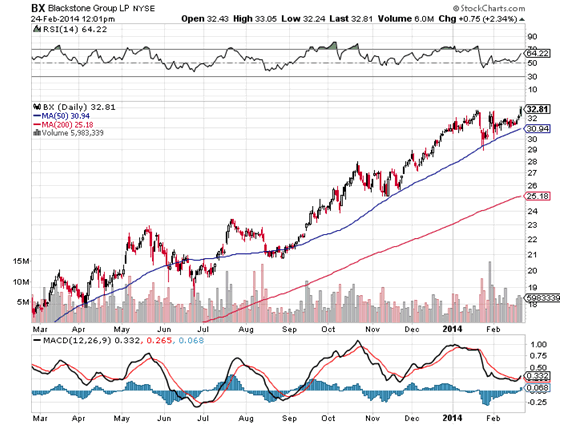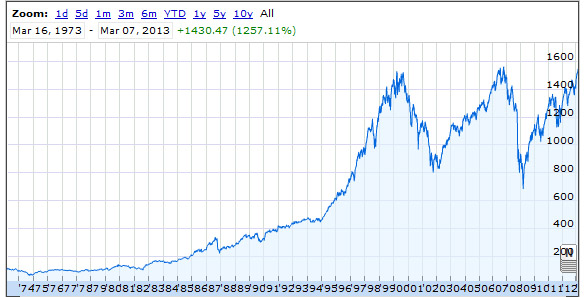
What is an example of a CD investment?
With a CD ladder, you divide your initial investment into equal parts and invest each portion in a CD that matures every year. For example, say Leo has $10,000. To build a CD ladder, he invests $2,000 each in a 1-year, 2-year, 3-year, 4-year and 5-year CD.
Are CDs worth it?
While traditional CDs may not be worth it in the current market, you may want to explore some alternative options for CDs. For example, Ally Bank offers a CD that gives you the option to request a rate increase that adjusts to the bank’s updated rate (once for the two-year CD and twice for the four-year product).
How to invest in CDs?
- Interest rate and APY. Similar to other types of savings accounts, the CD’s issuer will pay you interest on the money in your account. ...
- Term. When opening a certificate of deposit, you may be able to choose a term of less than a month to a decade or more. ...
- Minimum deposit requirements. ...
- Early withdrawal penalty. ...
- Other fees. ...
What are CDs stocks?
Specialty CDs: Bump-Up, Add-On, No-Penalty, Jumbo, and IRA
- Bump-up CDs. These are sometimes called raise-your-rate certificates. ...
- Add-on CDs. Add-on CDs let you play around with your deposit amount, instead of your interest rate. ...
- No-penalty CDs. ...
- Jumbo CDs. ...
- IRA CDs. ...

What is CDs in share?
The term credit default swap (CDS) refers to a financial derivative that allows an investor to swap or offset their credit risk with that of another investor. To swap the risk of default, the lender buys a CDS from another investor who agrees to reimburse the lender in the case the borrower defaults.
Are CDs better than stocks?
CDs are low-risk, relatively low-return financial vehicles that are best suited for short-term investors or the risk-averse. Stocks, in comparison, offer higher potential returns and greater risk and are best suited for long-term investors who can ride out price fluctuations.
How are CDs traded?
In a CDS, one party “sells” risk and the counterparty “buys” that risk. The “seller” of credit risk – who also tends to own the underlying credit asset – pays a periodic fee to the risk “buyer.” In return, the risk “buyer” agrees to pay the “seller” a set amount if there is a default (technically, a credit event).
Is it good to invest in CDs?
1. CDs are safe investments. Like other bank accounts, CDs have federal deposit insurance up to $250,000 (or $500,000 in a joint account for two people). There's no risk of losing money in a CD, except if you withdraw early.
Can you lose money in CDs?
Can you lose money in a brokered CD? Market interest rates frequently fluctuate, which means that the market value of a CD fluctuates, too. If a CD is sold on the secondary market at a lower value than its face value, it will have lost money.
Do CDs pay interest monthly?
Generally, CDs compound daily or monthly. The more often the CD compounds, the faster your savings will grow. The answer varies by account, but most CDs credit interest monthly.
What is a 5 year CDS spread?
The United States 5 Years CDS value is 18.30 (last update: 5 Jul 2022 9:45 GMT+0). This value reveals a 0.31% implied probability of default, on a 40% recovery rate supposed. CDS value changed +5.17% during last week, +15.09% during last month, +88.66% during last year.
How is CDS calculated?
When a bond defaults, the buyer of the CDS is entitled to the notional principal minus the recovery rate of the bond. The recovery rate of the bond is considered its value immediately after default. So if the recovery rate on $1,000,000 worth of bonds is 75%, then the CDS payoff = $1,000,000 × (1 – . 75) = $250,000.
What does a high CDS spread mean?
The increase in CDS rates indicates that the risk of the debt or the economy has increased. Thus, beyond the insurance function against the default risk, CDS provides insight into the countries' risks.
Are CDs safe?
CDs are one of the safest ways to store money and earn a set rate of interest, which can help you better plan your finances. CDs opened at FDIC-insured banks or credit unions backed by the NCUA are guaranteed by the federal government.
Can you make money with CDs?
APY. Like savings accounts, CDs earn compound interest—meaning that periodically, the interest you earn is added to your principal. Then that new total amount earns interest of its own, and so on.
Are CDs a good investment in 2021?
CD rates should stay low in 2021, but they probably won't drop as drastically as they did in 2020. Rates could go up if the US economy recovers from the pandemic more quickly than expected. Even with relatively low rates, a CD could be the right savings tool for you, depending on your goals.
What is CDS in trading?
The CDS provided the trading infrastructure and technology that enabled the Canadian Capital Markets Association (CCMA) to implement its T+2 initiative in 2017 that shortened trade settlements of investment funds, equities, and bonds from three to two business days. The move was made in conjunction with a similar T+2 settlement mandate overseen in the U.S. by the Securities and Exchange Commission .
What is a CDS?
The Canadian Depository for Securities Limited (CDS) responsibilities include the safe custody and movement of securities, post-trade transactions processing, accurate record-keeping, and the collection and distribution of securities entitlements such as dividends and interest payments. The CDS is regulated by the securities commissions of Ontario and Quebec and the Bank of Canada. 1
When did CDS start?
The CDS began working with U.S. clearing and custody firm The Depository Trust Company in 1979 to develop access to U.S. capital markets. Cross-border clearing and settlement of U.S. securities commenced in 1998. The CDS implemented a clearing system for Canadian bonds and money market instruments in the early 1990s. 2.
Who regulates CDS?
The CDS is regulated by the securities commissions of Ontario and Quebec and the Bank of Canada. 1. The CDS incorporated in June 1970, in response to rising costs for back-office functions and increased trading volumes in Canadian capital markets.
Is CDS part of TMX?
The CDS is now part of the TMX Group , a large Toronto-based financial services company that operates the Toronto Stock Exchange (TSX), TSX Venture Exchange, Montreal Exchange, and TSX Alpha Exchange.
What is a CD?
What are certificates of deposit? A certificate of deposit (CD) is a savings account that holds a fixed amount of money for a fixed period of time, such as six months, one year, or five years, and in exchange, the issuing bank pays interest.
Who sells CDs?
Broker certificates of deposit. Although most CDs are purchased directly from banks, many brokerage firms and independent salespeople also offer CDs. These individuals and entities, known as “deposit brokers,” can sometimes negotiate a higher rate of interest for a CD by promising to bring a certain amount of deposits to the institution.
How much insurance does a CD have?
Certificates of deposit are considered to be one of the safest savings options. A CD bought through a federally insured bank is insured up to $250,000. The $250,000 insurance covers all accounts in your name at the same bank, ...
What is the risk of CDs?
The risk with CDs is the risk that inflation will grow faster than your money, and lower your real returns over time.
What should the disclosure statement say about CDs?
The disclosure statement should outline the interest rate on the CD and say if the rate is fixed or variable.
Is a deposit broker a licensed broker?
Deposit brokers are not licensed or certified, and no state or federal agency approves them. Since anyone can claim to be a deposit broker, always check whether the deposit broker or the company he or she works for has a history of complaints or fraud. Many deposit brokers are affiliated with investment professionals.
Can a deposit broker offer CDs?
The deposit broker can then offer these “brokered CDs” to their customers. Thoroughly check out the background of the issuer or deposit broker to ensure that the CD is from a reputable institution. Deposit brokers are not licensed or certified, and no state or federal agency approves them. Since anyone can claim to be a deposit broker, always check ...
What happens to the buyer of a CDS?
The buyer of a CDS makes periodic payments to the seller until the credit maturity date. In the agreement, the seller commits that, if the debt issuer defaults, the seller will pay the buyer all premiums and interest that would’ve been paid up to the date of maturity. Through a credit swap, a buyer can take risk control measures by shifting ...
Why would a CDS buyer sell his protection?
A CDS buyer might also sell his protection if he thinks that the seller’s creditworthiness might improve. The seller is viewed as being long to the CDS and the credit while the investor who bought the protection is perceived as being short on the CDS and the credit. Most investors argue that a CDS helps in determining the creditworthiness ...
How much money was invested in credit default swaps in 2008?
The value of credit default swaps stood at $45 trillion compared to $22 trillion invested in the stock market, $7.1 trillion in mortgages and $4.4 trillion in U.S. Treasuries.
How much did CDS drop in 2008?
During the financial crisis of 2008, the value of CDS was hit hard, and it dropped to $26.3 trillion by 2010 and $25.5 trillion in 2012. There was no legal framework to regulate swaps, and the lack of transparency in the market became a concern among regulators.
What happens to CDS spread if outlook fails?
However, if the company’s outlook fails to improve, the CDS spread should widen and the stock price should decline. For example, when a company experiences an adverse event and its share price drops, an investor would expect an increase in CDS spread relative to the share price drop.
What happens when a CDS is transferred to another party?
The seller transfers the CDS to another party as a form of protection against risk, but it may lead to default. Where the original buyer drops out of the agreement, the seller may be forced to sell a new CDS to a third party to recoup the initial investment. However, the new CDS may sell at a lower price than the original CDS, leading to a loss. ...
How does a credit swap work?
Through a credit swap, a buyer can take risk control measures by shifting the risk to an insurance company in exchange for periodic payments. Just like an insurance policy, a CDS allows purchasers to buy protection against an unlikely event that may affect the investment.