par value is also the amount upon which the entity calculates the interest that it owes to investors.
Example of Par Value for Bonds
For example, ABC Company issues bonds having a $1,000 par value and 6% interest rate. An investor later buys an ABC bond on the open market for $800. ABC is still paying $60 in interest every year to whoever holds the bond. For the new investor, the effective interest rate on the bond is $60 interest ÷ $800 purchase price = 7.5%.
What is par value?
Definition of Par Value. Par value is a per share amount that will appear on some stock certificates and in the corporation's articles of incorporation. (Some states may require a corporation to have a par value while others states do not require a par value.) (Par value can also refer to an amount that appears on bond certificates.)
Who is Harold Averkamp?
Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as a university accounting instructor, accountant, and consultant for more than 25 years. He is the sole author of all the materials on AccountingCoach.com. Read more about the author.
