- Beta indicates how volatile a stock's price is in comparison to the overall stock market.
- A beta greater than 1 indicates a stock's price swings more wildly (i.e., more volatile) than the overall market.
- A beta of less than 1 indicates that a stock's price is less volatile than the overall market.
What stocks have the highest beta?
- Microsoft has a beta of around 1.25. This means an investor can reasonably expect that this stock is 25% more volatile than the market. ...
- Walt Disney Company has a beta right around 1.03. This puts its volatility right in line with the broader market. ...
- In contrast, Duke Energy has a beta of around 0.27. ...
What stock has the highest beta?
High beta stocks have historically outperformed the market, which is why they hold great significance for investors. While beta values have been historically used to calculate stocks' volatility ...
How to easily calculate the beta of a stock?
Top 3 Formula to Calculate Beta
- Covariance/Variance Method. To calculate the covariance Calculate The Covariance Covariance is a statistical measure used to find the relationship between two assets and is calculated as the standard deviation ...
- By Slope Method in Excel. We can also calculate Beta by using the slope function in excel. ...
- Correlation Method. ...
How do you calculate beta of stock?
Stock Beta formula. Stock’s Beta is calculated as the division of covariance of the stock’s returns and the benchmark’s returns by the variance of the benchmark’s returns over a predefined period. Below is the formula to calculate stock Beta. Stock Beta Formula = COV(Rs,RM) / VAR(Rm)

Is beta a good measure of stock risk?
Furthermore, the beta measure on a single stock tends to flip around over time, which makes it unreliable. Granted, for traders looking to buy and sell stocks within short time periods, beta is a fairly good risk metric. However, for investors with long-term horizons, it's less useful.
What does beta tell you about risk?
Key Takeaways Beta indicates how volatile a stock's price is in comparison to the overall stock market. A beta greater than 1 indicates a stock's price swings more wildly (i.e., more volatile) than the overall market. A beta of less than 1 indicates that a stock's price is less volatile than the overall market.
What does a beta of 1.5 mean?
Roughly speaking, a security with a beta of 1.5, will have move, on average, 1.5 times the market return. [More precisely, that stock's excess return (over and above a short-term money market rate) is expected to move 1.5 times the market excess return).]
What is a good beta for a portfolio?
Beta is used as a proxy for a stock's riskiness or volatility relative to the broader market. A good beta will, therefore, rely on your risk tolerance and goals. If you wish to replicate the broader market in your portfolio, for instance via an index ETF, a beta of 1.0 would be ideal.
What does a beta of 0.8 mean?
If the stock is more volatile than the market, its beta will be more than 1, and if it is less volatile than the market, its beta will be less than 1. For example, a stock with a beta of 0.8 would be expected to return 80% as much as the overall market.
What does a beta of 1.20 indicate?
Trading-Glossary. "A measure of a fund's risk, or volatility, compared to the market which is represented as 1.0. A fund with a beta of 1.20 is 20% more volatile than the market, while a fund with a beta of 0.80 would be 20% less volatile than the market."
What does a beta of 1.35 mean?
The market is described as having a beta of 1. The beta for a stock describes how much the stock's price moves compared to the market. If a stock has a beta above 1, it's more volatile than the overall market. For example, if an asset has a beta of 1.3, it's theoretically 30% more volatile than the market.
What is considered a high beta?
What are high-beta stocks? A high-beta stock, quite simply, is a stock that has been much more volatile than the index it's being measured against. A stock with a beta above 2 -- meaning that the stock will typically move twice as much as the market does -- is generally considered a high-beta stock.
What Is Beta Risk?
Beta risk is the probability that a false null hypothesis will be accepted by a statistical test. This is also known as a Type II error or consumer risk. In this context, the term "risk" refers to the chance or likelihood of making an incorrect decision. The primary determinant of the amount of beta risk is the sample size used for the test.
Understanding Beta Risk
Beta risk may be defined as the risk found in incorrectly accepting the null hypothesis when an alternative hypothesis is true. Put simply, it is taking the position that there is no difference when, in fact, there is one.
Examples of Beta Risk
An interesting application of hypothesis testing in finance can be made using the Altman Z-score. The Z-score is a statistical model meant to predict the future bankruptcy of firms based on certain financial indicators.
Beta Risk vs. Beta
Beta, in the context of investing, is also known as beta coefficient and is a measure of the volatility, or systematic risk, of a security or a portfolio in comparison to the market as a whole. In short, the beta of an investment indicated whether it is more or less volatile compared to the market.
What Is the Beta?
The value of any stock index, such as the Standard & Poor's 500 Index, moves up and down constantly. At the end of the trading day, we conclude that "the markets" were up or down. An investor considering buying a particular stock may want to know whether that stock moves up and down just as sharply as stocks in general.
Analyzing Beta
Beta is calculated using regression analysis. A beta of 1 indicates that the security's price tends to move with the market. A beta greater than 1 indicates that the security's price tends to be more volatile than the market. A beta of less than 1 means it tends to be less volatile than the market.
Why Beta Is Important
Are you prepared to take a loss on your investments? Many people are not and they opt for investments with low volatility. Others are willing to take on additional risk for the chance of increased rewards.
Where to Find the Beta Number
Many brokerage firms calculate the betas of securities they trade and then publish their calculations in a beta book. These books offer estimates of the beta for almost any publicly-traded company .
Warnings About Beta
The biggest drawback to using beta to make an investment decision is that beta is a historical measure of a stock's volatility. It can show you the pattern so far but it can't tell you what's going to happen in the future.
What Is Beta?
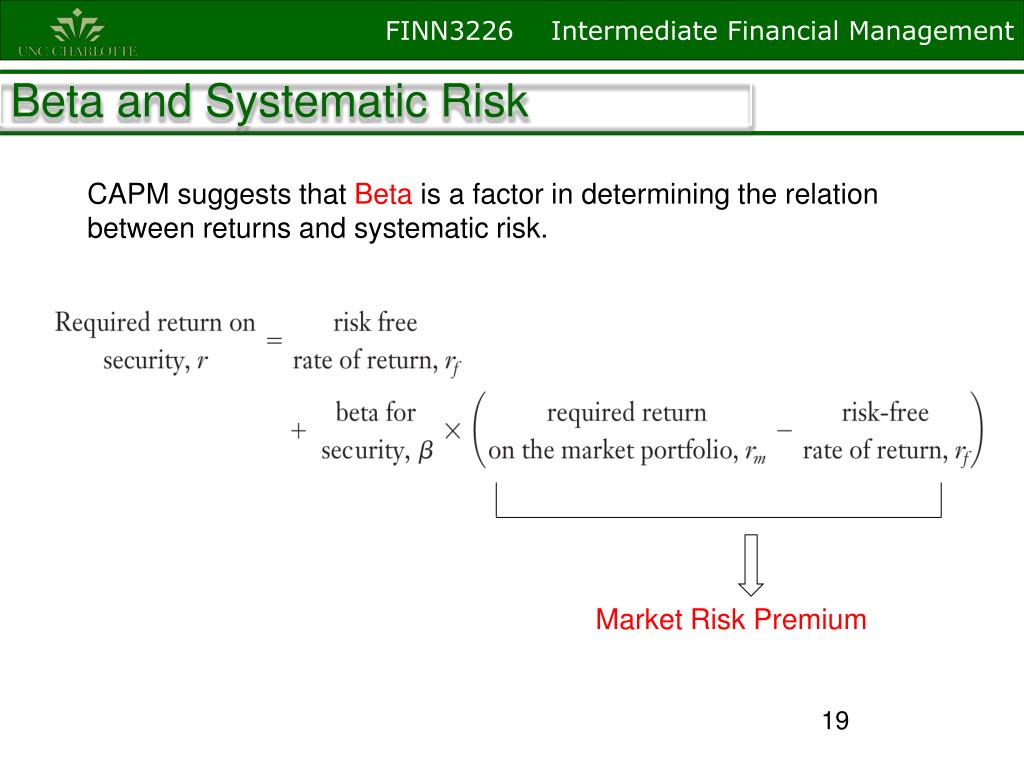
Beta is a measure of the volatility — or systematic risk — of a security or portfolio compared to the market as a whole. Beta is used in the capital asset pricing model (CAPM), which describes the relationship between systematic risk and expected return for assets (usually stocks).
How Beta Works
A beta coefficient can measure the volatility of an individual stock compared to the systematic risk of the entire market. In statistical terms, beta represents the slope of the line through a regression of data points. In finance, each of these data points represents an individual stock's returns against those of the market as a whole.
Types of Beta Values
If a stock has a beta of 1.0, it indicates that its price activity is strongly correlated with the market. A stock with a beta of 1.0 has systematic risk. However, the beta calculation can’t detect any unsystematic risk.
Beta in Theory vs. Beta in Practice
The beta coefficient theory assumes that stock returns are normally distributed from a statistical perspective. However, financial markets are prone to large surprises. In reality, returns aren’t always normally distributed. Therefore, what a stock's beta might predict about a stock’s future movement isn’t always true.
Disadvantages of Beta
While beta can offer some useful information when evaluating a stock, it does have some limitations. Beta is useful in determining a security's short-term risk, and for analyzing volatility to arrive at equity costs when using the CAPM.
Examples of beta
High β – A company with a β that’s greater than 1 is more volatile than the market. For example, a high-risk technology company with a β of 1.75 would have returned 175% of what the market returned in a given period (typically measured weekly).
Calculation
Below is an Excel β calculator that you can download and use to calculate β on your own. β can easily be calculated in Excel using the Slope function.
Download the Free Template
Enter your name and email in the form below and download the free template now!
Beta Calculator
Download the free Excel template now to advance your finance knowledge!
What are Equity Beta and Asset Beta?
Levered beta, also known as equity beta or stock beta, is the volatility of returns for a stock, taking into account the impact of the company’s leverage from its capital structure. It compares the volatility (risk) of a levered company to the risk of the market.
Levered Beta vs Unlevered Beta
Levered beta (equity beta) is a measurement that compares the volatility of returns of a company’s stock against those of the broader market. In other words, it is a measure of risk and it includes the impact of a company’s capital structure and leverage.
Calculation of Levered Beta
There are two ways to estimate the levered beta of a stock. The first, and simplest, way is to use the company’s historical β or just select the company’s beta from Bloomberg. The second, and more popular, way is to make a new estimate for β using public company comparables.
Beta Coefficient
The beta coefficient is calculated by dividing the covariance of the stock return versus the market return by the variance of the market. Beta is used in the calculation of the capital asset pricing model (CAPM). This model calculates the required return for an asset versus its risk.
Popular Indexes Used as a Beta Measure
The market against which to measure beta is often represented by a stock index. The most commonly used stock index is the S&P 500. The S&P 500 is used as the measure because of the high number of large-cap stocks included in the index and the broad number of sectors included.
Using Beta to Measure Hedge Fund Performance
Beta is an important concept for the analysis of hedge funds. It can show the relationship between a hedge fund’s returns and the market return. Beta can show how much risk the fund is taking in certain asset classes and can be used to measure against other benchmarks, such as fixed income or even hedge fund indexes.
Using Beta to Determine What Stocks to Trade
Active traders typically look for stocks with higher volatility than the broader stock market to exploit short-term price fluctuations. Scanning for stocks that have a beta above 2 quickly finds suitable trading candidates that move twice as much as the S&P 500 Index.
What is beta, and how does it work?
Beta is a way of measuring a stock’s volatility compared with the overall market’s volatility. The market as a whole has a beta of 1. Stocks with a value greater than 1 are more volatile than the market (meaning they will generally go up more than the market goes up, and go down more than the market goes down).
Pros and cons of using beta
History can hold important lessons: Beta uses a sizable chunk of data. Reflecting at least 36 months of measurements, beta gives you an idea of how the stock has moved vs the market over the last 3 years.
Stock Beta formula
Stock’s Beta is calculated as the division of covariance of the stock’s returns and the benchmark’s returns by the variance of the benchmark’s returns over a predefined period.
Calculate Stock Beta of MakeMyTrip
Let us calculate the Stock Beta of a NASDAQ Listed company MakeMyTrip (MMTY).
What Does Stock Beta Imply?
It may look like an overly mathematical formula, but it does provide both qualitative and quantitative actionable information. The sign (positive or negative) indicates the direction of the movement of the stock in question with respect to that of the underlying market or benchmark against which the stock’s movement is assessed.
Conclusion
It is one single statistical tool that investors frequently use to assess the risk that the stock may add to their portfolio, allowing them to gauge the risk in both qualitative and quantitative terms and to assess the risk and rewards associated with the stock.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to what is Stock Beta and its definition. Here we discuss the Stock Beta formula and calculate stock beta (step by step) along with practical examples. You can learn more about from the following articles –

Calculating Beta
- Beta is calculated using regression analysis. Numerically, it represents the tendency for a security's returns to respond to swings in the market. The formula for calculating beta is the covariance of the return of an asset with the return of the benchmarkdivided by the variance of t…
The Advantages of Beta
- To followers of CAPM, beta is useful. A stock's price variability is important to consider when assessing risk. If you think about risk as the possibility of a stock losing its value, beta has appeal as a proxy for risk. Intuitively, it makes plenty of sense. Think of an early-stage technology stock with a price that bounces up and down more than the market. It's hard not to think that stock wil…
The Disadvantages of Beta
- If you are investing based on a stock's fundamentals, beta has plenty of shortcomings. For starters, beta doesn't incorporate new information. Consider a utility company: let's call it Company X. Company X has been considered a defensive stockwith a low beta. When it entered the merchant energy business and assumed more debt, X's historic beta no longer captured the …
Assessing Risk
- The well-worn definition of risk is the possibility of suffering a loss. Of course, when investors consider risk, they are thinking about the chance that the stock they buy will decrease in value. The trouble is that beta, as a proxy for risk, doesn't distinguish between upside and downsideprice movements. For most investors, downside movements are a risk, while upside ones mean oppor…
The Bottom Line
- Ultimately, it's important for investors to make the distinction between short-term risk—where beta and price volatility are useful—and longer-term, fundamental risk, where big-picture risk factors are more telling. High betas may mean price volatility over the near term, but they don't always rule out long-term opportunities.
Examples of Beta
Calculation
- Below is an Excel β calculator that you can download and use to calculate β on your own. β can easily be calculated in Excel using the Slope function. Follow these steps to calculate β in Excel: 1. Obtain the weekly prices of the stock 2. Obtain the weekly prices of the market index (i.e., S&P 500 Index) 3. Calculate the weekly returns of the stock 4. Calculate the weekly returns of the market i…
What Are Equity Beta and Asset Beta?
- Levered beta, also known as equity beta or stock beta, is the volatility of returns for a stock, taking into account the impact of the company’s leverage from its capital structure. It compares the volatility (risk) of a levered company to the risk of the market. Levered beta includes both business risk and the risk that comes from taking on debt. ...
Levered Beta vs Unlevered Beta
- Levered beta (equity beta) is a measurement that compares the volatility of returns of a company’s stock against those of the broader market. In other words, it is a measure of risk, and it includes the impact of a company’s capital structure and leverage. Equity beta allows investors to assess how sensitive a security might be to macro-market risks. For example, a company with a …
Calculation of Levered Beta
- There are two ways to estimate the levered beta of a stock. The first, and simplest, way is to use the company’s historical β or just select the company’s beta from Bloomberg. The second, and more popular, way is to make a new estimate for β using public company comparables. To use the comparables approach, the β of comparable companies is taken from Bloomberg and the un…
Interpreting Beta
- A security’s β should only be used when its high R-squared value is higher than the benchmark. The R-squared value measures the percentage of variation in the share price of a security that can be explained by movements in the benchmark index. For example, a gold ETF will show a low β and R-squared in relation to a benchmark equity index, as gold is negatively correlated with equit…
Related Readings
- Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to beta (β) of an investment security. To continue learning and advancing your career these additional resources will be helpful: 1. Types of Valuation Multiples 2. Analysis of Financial Statements 3. Leverage Ratios 4. Valuation Methods